5.8 Setting Up Conversion Networking
For each workload portability and protection job, you must properly configure workload networking so that:
-
Source workloads and targets can communicate with each other and Portability Suite Server during the conversion process.
-
The network configuration of a target workload is in line with its end state.
A job configuration interface provides configuration settings for:
Take Control Networking: Also called Temporary Network Settings; they apply to source and target workloads booted into a temporary pre-execution environment. See Offline Transfer with the Take Control Mechanism.
Target Post-conversion Networking: In peer-to-peer conversion and image deployment jobs, they apply to target virtual or physical NICs.
5.8.1 Take Control (Temporary) Network Settings
Take Control (Temporary) Network Settings control how source workloads, targets, and the Portability Suite Server communicate among each other during the conversion. If required, you can manually specify a temporary network address to your source and target, or configure them to use a DHCP-assigned IP address during the conversion.
During Windows and Linux workload conversions, the Take Control (Temporary) Network Settings control the Portability Suite Server’s communication with the source and target workloads that are booted into a temporary pre-execution environment. See Offline Take Control Transfer of Windows and Linux Workloads.
During Solaris workload conversions, temporary network settings for the target are not required, and the corresponding option is disabled. For source workloads, the capability to assign temporary network settings is subject to the following conditions:
-
Temporary network settings can be assigned to a Solaris source workload if it is a physical machine with no non-global zones.
-
Temporary network settings cannot be assigned to a source workload that is a Solaris zone with its network interface in exclusive mode.
See Offline Take Control Transfer of Solaris Workloads.
To configure Take Control (Temporary) network settings:
-
In Advanced mode: In the Conversion Job window, under the Job Configuration section, click . To access network interface mapping and TCP/IP settings, click in the source and target areas as applicable.
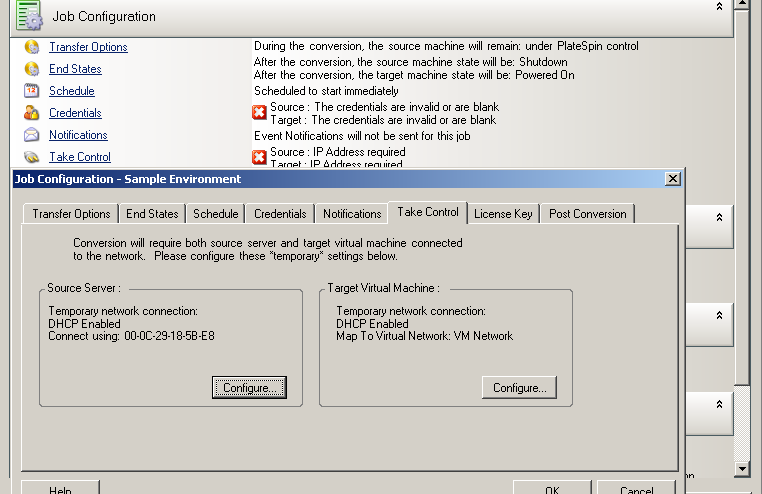
-
In Wizard mode: In the wizard’s navigation pane, click In the or row, in either or drop-down menu, select . To quickly select DHCP without opening configuration options, select .
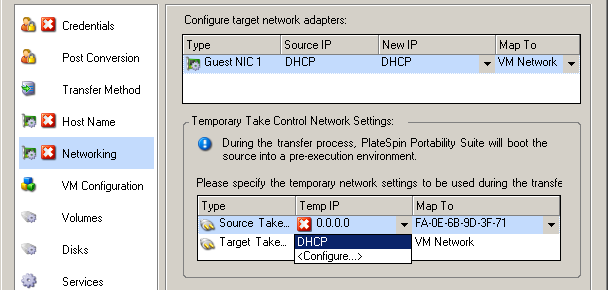
Configuration options for the Take Control (Temporary) networking vary and depend on whether the network interface is virtual or physical, and whether it is connecting a Windows or a Linux workload.
Target Take Control network settings are only used during a Take Control conversion process. On completion, target network settings are read from settings you specify for Target Post-conversion Networking. See Target Post-conversion Networking:.
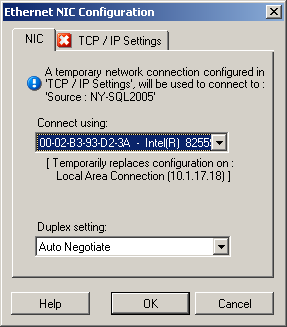
Take Control (Temporary) Network Settings: Physical Network Interfaces
These settings apply only to source physical machines. For target physical machines, Take Control (Temporary) Network settings are configured during the boot process that uses the Take Control ISO image. See Discovering and Registering Target Physical Machines.
|
If multiple network adapters are present, select the adapter that can communicate with both the Portability Suite Server and the target. Use the drop-down list to select network card duplexing. It must match the duplex setting for the switch to which the network interface is connected. When the source is connected to switch ports that are set to 100 Mbit full duplex and cannot be changed to auto negotiation, select . tab: Click to access TCP/IP and advanced network settings. See TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings. |
|
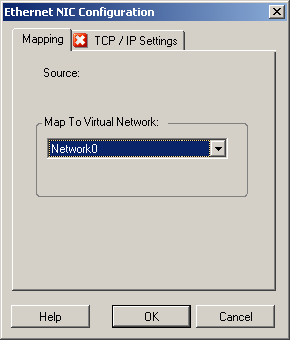
Take Control (Temporary) Network Settings: Virtual Network Interfaces
These settings apply to both source and target Take Control (Temporary) network settings.
|
From the drop-down list, select the virtual switch or network to use for communication during a Take Control conversion. If multiple virtual network adapters are present, select the adapter that can communicate with both the Portability Suite Server and the source machine. This network can differ from the network on which the target virtual machine will run after the conversion. tab: Click to access TCP/IP and advanced network settings. See TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings. |
|
5.8.2 Target Post-conversion Networking
Target post-conversion network settings defined in a conversion job control the network configuration of a target after the conversion is complete. This applies to both physical and virtual network interfaces.
During the migration of Windows and Linux workloads, the target workload’s post-conversion network settings are configured while the workload is booted into a pre-execution environment. during the migration of Solaris workloads, the target’s post-conversion network settings are configured through the target zone’s host.
To configure target post-conversion network settings:
-
In Advanced mode: In the Conversion Job window, under the Network Configuration section, click (for target virtual machines) or (for target physical machines).
-
In Wizard mode: In the wizard’s navigation pane, click In the Configure Target Network Adapters section, in either or drop-down menu, select . To quickly select DHCP without opening configuration options, select .
Configuration options for the target post-conversion network settings vary and depend on whether the network interface is virtual or physical, and whether it is connecting a Windows or a Linux workload.
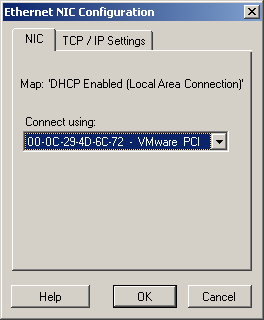
Post-conversion Networking for Physical Network Interfaces (Windows and Linux)
Use these settings to configure the post-conversion network settings of a workload being migrated to physical hardware.
|
If multiple network adapters are present, select the adapter that can communicate with the Portability Suite Server. tab: Click to access TCP/IP and advanced network settings. See TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings. |
|
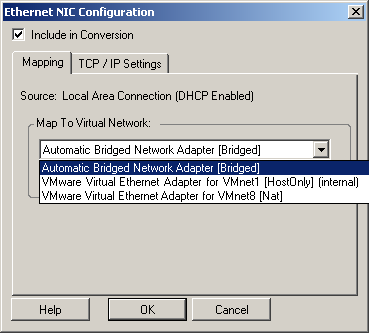
Post-conversion Networking for Virtual Network Interfaces (Windows and Linux)
By default, Portability Suite configures a conversion job to create a virtual NIC for each NIC found on the source. For post-conversion connectivity, ensure that the target virtual NIC is mapped to the appropriate virtual network on the target virtualization platform.
|
When this options is selected, Portability Suite creates a virtual NIC for a source NIC. Select the virtual adapter that will be used on the target machine after the conversion is complete. Enable this option to connect the virtual network interface when starting the target machine. tab: Click to access TCP/IP and advanced network settings. See TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings. |
|
5.8.3 TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings
Portability Suite provides a standard network configuration interface to both source and target network settings, and for both Take Control (Temporary) and target post-conversion networking. Configuration settings vary slightly, depending on the operating system.
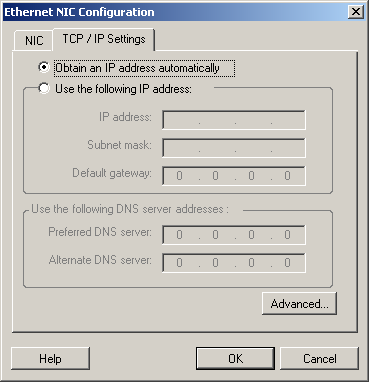
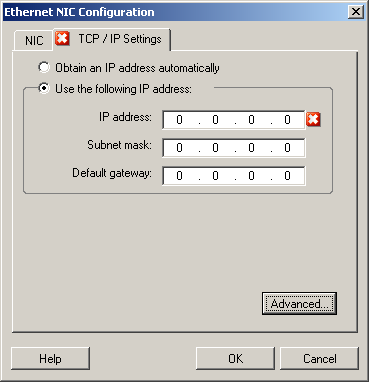
TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings (Windows)
The following are standard TCP/IP and advanced network settings for Windows workloads:
TCP/IP and Advanced Network Settings (Linux and Solaris)
The following are standard TCP/IP and advanced network settings for Linux workloads: