3.3 Managing Access Gateways
The following sections contain information about settings available with Access Gateways, changing the settings, and their impact on users:
3.3.1 Viewing and Modifying Gateway Settings
Use the Servers page to view the status of Access Gateways, to modify their configuration, and to perform other actions such as creating a new cluster or stopping and starting an Access Gateway or its Embedded Service Provider.
-
In the Administration Console, click > .
-
Select one of the following:
New Cluster: To create a new cluster of Access Gateways, click . A cluster can be one or more Access Gateways. For configuration information, see Section 6.4.1, Creating a New Cluster.
Stop: To stop an Access Gateway Appliance, select the appliance, then click . You must have physical access to the Access Gateway Appliance machine to start it again. To stop an Access Gateway Service, select the service, then click . You can use the option to start the Access Gateway Service.
Restart: To reboot an Access Gateway Appliance, select the appliance, then click . The Access Gateway Appliance is stopped, the operating system is rebooted, then the appliance is started. To stop and start the Access Gateway Service, select the service, then click . If the Access Gateway Service is already stopped, use to start it.
Refresh: To update the list of Access Gateways and the status columns (, , , ), click .
-
To perform an action available in the drop-down menu, select an Access Gateway, then select one of the following:
Assign to Cluster: To add the selected Access Gateway to a cluster, select , then select the cluster. This Access Gateway is reconfigured with the configuration of the primary cluster server. A Gateway Appliance can only be added to a cluster that already contains a Gateway Appliance. A Gateway Service can be added to any cluster.An Access Gateway Appliance can only be added to a cluster of Access Gateway Appliances. An Access Gateway Service can only be added to a cluster of Access Gateway Services.
Remove from Cluster: To remove the selected Access Gateway from a cluster, select . The Access Gateway retains its configuration from the cluster, but no traffic is sent to it until it is reconfigured. You can assign it to a different cluster and have it updated with this cluster’s configuration, or you can delete all of its reverse proxies and start a new configuration.
Delete: To remove the selected Access Gateway server from the list of servers that can be managed from this Administration Console, select . If the Access Gateway is a member of a cluster, you must first remove it from the cluster before you can delete it.
IMPORTANT:When an Access Gateway is deleted from the Administration Console, you can no longer manage it. To access it again, you must manually trigger an auto-import, which causes it to import into an Administration Console.
Schedule Restart: To schedule when the selected Access Gateway should be stopped and then started, select . On an Access Gateway Appliance, a restart stops the operating system, then starts the operating system and the Access Gateway. On an Access Gateway Service, a restart stops the Access Gateway Service, then starts it. For information on how to schedule this command, see Section 3.3.4, Scheduling a Command.
Schedule Stop: To schedule when the selected Access Gateway or cluster should be stopped, select .
-
When you stop an Access Gateway Appliance, you shut down the Access Gateway Appliance and the operating system. You must have physical access to the machine to start it again.
-
When you stop an Access Gateway Service, you stop just the Access Gateway Service. You can use the option to start it again.
For more information on how to schedule this command, see Section 3.3.4, Scheduling a Command
Purge List Now: Click to cause all objects in the current purge list to be purged from the cache of the selected server or cluster.
Purge All Cache: Click to purge the server cache for the selected server or cluster. All cached content is lost.
When you make certain configuration changes such as updating or changing certificates, changing the IP addresses of Web servers, or modifying the rewriter configuration, you are prompted to purge the cache. The cached objects must be updated for users to see the effects of such configuration changes. If your Access Gateways are in a cluster, you need to manage the purge process so your site remains accessible to your users. You should apply the configuration changes to one member of a cluster. When its status returns to healthy and current, issue the command to purge its cache. Then apply the changes to the next cluster member.
IMPORTANT:Do not issue a purge cache command when an Access Gateway has a pending configuration change. Wait until the configuration change is complete.
Update Health from Server: Click this action to send a request to the server for updated health information. If you have selected multiple servers, a request is sent to each one. The health status changes to an animated circle until the reply returns.
Service Provider: Select one of the following actions:
-
Start Service Provider: To start the Embedded Service Provider associated with the selected Access Gateway, click . The Embedded Service Provider is the module within the Access Gateway that communicates with the Identity Server.
The service provider should be restarted whenever you enable or modify logging on the Identity Server.
-
Stop Service Provider: To stop the Embedded Service Provider associated with the selected Access Gateway, click . The Embedded Service Provider is the module within the Access Gateway that communicates with the Identity Server.
When an Access Gateway is not functioning correctly, you should always try stopping and starting the service provider before stopping and starting the Access Gateway.
-
Restart Service Provider: To restart the Embedded Service Provider associated with the selected Access Gateway, click . This command stops the Embedded Service Provider and then starts it. The Embedded Service Provider is the module within the Access Gateway that communicates with the Identity Server.
When an Access Gateway is not functioning correctly, you should always try restarting the service provider before stopping and starting the Access Gateway.
-
-
Use the following links to manage a cluster or an Access Gateway.
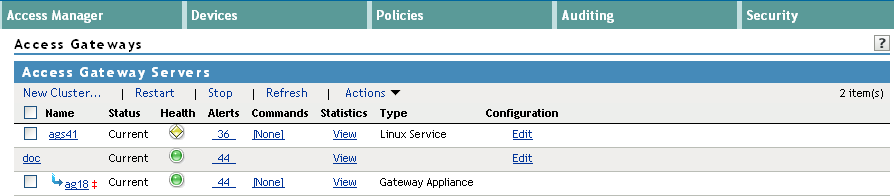
Name: Displays a list of the Access Gateway servers and the clusters that can be managed from this Administration Console.
-
To view or modify the general details of a particular server, click the name of the server.
-
To view or modify general details of a cluster, click the name of the cluster.
Status: Indicates the configuration status of the clusters and the Access Gateways. Possible states are pending, update, current, and update all. For more information, see Section 3.3.2, Configuration Options.
Health: Indicates whether a cluster or an Access Gateway is functional. Click the icon to view additional information about the operational status of an Access Gateway.
-
For information about the health of a specific Access Gateway, click the health icon on the Access Gateway row. For more information, see Section 4.8.2, Monitoring the Health of an Access Gateway.
-
For information about the health of a Access Gateway cluster, click the health icon on the cluster row. For more information, see Section 4.8.3, Viewing the Health of an Access Gateway Cluster.
Alerts: Indicates whether any alerts have been sent. If the alert count is non-zero, click the count to view more information.
-
For information about the alerts of a specific Access Gateway, click the link on the Access Gateway row. For more information, see Section 4.6.1, Viewing Access Gateway Alerts.
-
For information about the alerts sent to the cluster, click the link on the cluster row. For more information, see Section 4.6.2, Viewing Access Gateway Cluster Alerts.
Commands: Indicates the status of the last executed command and whether any commands are pending. Click the link to view more information. For more information, see Section 4.9, Viewing the Command Status of the Access Gateway.
Statistics: Provides a link to the statistic pages.
-
For information about the statistics of a specific Access Gateway, click the link on the Access Gateway row and see Section 4.4, Viewing Access Gateway Statistics.
-
For information about statistics sent to the cluster, click the link on the cluster row and see Section 4.5, Viewing Cluster Statistics.
Edit: Provides a link to the configuration page. If the server belongs to a cluster, the link appears on the cluster row. Otherwise, the link is on the server row. See Section 3.1, Configuration Overview.
-
3.3.2 Configuration Options
Use the information in this section to modify the Status options described in Step 4
-
In the Administration Console, click > .
-
View the column and make changes as necessary.
Status
Description
Current
Indicates that all configuration changes have been applied.
Update
Indicates that a configuration change has been made, but not applied. To apply the changes, click the Update link, then select one of the following:.
-
All Configuration: The option causes the Access Gateway to read its complete configuration file and restarts the Embedded Service Provider.
The configuration update causes logged-in users to lose their connections unless the server is a member of a cluster. When the server is a member of a cluster, the users are sent to another Access Gateway and they experience no interruption of service.
-
Logging Settings: When the ESP logging settings have been modified on the Identity Server, the update option for is available. The option causes no interruption in services. When you modify Access Gateway logging settings, this option is not available because they are considered configuration settings.
-
Policy Settings: If a policy is modified for a protected resource of the Access Gateway and the policy change is the only modification that has occurred, the update option for is available. This option causes no interruption in services.
-
Rewriter Profile Changes: When the administrator changes the rewriter profile, a purge cache command is issued to a Gateway from the administration console, the connection is lost and the service is interrupted for a few seconds. Similar experience is observed during the rewriter profile configuration change, as this internally triggers the purge cache command.
-
Changing Certificates: When a certificate configuration is changed from the administration console, the service is interrupted due to the Tomcat restart.
Update All
This link is available when a server belongs to a cluster. You can select to update all the servers at the same time, or you can select to update them one at a time. If the modification is a policy or a logging change, then use . If the modification is a configuration change, we recommend that you update the servers one at a time.
-
When you select for a configuration change, users experience an interruption of service.
-
When you update servers one at a time for a configuration change, users experience no interruption of service.
When you make the following configuration changes, the option is the only option available and your site will be unavailable while the update occurs:
-
The Identity Server configuration that is used for authentication is changed (> > , then select a different value for the option).
-
A different reverse proxy is selected to be used for authentication ( >> , then select a different value for the option).
-
The protocol or port of the authenticating reverse proxy is modified ( > > > , then change the SSL options or the port options).
-
The published DNS name of the authentication proxy service is modified ( > > > > [, then modify the option).
For more information, see Section 6.4.6, Applying Changes to Cluster Members.
Update

If the configuration update contains a configuration error, the link is disabled and the icon is displayed. Click the icon to discover which objects have been misconfigured. You need to fix the error by either canceling or modifying the changes before you can perform an update.
Update All

If the configuration update contains a configuration error, the and the member links are disabled and the icon is displayed. Click the icon to discover which objects have been misconfigured. You need to fix the error by either canceling or modifying the changes before you can perform an update.
Pending
Indicates that the server is processing a configuration change, but has not completed the process.
Locked
Indicates that another administrator is making configuration changes. Before you proceed with any configuration changes, you need to coordinate with this administrator and wait until the Access Gateway has been updated with the other administrator’s changes.
-
3.3.3 Impact of Configuration Changes
This section covers the impact of some of the common Novell Access Gateway configuration settings on users.
NOTE:Do not push the configuration from the Administration Console to devices during peak system usage times.
Devices > Access Gateways
-
Purge List Now/ Purge Cache: Causes a process level restart and terminates all the existing connections and downloads. The users do not need to reauthenticate, but issuing a purge list or cache command might result in a higher load on the service provider. If there is a single gateway, issuing a purge list or cache command can cause temporary service disruption for users.
-
Stop: Stops the proxy component in the Access Gateway Appliance, makes it unavailable for user requests and terminates all the existing connections and downloads. The users do not need to reauthenticate, but stopping the proxy component can result in a higher load on the identity provider and other gateway cluster members.
-
Restart: Triggers a restart of the operating system of the Access Gateway Appliance, where all existing connections and downloads are terminated. The users do not need to reauthenticate, but restarting the operating system can result in a higher load on the identity provider and other gateway cluster members.
-
Service Provider > Restart: Causes the ESP and proxy to clear the user session information and refresh the policy information. Access might be denied to protected resources and resources that need policy evalutation during the restart process.
-
Service Provider > Stop: Causes the ESP and proxy to clear the user session information. You cannot access the protected resources and resources that need policy evaluation.
Devices > Access Gateways > < your gateway/cluster> Services
-
Rewriter Profile Change: Changing the rewriter profile causes the Administration Console to issue a purge cache command to the Access Gateway. Issuing a purge cache command causes a process level restart and terminates all the existing connections and downloads.
-
Accelerated Web Service Change: Changing the accelerated Web server details causes the Administration Console to issue a purge cache command to the Access Gateway. Issuing a purge cache command causes a process level restart and terminates all the existing connections and downloads
-
Service Creation: If your gateway cluster is behind an L4 switch, ensure that you review or modify the L4 configuration to reflect any new service that you can create.
-
TCP Connect Options: Increasing the Data Read Timeout values or the Idle Timeout values impacts the user experience if the Web servers are unreachable. Disabling the persistent connections also impacts the user experience.
System Settings
-
Date and Time: Changing date and time or the NTP server configuration impacts the existing user session timeout values. It is critical to keep the time settings in Access Gateways and Identity Servers synchronized in order to prevent authentication failures and unexpected session timeouts. There is no other impact than authentication failures and unexpected session timeouts.
Monitoring
-
Audit Configuration Changes or Audit Server Health: If the audit server is busy or unreachable, it causes a delay in browsing, including Administration Console access. There is no other impact than delay in browsing and accessing the Administration Console.
Network Settings
-
Network Related Changes: Be cautious in making changes to the network parameters like Adapter, IP address, Netmask, Gateways, DNS, Hosts, and Route. The users can be impacted by these changes because the connections are reset; however, user reauthentication might not be required. Incorrect configuration leads to system inaccessibility on the network and you cannot access the Access Gateway service.
Security Settings
You should not change security setting options during the peak system usage hours.
-
Signing: Before changing it, ensure that the Identity Server trust store contains the root CA certificate and possible intermediate CA certificates to complete the trust chain.
-
Trust Store: Before changing it, ensure that you have all the root CA certificates and possible intermediate CA certificates to complete the trust chain to trust any certificates used by the Identity Server.
Content Settings
-
Cache Options: Be cautious in making changes to the cache options. Changing cache options can impact the performance of your Access Manager system. You might see an increase or decline in the Access Gateway performance, depending on the changes made to the cache options.
3.3.4 Scheduling a Command
Use the Schedule New Command page to schedule a command, such as a shutdown, restart, or upgrade.
-
In the Administration Console, click > .
-
(Conditional) To schedule a shutdown or restart, select a server, then click > or . Continue with Step 4.
-
(Conditional) To schedule an upgrade for the Access Gateway Appliance, click > > .
-
Fill in the following fields:
Name Scheduled Command: (Required) Specify a name for this scheduled command. This name is used in log files.
Description: (Optional) Specify a reason for the command.
Date & Time: Select the day, month, year, hour, and minute when the command should execute.
The following fields display information about the command you are scheduling:
Type: Displays the type of command that is being scheduled, such as Access Gateway Shutdown, Access Gateway Restart, or Access Gateway Upgrade.
Server: Displays the name of the server that the command is being scheduled for.
-
Click to schedule the command.