1.3 Access Manager Components and Their Features
1.3.1 Administration Console
The Administration Console is the central configuration and management tool for the product. It contains a Dashboard option, which allows you to assess the health of all Access Manager components.
The Administration Console allows you to configure and manage each component. It also allows you to manage resources, such as policies, hardware, and certificates, which are used by multiple components.
1.3.2 Identity Servers
The Identity Server is the central authentication and identity access point for all other services. It is responsible for authenticating users and distributing role information to facilitate authorization decisions. It also provides the Liberty Alliance Web Service Framework to distribute identity information.
An Identity Server always operates as an identity provider and can optionally be configured to run as an identity consumer (also known as a service provider), by using Liberty, SAML 1.1, SAML 2.0 or OAuth protocols. As an identity provider, the Identity Server validates authentications against the supported identity user store. It is the heart of the user’s identity federations or account linkage information.
In an Access Manager configuration, the Identity Server is responsible for managing the following tasks:
-
Authentication: Verifies user identities through various forms of authentication, both local (user supplied) and indirect (supplied by external providers). The identity information can be some characteristic attribute of the user, such as a role, e-mail address, name, or job description. Advanced authentication mechanisms include Time-Based One-Time Password(TOTP), social authentication using external OAuth providers, and risk-based authentication.
-
Identity Stores: Links to user identities stored in eDirectory, Microsoft Active Directory, or Sun ONE Directory Server.
-
Identity Federation: Enables user identity federation and provides access to Liberty-enabled services.
-
Account Provisioning: Enables service provider account provisioning, which automatically creates user accounts during a federation request.
-
Custom Attribute Mapping: Allows you to define custom attributes by mapping Liberty Alliance keywords to LDAP-accessible data, in addition to the available Liberty Alliance Employee and Person profiles.
-
SAML Assertions: Processes and generates SAML assertions. Using SAML assertions in each Access Manager component protects confidential information by removing the need to pass user credentials between the components to handle session management.
-
Single Sign-On and Logout: Enables users to log in only once to gain access to multiple applications and platforms. Single sign-on and single logout are primary features of Access Manager and are achieved after the federation and trust model is configured among trusted providers and the components of Access Manager.
-
Identity Integration: Provides authentication and identity services to Access Gateways that are configured to protect Web servers. The Access Gateway and other Access Manager components include an embedded service provider that is trusted by Access Manager Identity Servers.
-
Roles: Provides RBAC (role-based access control) management. RBAC is used to provide a convenient way to assign a user to a particular job function or set of permissions within an enterprise to control access. The identity provider service establishes the active set of roles for a user session each time the user is authenticated. Roles can be assigned to particular subsets of users based on constraints outlined in a role policy. The established roles can then be used in authorization policies to form the basis for granting and restricting access to particular Web resources.
1.3.3 Access Gateways
An Access Gateway provides secure access to existing HTTP-based Web servers. It provides security services (authorization, single sign-on, and data encryption) previously provided by Novell iChain, and is integrated with the new identity and policy services of Access Manager.
Figure 1-3 Access Gateway Component
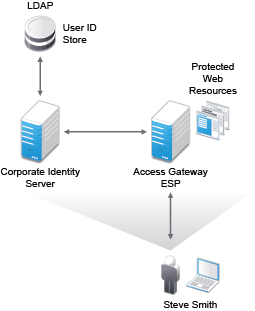
The Access Gateway is designed to work with the Identity Server to enable single sign-on to protected Web services. The following features facilitate single sign-on to Web servers that are configured to enforce authentication or authorization policies:
-
Identity Injection: Injects the information into HTTP headers that Web server requires.
-
Form Fill: Automatically fills in the requested form information.
If your Web servers have not been configured to enforce authentication and authorization, you can configure the Access Gateway to provide these services. Authentication contracts and authorization policies can be assigned so that they protect the entire Web server or a single page.
The Access Gateway can also be configured to cache requested pages. When a user meets the authentication and authorization requirements, the user is sent the page from cache rather than requesting it from the Web server, which enhances the content delivery performance.
There are two types of Access Gateways. Both are based on the same core technology and differ only in their deployment method.
Access Gateway Appliance: It is installed as a soft appliance, which includes the operating system.
Access Gateway Service: It requires you to provide the operating system.
Previous versions of Access Manager also provided a flexible deployment model for the Access Gateway that included both an appliance option (Linux Access Gateway) and a service option (Access Gateway Service). Features of the Access Gateway Appliance and the Access Gateway Service are same but differ from the Linux Access Gateway.
For more information about the differences, see Feature Comparison of Different Types of Access Gateways in the NetIQ Access Manager 4.1 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
For information about how to upgrade your chosen Access Gateway technology, see UpgradingAccess Manager in the NetIQ Access Manager 4.1 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Embedded Service Provider
The Access Gateway uses an Embedded Service Provider to redirect authentication requests to the Identity Server. The Identity Server requires requests to be digitally signed and encrypted and allows only trusted devices to participate. To become trusted, devices must exchange metadata. The Embedded Service Provider performs this task automatically for the Access Gateway .
1.3.4 User Portal
The Access Manager User Portal is a customizable application where end users can access and manage their authentications, federations, and profile data. The authentication methods you create in the Administration Console are reflected in the Portal.
Help information for the end users is provided in the user interface. If you know how to customize JSP* pages, you can customize the portal for rebranding purposes and for creating custom login pages.