2.3 Configuring the IP Address, Port, and Network Address Translation (NAT)
The Gateway Configuration page displays the current configuration of the SSL VPN server, such as the external IP address if the SSL VPN server is behind NAT, the listening IP address, TCP encryption port, Connection Manager port, and the type of encryption used.
This section describes how to configure the IP addresses, port, subnet address and subnet mask, and protocol for SSL VPN.
2.3.1 Configuring the SSL VPN Gateway behind NAT or L4
To configure SSL VPN behind NAT or by using an L4 switch:
-
In the Administration Console, click > > .
The Server configuration page is displayed.
-
Select from the section.
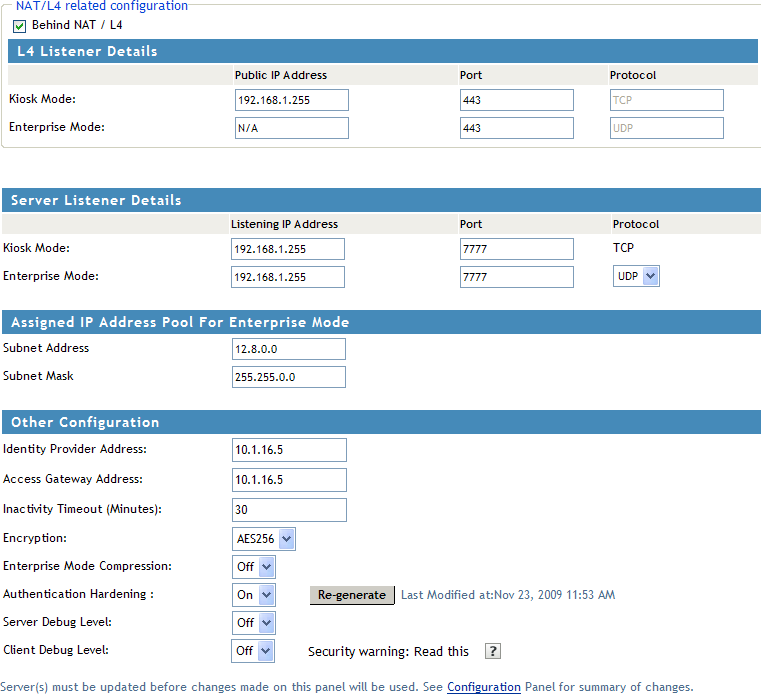
-
Specify the following NAT/L4 configuration as follows:
Behind NAT/L4: Select the check box to specify that the SSL VPN Gateway is behind NAT.
Public IP Address: This field is enabled when the check box is selected. Specify the public IP address (that is, the address exposed to the Internet user) that translates into the SSL VPN Gateway IP address. This is the IP address where the external user on the Internet must be able to access the SSL VPN server.
Port: Specify a port number for Kiosk mode as well as for Enterprise mode when the SSL VPN server is behind an L4 switch or a behind NAT.
Protocol: Specify a protocol for Kiosk mode as well as for Enterprise mode, when the SSL VPN server is behind an L4 switch or behind NAT. The protocol is TCP for Kiosk mode and UDP for Enterprise mode.
-
Specify the device-specific configuration as follows:
Cluster Member: Select the cluster member from a list of IP addresses.
Listening IP Address: Specify the IP address that the SSL VPN listens on.
Port: Specify a port number for Kiosk mode as well as for Enterprise mode when the SSL VPN server is behind an L4 switch or behind NAT. Make sure that the port you specify here is free.
Protocol: Specify a protocol for Kiosk mode as well as for Enterprise mode, when the SSL VPN server is behind an L4 switch or behind NAT. The protocol is TCP for Kiosk mode, but it can either be TCP or UDP for Enterprise mode.
-
Specify the following information to configure the assigned IP address pool for Enterprise mode:
Subnet Address: Specify the IP address of the subnet pool where SSL VPN assigns the IP address to each client in Enterprise mode. For this assigned IP address pool to work properly, you must configure the routing table and source NAT. For more information, see Section 2.4, Configuring Route and Source NAT for Enterprise Mode.
Subnet Mask: Specify the subnet mask for Enterprise mode.
The values specified in the and fields determine the IP addresses that are assigned to the clients. Make sure that the assigned IP address and the IP address of the client do not match.
NOTE:IP pooling is not applicable for Kiosk mode. In Enterprise mode, if you have only one SSL VPN server installed, then you can configure only one IP pool. However, if you have multiple SSL VPN servers in a cluster, then each SSL VPN server must have separately defined IP pools. In the Enterprise mode, each connection requires two IP addresses. Make sure that the IP pool has two IP addresses for each connection.
-
Specify the other configuration as follows:
Cluster Communications Port: Specify the port that is used for communication between the cluster members.
Identity Provider Address: Specify the public IP addresses or the public DNS name of the Identity Server if you are configuring SSL VPN for the full tunneling mode. This configuration is required to split the management traffic from the tunneled traffic. For more information on full tunneling, see Section 3.4, Configuring Full Tunneling.
Access Gateway Address: Specify the IP address or DNS name of the Access Gateway if your server is accelerated by the Access Gateway. This field is not present if you have installed the ESP-enabled SSL VPN.This configuration is required to split the management traffic from the tunneled traffic. For more information on full tunneling, see Section 3.4, Configuring Full Tunneling.
Inactivity Timeout (Minutes): You can configure the time in minutes. If no data exchange takes place during the stipulated time, the connection is closed so that the resources are freed to allow additional incoming connections. The inactivity timeout period can be one minute to 1800 minutes. The default inactive timeout period is 30 minutes.
Encryption: Select the type of encryption. It can be either AES128 or AES 256.
Enterprise Mode Compression: Specify if you want to enable compression in Enterprise mode in order to reduce the time taken to establish connection.
Authentication Hardenings: This option is applicable to Enterprise mode clients only. When this option is enabled, it provides protection against active attacks by using a keyed Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) cryptographic hash such as SHA1 to sign and verify packets. When this option is enabled, a packet is examined by a stateless filter and dropped if the HMAC signature does not match.
To enable select . To manually regenerate the key click . This option uses random number generation to regenerate the key.
Server Debug Level: Set this option to if you want to get more debug information from the server. This option is set to by default.
Client Debug Level: Set this option to if you want to get more debug information from the client.This option is set to by default.
-
To save your modifications, click then click on the Configuration page.
2.3.2 Configuring the SSL VPN Gateway without NAT or an L4 Switch
-
In the Administration Console, click > > .
The Server configuration page is displayed.
-
Select from the section.
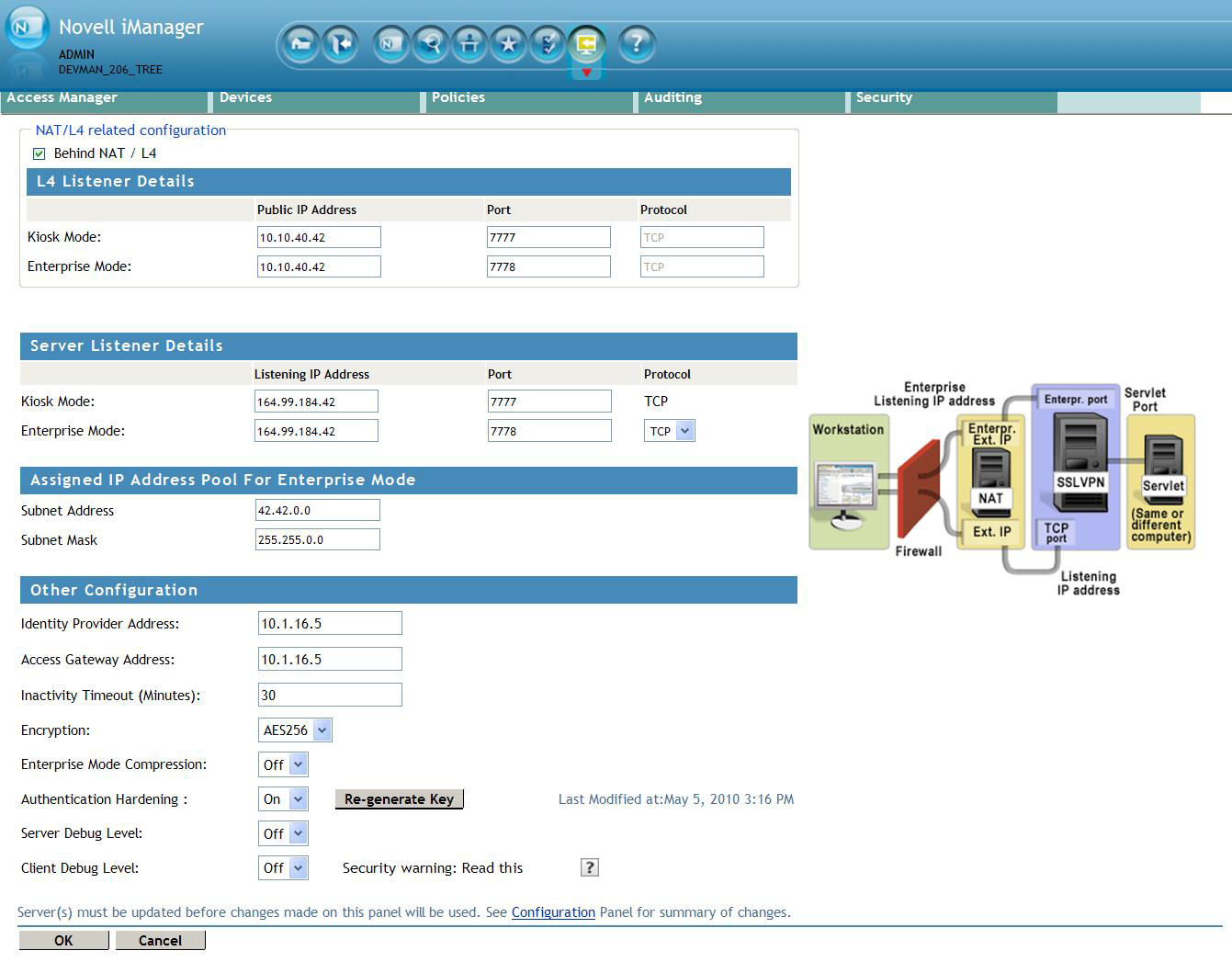
-
Specify the device-specific configuration as follows:
Cluster Member: Select the cluster member from a list of IP addresses.
Listening IP Address: Specify the IP address that the SSL VPN listens on.
Port: Specify a port number for Kiosk mode as well as for Enterprise mode when the SSL VPN server is behind an L4 switch or behind NAT. Make sure that the port you specify here is free.
Protocol: Specify a protocol for Kiosk mode as well as for Enterprise mode, when the SSL VPN server is behind an L4 switch or behind NAT. The protocol is TCP for Kiosk mode, but it can either be TCP or UDP for Enterprise mode.
-
Specify the following information to configure the assigned IP address pool for Enterprise mode:
Subnet Address: Specify the IP address of the subnet pool where SSL VPN assigns the IP address to each client in Enterprise mode. For this assigned IP address pool to work properly, you must configure the routing table and source NAT. For more information, see Section 2.4, Configuring Route and Source NAT for Enterprise Mode.
Subnet Mask: Specify the subnet mask for Enterprise mode.
The values specified in the and fields determine the IP addresses that are assigned to the clients. Make sure that the assigned IP address and the IP address of the client do not match.
-
Specify the other configuration as follows:
Cluster Communications Port: Specify the port that is used for communication between the cluster members.
Identity Provider Address: Specify the IP addresses or the DNS name of the Identity Server if you are configuring SSL VPN for the full tunneling mode. For more information on full tunneling, see Section 3.4, Configuring Full Tunneling.
Access Gateway Address: Specify the IP address or DNS name of the Access Gateway if your server is accelerated by the Access Gateway and if you are configuring SSL VPN for the full tunneling mode. This field is not present if you have installed the ESP-enabled SSL VPN. For more information on full tunneling, see Section 3.4, Configuring Full Tunneling.
Inactivity Timeout (Minutes): You can configure the time in minutes. If no data exchange takes place during the stipulated time, the connection is closed so that the resources are freed to allow additional incoming connections. The inactivity timeout period can be one minute to 1800 minutes. The default inactive timeout period is 30 minutes.
Encryption: Select the type of encryption. It can be either AES128 or AES 256.
Enterprise Mode Compression: Specify if you want to enable compression in Enterprise mode in order to reduce the time taken to establish connection.
Authentication Hardening: This option is applicable to Enterprise mode clients only. When this option is enabled, it provides protection against active attacks, by using a keyed Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) cryptographic hash such as SHA1 to sign and verify packets. When this option is enabled, a packet is examined by a stateless filter and dropped if the HMAC signature does not match.
To enable select . To manually regenerate the key click . This option uses random number generation to regenerate the key
Server Debug Level: Set this option to if you want to get more debug information from the server. This option is set to by default.
Client Debug Level: Set this option to if you want to get more debug information from the client. This option is set to by default.
-
To save your modifications, click then click on the Configuration page.