4.2 Converting a Workload to a Physical Machine (P2P, V2P)
To initiate a peer-to-peer workload migration to a physical machine:
-
Discover your source workload.
-
Discover and register your target physical machine with PlateSpin Migrate.
-
(Recommended) Use PlateSpin Analyzer to ensure that:
-
Your source operating system and hardware are supported by PlateSpin Migrate.
-
PlateSpin Migrate’s X2P device driver library contains device drivers that your target requires for the operating system being ported.
-
-
(Conditional) If drivers for the physical target are missing, upload the required drivers to the PlateSpin Migrate’s X2P device driver library.
-
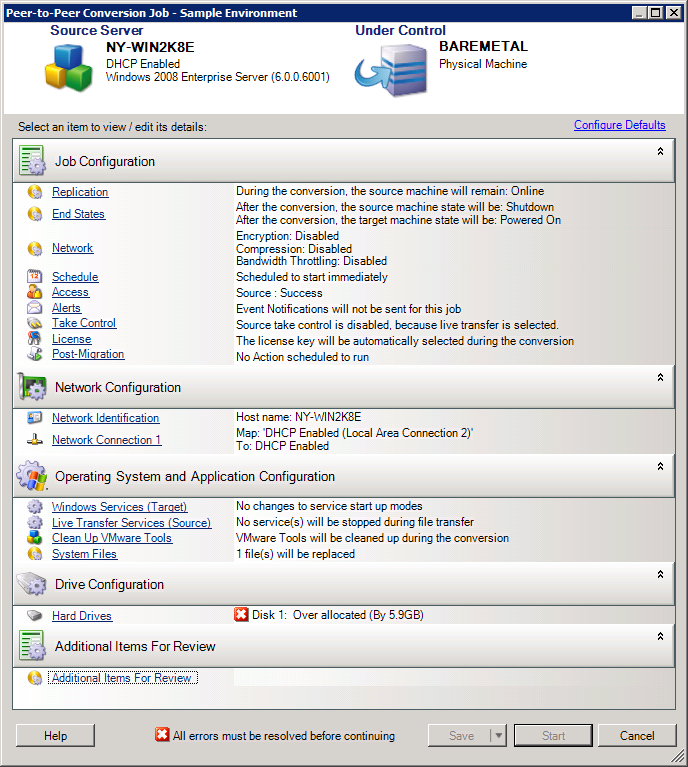
Start a migration job.
-
Configure the required parameters of the job.
-
Run the job.
Figure 4-2 Peer-to-Peer Conversion Job Window (V2P in Advanced Mode)
4.2.1 Best Practices (X2P)
-
When you are migrating a workload from one vendor to a target hardware infrastructure from another vendor (for example, from HP to Dell), or if your source is a virtual machine, make sure that you disable vendor-specific or VM-specific services during the transfer. For example, the HP Insight service and the VMware Tools service.
-
When you are using the Offline transfer method for P2P and V2P migrations, make sure that you select the appropriate Full Duplex speed that matches your network Full Duplex mode.
-
Ensure that vendor partitions are not being copied from the source.