1.1 About Workload Portability
PlateSpin Migrate automates the migration of workloads among three infrastructures: physical, virtual machine, and volume imaging.
Figure 1-1 Workload Portability
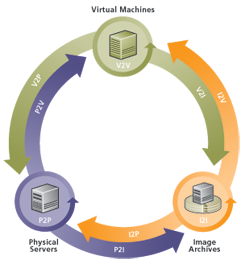
Table 1-1 Workload Portability Operations
|
Category of Operation |
Migration Infrastructures |
|---|---|
|
Workload Portability: Peer-to-peer |
|
|
Workload Portability: Imaging |
|
PlateSpin Migrate supports multiple workload types and virtualization platforms. Imaging is supported for workloads with Microsoft Windows operating systems. For a more detailed list of supported workloads and infrastructures, see Supported Configurations.
PlateSpin Migrate 12.0 introduces a Web Interface that supports large scale migration of workloads to VMware containers. Do not use the PlateSpin Migrate Client and the PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface interchangeably to perform the migration tasks during the migration process of a workload. NetIQ Corporation strongly recommends that you either use the PlateSpin Migrate Client or the PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface throughout the migration cycle of a workload. For information about the tasks you can perform using the PlateSpin Migrate Client and the PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface, see Section 1.1.3, Migration Tasks Matrix for PlateSpin Migrate Client and PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface.
1.1.1 Business Applications for PlateSpin Migrate
PlateSpin Migrate is designed to be used for the following scenarios:
-
Consolidation. Automating large-scale migrations of physical machines to virtual machines, accelerating consolidation projects, and reducing administrative effort and errors.
-
Migration. Moving fully configured workloads from old hardware to new hardware without rebuilding the entire software stack.
-
Test Lab Deployment. Consolidating test lab workloads by running multiple virtual machines on a single VM host, quickly deploying virtual test lab environments with ease, and replicating an entire production environment in matter of hours or days.
-
Maintenance and Support Agreement Integrity. De-virtualizing workloads along with the applications installed on them and moving them back to physical machines over the network so that the support agreements can remain valid.
-
Machine Provisioning. Easily capturing an entire library of hardware-independent PlateSpin Images and deploying them to new infrastructures over the network without manually configuring the hardware, drivers, and so on.
-
Continuous Workload Optimization. Moving workloads to and from any geographical location, onto any platform, in any direction. Workloads can be virtualized or de-virtualized during ongoing and continuous optimization of resources.
1.1.2 Workload Migration Tasks
PlateSpin Migrate enables you to define, save, schedule, execute, and monitor the following migration tasks.
Table 1-2 PlateSpin Migrate Workload Migration Tasks
|
Task |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Copy Workload |
Results in a virtual or physical duplicate of a selected physical or virtual workload, except that the new workload is assigned a new network identity. Use this migration task when you intend to keep the source workload operational. |
|
Move Workload |
Results in an exact virtual or physical duplicate of a selected physical or virtual workload. Use this migration task when you intend to retire or repurpose the original infrastructure. |
|
Server Sync |
Synchronizes a virtual or physical workload with another virtual or physical workload without transferring the entire source volume data over the network. |
|
Capture Image |
Creates an image of a physical or virtual workload as a single entity, in PlateSpin Image format. |
|
Deploy Image |
Converts a PlateSpin Image into a booted or bootable workload on a physical or virtual machine. |
1.1.3 Migration Tasks Matrix for PlateSpin Migrate Client and PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface
To migrate a workload, you should either use the PlateSpin Migrate Client or the PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface throughout the migration cycle of the workload.
The following table lists the tasks that you can perform using the PlateSpin Migrate Client and the PlateSpin Migrate Web Interface:
|
Tasks |
PlateSpin Migrate Client |
PlateSpin Migrate web Interface |
|---|---|---|
|
Workload Migration Workflow |
✗ |
✓ |
|
Workload Migration to VMware targets |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Workload migrations to non-VMware targets such as Hyper-V or physical machine |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Discovery of VMware target |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Discovery of Hyper-V Container |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Discovery of Windows or Linux workloads |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Live Transfer Workload Migration |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Offline Transfer Workload Migration |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Incremental Replication Recurrence Scheduler |
✗ |
✓ |
|
Windows workload migration using BBT driver |
✗ |
✓ |
|
Linux workload migration using BBT driver |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Migrating Windows workloads using File-Based transfer method |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Migrating Linux workloads using File-Based transfer method |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Migrating workloads using Block-Based transfer |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Migrating staged workloads using imaging |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Support for post migration scripts |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Adding new disks during migration |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Changing disk volume mapping for target workload |
✓ |
✗ |
|
Migrating a VM to a folder inside the resource pool |
✗ |
✓ |
|
Moving a VM to a resource pool |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Compression level |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Bandwidth throttling |
✓ |
✓ |
|
encryption |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Creating tags |
✗ |
✓ |
|
Workload migration report |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Workload migration status reports |
✗ |
✓ |
|
Adding or removing of licenses |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Checking the status of licenses |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Security Groups |
✗ |
✓ |