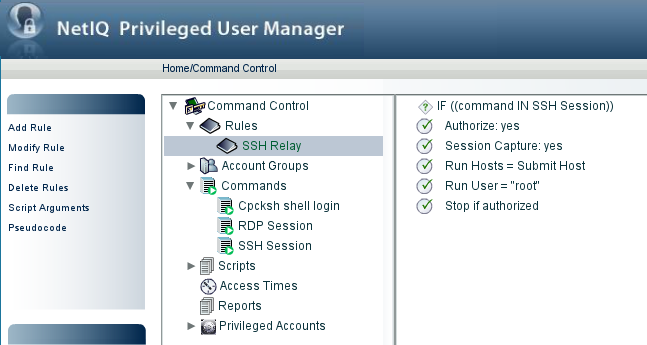
5.15 Secure Shell Relay
Secure Shell Relay (SSH Relay) provides the ability to access privileged accounts using a standard SSH client. This feature provides the ability to access Privileged User Manager functionality without a PUM agent on the target host. SSH Relay allows users to connect to a remote host using secure shell without knowing the privileged account credentials such as password or identity certificate of the user.
Configuring an SSH Relay Session
The packages are:
-
SSH Relay Agent
-
SSH Agent
SSH Relay listens on port 2222. You need to verify port 2222 is assigned for hosts running the SSH Relay Agent package.
Configuring an agent-less host for SSH Relay involves the following:
-
Create a Privileged Account Domain: For information on creating a privileged account domain, see Creating an Account Domain for Linux or Unix Systems.
-
Add a Rule: After creating an account, you need to set up the rules for the user to log in with a credential. For detailed information on adding a rule, see Section 5.6.1, Adding a Rule
Starting an SSH Relay Session
-
Start an SSH client, using the following format for the command:
ssh -t -p2222 <PUMframeworkuser@sshrelayhost> <root@hostname>
-
Provide credentials details for the SSH Relay user.
NOTE:Starting a SSH relay session with the above syntax will list all available sessions to the authenticated PUM framework user.
5.15.1 Using usrun for SSH Relay
This feature extends the SSH relay functionality by supporting the ability to issue a usrun command to access a machine through SSH and a credential vault.
Creating an Account Domain with Credentials
-
Click on the home page of the console.
-
In the navigation pane, select .
-
In the task pane, click .
-
Specify the following information:
Name: Specify the IP address or full DNS name of the host.
Type: Select as the account type for the user.
SSH Host: Select the host for the user.
SSH Host Key: Click to populate the host key; otherwise, manually specify the SSH host key.
Credential Type: In the drop-down list, select either or .
Account: Specify the account name of the domain user. Example: root.
Password: Specify the password for the domain user account, if you have selected credential type as .
SSH Key: Generate the key pair and copy the private key content here, if you have selected credential type as .
To generate the key pair:
-
Open an terminal as root to the remote agentless host and browse to the /.ssh folder.
-
Enter ssh-keygen -t rsa.
Public and private keys are generated.
-
Copy the content of the public key from the remote agentless host to the authorized_keys file.
-
Copy the content of the private key from the remote agentless host to the Privileged User Manager SSH private key.
Passphrase: Specify the passphrase that was entered while generating the key pair.
-
-
Click to save the account domain details.
Creating a Rule
-
Click on the home page of the console.
-
Click in the navigation pane.
-
Click in the task pane.
-
Specify a name for the rule.Click . The new rule is added.
-
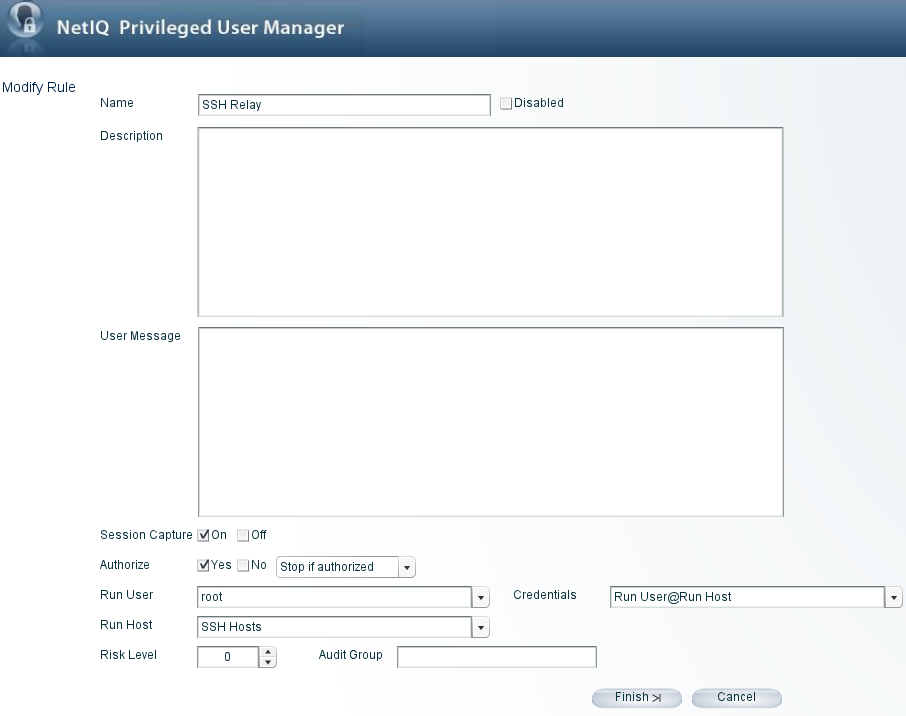
To configure the rule, select the rule, then click in the task pane.
Make the following changes:
Run User: Specify the user as root.
Credentials: From the drop-down list, select the required account domain. The Run User is automatically populated with the domain user provided in the account domain.
Run Host: Specify as Submit Host.
-
Click . The settings you have defined for the rule are displayed in the console.
Import SSH Session Command
-
Click on the home page of the console.
-
Click in the task pane.
-
Expand and select .
-
Click Finish. The samples are added to the appropriate section of the configuration.
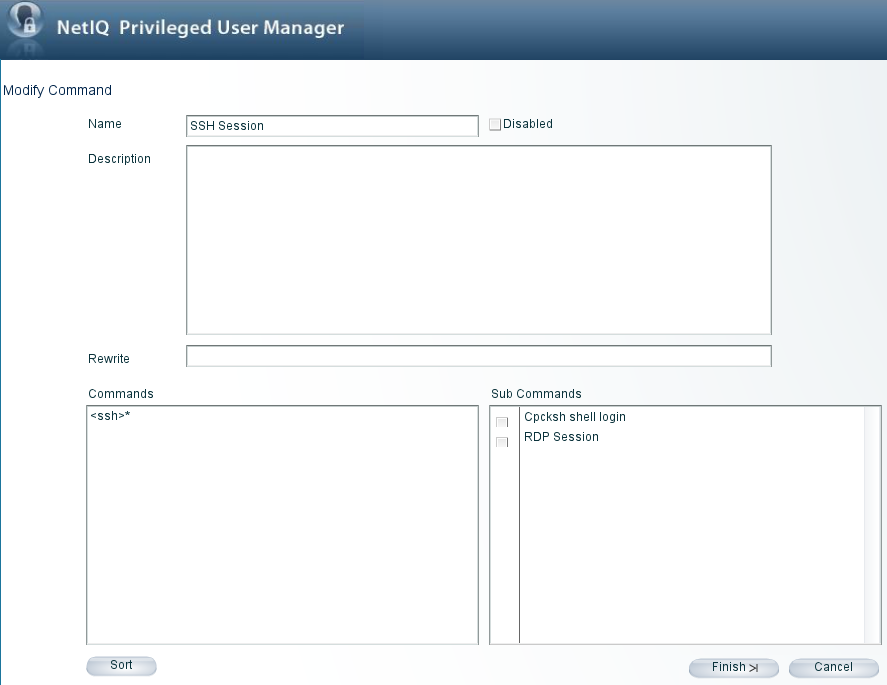
Adding a Command to a Rule
After creating a rule and a command, you need to add command definitions to your rule conditions to control whether the rule is processed, depending on the command that is submitted by the user.
To add a command to your rule:
-
Drag the command definition to the rule in the navigation pane.