1.1 About the User Application
The Identity Manager User Application is a browser-based Web application that allows you to perform the following identity self-service tasks.
-
Conveniently perform roles-based provisioning actions
You can map role assignments to resources within your organization, such as user accounts, computers, and databases.
For details on setting up the Roles and Resources tab, see Section 2.7, Configuring the Roles and Resources Tab.
-
Ensure that your organization has a method for verifying that personnel are fully aware of organizational policies and are taking steps to comply with these policies.
For details on setting up the Compliance tab, see Section 2.8, Configuring the Compliance Tab.
-
Ensure that access to corporate resources complies with organizational policies and that provisioning occurs within the context of the corporate security policy.
You can grant users access to identity data within the guidelines of corporate security policies.
For more information, see Section 2.2, Security.
-
Reduce the administrative burden of entering, updating, and deleting user information across all systems in the enterprise.
You can create customized workflows to provide a Web-based interface for users to manipulate distributed identity data triggering workflows as necessary.
For more information, see Section IV, Configuring and Managing Provisioning Workflows.
-
Support complex workflows and manage manual and automated provisioning of identities, services, resources, and assets.
You can implement manual provisioning by creating workflows that route provisioning requests to one or more authorities. For automated provisioning, you can configure the User Application to start workflows automatically in response to events occurring in the Identity Vault.
For more information, see Section IV, Configuring and Managing Provisioning Workflows.
IMPORTANT:The User Application is an application and not a framework. The areas within the User Application that are supported to be modified are outlined within the product documentation. Modifications to areas not outlined within the product documentation are not supported.
1.1.1 About Identity Self-Service
Identity is the foundation of the User Application. The application uses identity as the basis for authorizing users’ access to systems, applications, and databases. Each user’s unique identifier—and each user’s roles—have specific access rights to identity data. For example, users who are identified as managers can access salary information about their direct reports, but not about other employees in their organization.
The Identity Self-Service tab within the application allows your organization to be more responsive by giving users a convenient way to view and work with identity information at any time. For example, users can use the Identity Self-Service tab to:
-
Manage their own user accounts directly
-
Look up other users and groups in the organization on demand
-
Visualize how those users and groups are related
-
List applications with which they are associated
The User Application Administrator sets up the contents of the Identity Self‐Service tab, which determines what business users can see and do. A user's job requirements and level of authority also affect what is available.
NOTE:In Identity Manager 4.5 and later, if you log on as a business user, the Identity Self-Service tab is the only tab you will see in the User Application. If you log on as a User Application Administrator, you see the Administration tab as well.
1.1.2 About Roles-Based Provisioning
The purpose of the Roles and Resources tab within the User Application is to give you a convenient way to manage role definitions and role assignments within your organization. You can map role assignments to resources within a company, such as user accounts, computers, and databases. For example, you might use the Roles and Resources tab to:
-
Make role requests for yourself or other users within your organization
-
Create roles and role relationships within the roles hierarchy
-
Create separation of duties (SoD) constraints to manage potential conflicts between role assignments
-
Look at reports that provide details about the current state of the Role Catalog and the roles currently assigned to users, groups, and containers
When a role assignment request requires permission from one or more individuals in an organization, the request starts a workflow. The workflow coordinates the approvals needed to fulfill the request. Some role assignment requests require approval from a single individual; others require approval from several individuals. In some instances, a request can be fulfilled without any approvals.
When a role assignment request results in a potential SoD conflict, the initiator has the option to override the SoD constraint and provide a justification for making an exception. In some cases, a SoD conflict can cause a workflow to start. The workflow coordinates the approvals needed to allow the SoD exception to take effect.
Your workflow designer and system administrator are responsible for setting up the contents of the Roles and Resources tab for you and the others in your organization. The flow of control for a roles-based workflow or SoD workflow, as well as the appearance of forms, can vary depending on how the workflow designer defined the workflow's approval definition in the Designer for Identity Manager. In addition, your job requirements and level of authority determine what you can see and do.
For details on setting up the Role Subsystem, see Section 2.7, Configuring the Roles and Resources Tab. For details on using the Roles and Resources tab, see the discussion of the Roles and Resources tab in the Identity Manager User Application: User Guide.
NOTE:The ability to define custom roles is only available with Identity Manager 4.5 and later.
1.1.3 About Resource-Based Provisioning
The purpose of the resource functionality within the User Application is to give you a convenient way to manage resource definitions and resource assignments within your organization. You can map resource assignments to users or to roles within a company. For example, you might use resources to:
-
Make resource requests for yourself or other users within your organization
-
Create resources and map them to entitlements
When a resource assignment request requires permission from one or more individuals in an organization, the request starts a workflow. The workflow coordinates the approvals needed to fulfill the request. Some resource assignment requests require approval from a single individual; others require approval from several individuals. In some instances, a request can be fulfilled without any approvals.
The following business rules govern the behavior of resources within the User Application:
-
Resources can only be assigned to a user. The resource can be granted to users in a container or group based on implicit role assignment. But the resource assignment will only be associated with a user.
-
Resources can be assigned in any of the following ways:
-
Directly by a user through UI mechanisms
-
Through a provisioning request
-
Through a role request assignment
-
Through a Rest or SOAP interface
-
-
The same resource can be granted to a user multiple times (if this capability has been enabled in the resource definition).
-
A resource definition can have no more than one entitlement bound to it.
-
A resource definition can have one or more same-entitlement references bound to it. This capability provides support for entitlements where the entitlement parameters represent provisionable accounts or permissions on the connected system.
-
Entitlement and decision support parameters can be specified at design time (static) or at request time (dynamic).
Your workflow designer and system administrator are responsible for setting up the User Application for you and the others in your organization. The flow of control for a resource-based workflow, as well as the appearance of forms, can vary depending on how the workflow designer defined the workflow's approval definition in the Designer for Identity Manager. In addition, your job requirements and level of authority determine what you can see and do.
Resources
A resource is any digital entity such as a user account, computer, or database that a business user needs to be able to access. The User Application provides a convenient way for end users to request the resources they need. It also provides tools that administrators can use to define resources.
Each resource is mapped to an entitlement. A resource definition can have no more than one entitlement bound to it. A resource definition can be bound to the same entitlement more than once, with different entitlement parameters for each resource.
Resource Requests
Resources can be assigned to users only. They cannot be assigned to groups or containers. However, if a role is assigned to a group or container, the users in the group or container may automatically be granted access to the resources associated with the role.
Resource requests may require approvals. The approval process for a resource may be handled by one of the following:
-
a provisioning request definition
-
an external system, by setting the status code on the resource request
If a resource grant request is initiated by a role assignment, it is possible that the request will not be granted, even though the role is provisioned. The most likely reason for this would be that the necessary approvals were not provided.
A resource request can grant a resource to a user or revoke a resource from a user.
Role and Resource Service Driver
The User Application uses the Role and Resource Service Driver to manage back-end processing of resources, such as:
-
managing all resource requests
-
starting workflows for resource requests
-
initiating the provisioning process for resource requests
Resource Request Process Flow
The following example shows the process flow for a resource assignment request. In this example, a user requests a resource that grants access to an SAP profile:
Figure 1-1 Process Flow for a Resource Request
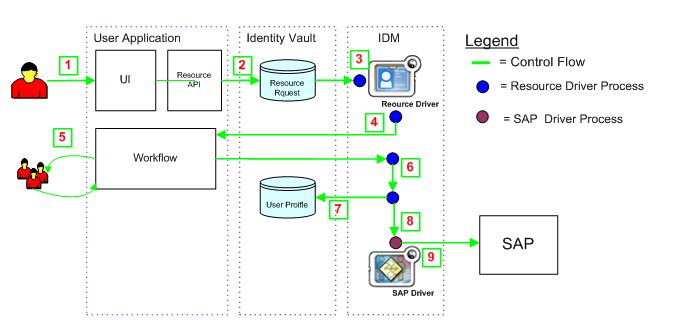
The steps in the process are described below:
-
A user requests a resource within the User Application.
-
A User Request object is created in the Identity Vault.
-
The Role and Resource Service Driver processes the new request.
-
The Role and Resource Service Driver starts a workflow, and changes the request status.
-
The approval process is performed within the User Application. Upon completion of the approval process, the workflow activity changes the request status.
-
The Role and Resource Driver picks up the change in the status and begins to provision the resource if all of the necessary approvals have been provided.
-
The User Object attributes are updated to include the resource binding and approval information.
-
An entitlement request is made for the SAP Profile.
-
The SAP Driver processes the entitlement and creates the profile in SAP.
1.1.4 About Workflow-Based Provisioning
Workflow‐based provisioning allows you to initiate workflow processes to manage the approval and revocation of user access to your organization’s secure systems.
The Work Dashboard tab in the User Application allows users to make workflow provisioning requests. A provisioning request is a user or system action intended to initiate a process, and can be in the following ways:
-
Directly by the user through the Work Dashboard tab
-
Indirectly in response to events occurring in the Identity Vault
When a provisioning request requires permission from one or more individuals in an organization, the request starts one or more workflows. The workflows coordinate the approvals needed to fulfill the request. Some provisioning requests require approval from a single individual; others require approval from several individuals. In some instances, a request can be fulfilled without any approvals.
By default, the Work Dashboard tab does not display any provisioning requests. To configure a provisioning request, a designer familiar with your business needs creates a provisioning request definition, which binds the resource to a workflow.
The designer can configure workflows that proceed in one of the following ways:
-
Sequential fashion, with each approval step being performed in order
-
Parallel fashion, which allows more than one user to act on a workflow task concurrently
Identity Manager provides a set of Eclipse-based tools for designing the data and the flow of control within the workflows. In addition, Identity Manager provides a set of Web-based tools that allow users to view existing provisioning requests and manage workflows that are in process. For more information, see Section 1.4, Design and Configuration Tools.
The Provisioning Administrator is responsible for managing the workflow-based provisioning features of the User Application. For more information, see Section 1.3, User Application User Types.
1.1.5 About Compliance
Compliance is the process of ensuring that an organization conforms to relevant business laws and regulations. One of the key elements of compliance is attestation, which provides a method for organizations to verify that personnel are fully aware of organizational policies and are taking steps to comply with these policies. By requesting that employees or administrators regularly attest to the accuracy of data, management ensures that personnel information such as user profiles, role assignments, and approved SoD exceptions are up-to-date and in compliance.
To allow individuals within an organization to verify the accuracy of corporate data, a user makes an attestation request, which initiates one or more workflow processes. The workflow processes give the attesters an opportunity to attest to the correctness of the data. A separate workflow process is initiated for each attester. An attester is assigned a workflow task in the My Tasks list on the Requests & Approvals tab. To complete the workflow process, the attester opens the task, reviews the data, and attests that it is correct or incorrect.
The Roles Based Provisioning Module supports four types of attestation:
-
User profile
-
SoD violations
-
Role assignment
-
User assignment
For details on setting up the Compliance tab, see Section 2.8, Configuring the Compliance Tab. For details on using the Compliance tab, see the discussion of the Compliance tab in the Identity Manager User Application: User Guide.
NOTE:For compliance and attestation processes, use NetIQ Access Review instead of the User Application. Access Review enables administrators and managers to easily collect all user and access information in one central location and certify that each user has only the level of access that they need to do their job. Following the principle of least privilege, Access Review helps you ensure that your users have focused access to those applications and resources that they use and cannot access resources that they do not need to access. You can review all permissions assigned to your employees, either individually or as a group, and decide whether those permission assignments are appropriate. For more information, see the NetIQ Access Review documentation.