5.7 Failback
A Failback operation is the next logical step after a failover; it transfers the failover workload to its original infrastructure or, if necessary, a new one.
Supported failback methods depend on the target infrastructure type and the degree of automation of the failback process:
-
Automated Failback to a Virtual Machine: Supported for VMware ESX platforms and VMware DRS Clusters.
-
Semi-Automated Failback to a Physical Machine: Supported for all physical machines.
-
Semi-Automated Failback to a Virtual Machine: Supported for Xen on SLES and Microsoft Hyper-V platforms.
The following topics provide more information:
5.7.1 Automated Failback to a VM Platform
The following containers are supported as automated failback targets:
|
Target |
Notes |
|---|---|
|
VMware DRS Cluster in vSphere 5.1 |
|
|
VMware DRS Cluster in vSphere 5.0 |
|
|
VMware DRS Cluster in vSphere 4.1 |
|
|
VMware ESXi 4.1, 5.0, 5.1 |
ESXi versions must have a paid license; protection is unsupported with these systems if they are operating with a free license. |
|
VMware ESX 4.1 |
|
Use these steps to do an automated failback of a failover workload to a target VMware container.
-
Following a failover, select the workload on the Workloads page and click .
The system prompts you to make the following selections
-
Specify the following sets of parameters:
-
Workload Settings: Specify the failover workload’s hostname or IP address and provide administrator-level credentials. Use the required credential format (see Guidelines for Workload Credentials).
-
Failback Target Settings: Specify the following parameters:
-
Replication Method: Select the scope of data replication. If you select , you must a target. See Initial Replication Method (Full and Incremental).
-
Target Type: Select . If you don’t yet have a failback container, click and inventory a supported container.
-
-
-
Click and monitor the progress on the Command Details screen.
Upon successful completion, PlateSpin Forge loads the Ready for Failback screen, prompting you to specify the details of the failback operation.
-
Configure the failback details. See Failback Details (Workload to VM).
-
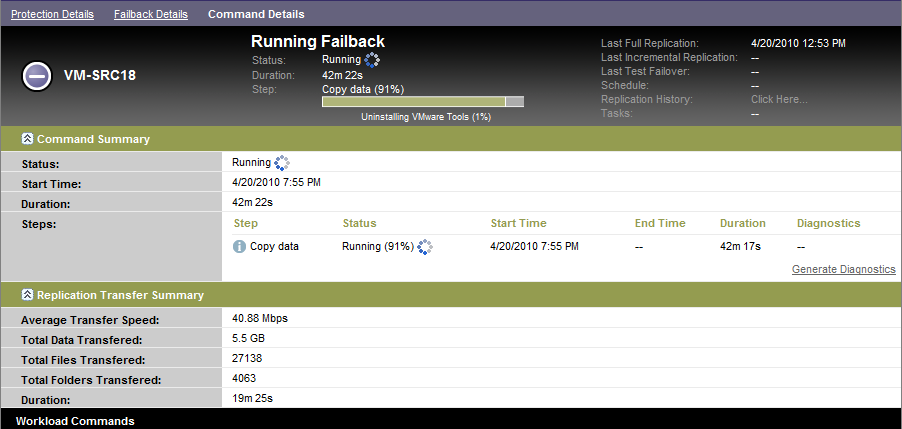
Click and monitor the progress on the Command Details page. See Figure 5-2.
PlateSpin Forge executes the command. If you selected in the Post-Failback parameter set, a command is shown in the PlateSpin Forge Web Interface.
Figure 5-2 Failback Command Details
Failback Details (Workload to VM)
Failback details are represented by three sets of parameters that you configure when you are performing a workload failback operation to a virtual machine.
Table 5-2 Failback Details (VM)
|
Parameter Set (Settings) |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Failback |
Transfer Method: Enables you to select a data transfer mechanism and security through encryption. See Data Transfer. Failback Network: Enables you to direct failback traffic over a dedicated network based on virtual networks defined on your appliance host. See Networking. VM Datastore: Enables you to select a datastore associated with your failback container for the target workload. Volume Mapping: When the initial replication method is specified as “incremental”, enables you to select source volumes and map to volumes on the failback target for synchronization. Services/Daemons to stop: Enables you to select Windows services or Linux daemons that are automatically stopped during the failback. See Service and Daemon Control. Alternative Address for Source: Accepts input of an additional IP address for the failed-over VM if applicable. See Protection Across Public and Private Networks Through NAT. |
|
Workload |
Enables you to specify the required number of vCPUs assigned to the target workload. VM Memory: Enables you to assign the required RAM to the target workload . Hostname, Domain/Workgroup: Use these options to control the identity and domain/workgroup affiliation of the target workload. For domain affiliation, domain administrator credentials are required. Network Connections: Use these options to specify the network mapping of the target workload based on the virtual networks of the underlying VM container. Service States to Change: Enables you to control the startup state of specific application services (Windows) or daemons (Linux). See Service and Daemon Control. |
|
Post-Failback |
Reprotect Workload: Use this option if you plan to re-create the protection contract for the target workload after deployment. This maintains a continuous event history for the workload and auto-assigns/designates a workload license.
|
5.7.2 Semi-Automated Failback to a Physical Machine
Use these steps to fail a workload back to a physical machine after a failover. The physical machine might be either the original infrastructure or a new one.
-
Register the required physical machine with your PlateSpin Server. See Failback to Physical Machines.
-
If there are missing or incompatible drivers, upload the required drivers to the PlateSpin Forge device driver database. See Managing Device Drivers.
-
Following a failover, select the workload on the Workloads page and click .
-
Specify the following sets of parameters:
-
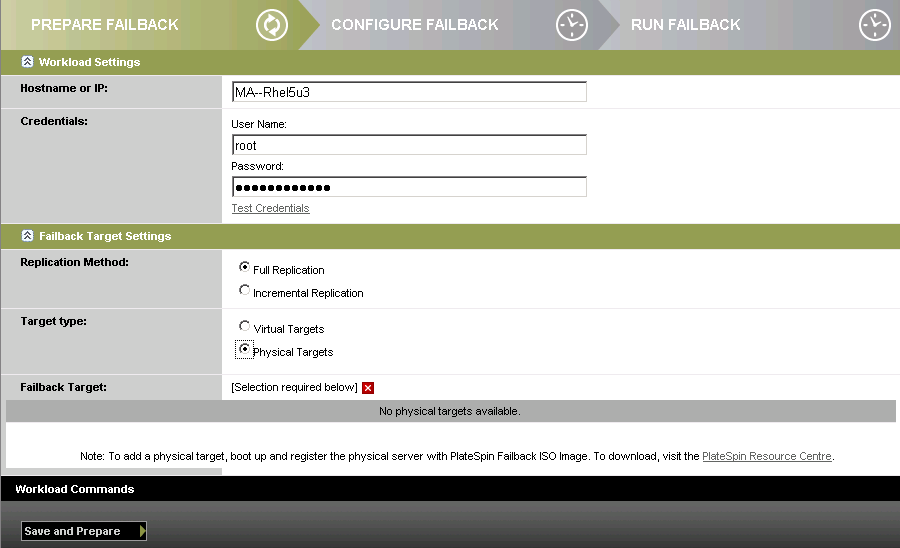
Workload Settings: Specify the failover workload’s hostname or IP address and provide administrator-level credentials. Use the required credential format (see Guidelines for Workload Credentials.
-
Failback Target Settings: Specify the following parameters:
-
Select the scope of data replication.
-
Select the option and then select the physical machine you registered in Step 1.
-
-
-
Click and monitor the progress on the Command Details screen.
Upon successful completion, PlateSpin Forge loads the Ready for Failback screen, prompting you to specify the details of the failback operation.
-
Configure the failback details, then click .
Monitor the progress on the Command Details screen.
5.7.3 Semi-Automated Failback to a Virtual Machine
This failback type follows a process similar to the Semi-Automated Failback to a Physical Machine for a VM target other than a natively-supported VMware container. During this process, you direct the system to regard a VM target as a physical machine.
A semi-automated failback to a VM is supported for the following target VM platforms:
-
Xen on SLES 10 SP2
-
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 (not R2)
You can also do a semi-automated failback to a container, for which there is fully-automated failback support (VMware ESX and DRS Cluster targets).