NetIQ PlateSpin Forge 11.2 Release Notes
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 includes new features, improves usability, and resolves several previous issues. It also resolves important performance and reliability issues. This version of Forge is a software only release.
The documentation for this product is available in HTML and PDF formats at the PlateSpin Forge 11.2 Documentation website.
For information about how to purchase and download this product, see the PlateSpin Forge product website.
1.0 Documentation Updates
The following updates have been made to this document since the initial release of PlateSpin Forge 11.2. The modified content does not appear in translated versions of this document.
1.1 October 2017
-
Desktop (workstation) platforms are no longer supported for protection. See Section 3.0, Unsupported Platforms.
-
Updated cross-references to Product and Support websites.
1.2 August 2016
-
Added the following item to Known Issues: 983567 Full Replication Breaks Differential Backup for SQL Server..
2.0 What’s New?
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 provides new key features and enhancements, and resolves several issues.
Many of these improvements were made in direct response to suggestions from our customers. We thank you for your time and valuable input. We hope you continue to help us ensure our products meet all your needs. You can post feedback in the PlateSpin Forge discussion on Micro Focus Forums, our community website that also includes product notifications, blogs, and product user groups.
2.1 Supported Configurations
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 includes expanded support for the following configurations:
Workloads
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 adds support for the following operating systems as workloads:
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 failover clusters
-
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.6
-
CentOS 4, 5, 6, and 7
For information about the workload configurations supported by PlateSpin Forge 11.2, see Supported Configurations
in the PlateSpin Forge User Guide.
VM Containers
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 adds support for VMware ESXi 6.0 as a VM container.
For information about the VM containers supported by PlateSpin Forge 11.2, see Supported VM Containers
in the PlateSpin Forge User Guide.
Blkwatch Drivers
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 adds blkwatch drivers for the following Linux distributions:
-
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.6
For a list of the non-debug Linux distributions for which PlateSpin Forge has a blkwatch driver, see Linux Distributions Supported by PlateSpin Forge
in the PlateSpin Forge User Guide.
2.2 Security Enhancements
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 provides the following security enhancements:
-
Windows cluster discovery: The ability to discover a Windows cluster based on its active node, instead of using the virtual cluster name and an administrative share.
-
Administrator user password: The ability to set the Administrator user password on the Forge Management VM using native Windows management tools.
2.3 Software Features and Enhancements
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 provides the following key features and enhancements for usability and management:
-
Virtual cores and sockets: The ability to define the number of cores and the number of cores per socket for the CPU of the replication workload on a VM container using VMware ESXi 5.1, 5.5, or 6.0.
-
Windows cluster discovery: The ability to discover Windows clusters based on their active node, and add them as cluster workloads. You can enable or disable Windows cluster discovery for your PlateSpin environment.
2.4 Software Fixes
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 addresses the following software issues:
-
942967 On the first full replication, the target VM boots up into bootofx.iso but it is waiting for the address of the PlateSpin Server. For some configurations of the Cores per Socket setting for workloads, PlateSpin did not properly load the floppy image, so the target VM is not configured correctly. This issue is resolved in this release.
-
940798 Block based transfer exclude file list not working. The Block Based Volume Server Exclude and Include lists can accept new files in the lists, in addition to the default files. You can add a new list by using the following parameters in the Platespin Configuration settings:
- BlockBasedTransferExcludeFileList
- BlockBasedTransferIncludeFileList
-
940228 Target does not boot, error "Volume with serial number 00000000 does not exist among these known serial numbers". An exception occurred when a tmp or temp folder environment variable was mapped to a drive that was not included in the replication contract. This issue is resolved.
-
932222 2TB MBR Drive does not validate when partitioning targets. Previously, a workload on a 2 TB drive using the MBR partition table was automatically converted to use the GPT partition table at the target workload on the ESXi 5.5 VM container, and failed validation because of the mismatch. This issue is resolved.
-
931518 Protect Web UI throws unexpected error when doing a workload 'Prepare and Save'. This issue is resolved.
-
929770 After upgrade from 11.0 to 11.1, the source OFX connection is not established "An invalid IP address was specified”. For Windows Server 2003 R2 32-bit cluster workloads with multiple NICs, PlateSpin was unable to verify the server and network, and the OFX Controller could not start to perform a heartbeat check. In prior releases, PlateSpin would use any source NIC to retrieve the Gateway and DHCP server IP addresses. However, in version 11.1, the OFX Controller uses a specific NIC to retrieve them. If the IP addresses are not specified, Windows Server 2003 R2 32-bit does not provide default values for them, and the action fails. This issue is resolved.
-
927013 Number of CPUs is incorrect. Previously, discovery treated the number of sockets as the number of CPUs, assuming one core per socket. This release provides the ability to define the number of cores and the number of cores per socket for the CPU of the replication workload on a VM container using VMware ESXi 5.1, 5.5, or 6.0.
-
926354 Error "No Valid snapshot transfer method provider" at first replication. File-based and block-based replications use the Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to enable PlateSpin to copy data from a frozen file system. Previously, PlateSpin checked for the VSS shadow provider existence during the first replication. PlateSpin now checks for the existence of the VSS shadow provider during workload discovery.
-
926291 Block-based transfer driver is causing the Source Server to fail to boot. Previously, the block-based transfer driver detected stale and unavailable Volume Shadow Copies, which created problems that caused the source server to fail to boot. The driver now ignores the shadow copies of file server.
-
922954 Error "Cannot be negative" at first replication. Previously, if files used an Alternate Data Stream extended attribute with a $ (dollar character) in the alternate data stream name, an exception occurred during file-based transfers for a replication. File-based transfers can now handle this use case.
-
921103 Unable to load DLL ZLibWrapper. Previously, you had to manually add the current directory to the DLL loading paths by using SetDllDirectory for ZLibWrapper.dll if the environment did not include the current directory in the dll search path. To resolve this issue, the product now checks the current directory when searching for the ZLibWrapper.dll file when doing a compressed replication.
-
918295 Failed creating partition on 4.9 T volume. Previously, PlateSpin detected only MBR type partitions. PlateSpin now detects and handles both MBR and GPT (GUID Partition Table) disk partition schemes during WMI discovery.
-
912149 Windows Server 2003 "[80004005] System error code/HRESULT: [80004005]" at data transfer step. Previously, PlateSpin process invalid MFT index data and tried to read the records of invalid indexes, which caused replications to fail. PlateSpin now filters out invalid index data so that it does not attempt to read the records of invalid indexes.
-
906633 Dashboard needs to support more than 60 workloads. Previously, the Workload Summary in the PlateSpin Server dashboard displayed 60 dot icons. The maximum number of workload status dot icons now matches the number of installed workload licenses on the PlateSpin Server. For an unlimited license, the summary displays 96 dot icons.
-
886325 Windows Server 2012 Workload's network configuration UI should not show up as DHCP enabled when it has a static IP address. Although the source workload and target workload had static IP network configurations, the Windows network adapter properties reported that the network configuration had DHCP enabled. The PowerShell commands showed that DHCP was disabled. No loss of network functionality was observed. This issue is resolved in this release.
-
865570 File Based Transfer breaks for Windows Server 2012 R2 UEFI workload. X2P File-based transfer of Windows 6.2 and above kernel versions fails during the sending and receiving files stage.
To force file transfer to work in this X2P scenario, you need to disable the CPU advanced flags in the firmware: VT-d, VT-s, Execute Disable Bit. For more information, see Knowledgebase Article 7014698.
3.0 Unsupported Platforms
PlateSpin Forge 11.2 no longer supports the protection of desktop (workstation) platforms for any operating system, effective October 17, 2017.
4.0 Updating PlateSpin Forge
To update your PlateSpin Server to PlateSpin Forge 11.2, you must have an existing installation of any of the following versions of the product, with or without hotfixes or field patches:
-
PlateSpin Forge 11.0
Other direct updates are not supported. For earlier versions of PlateSpin Forge, you must first upgrade to one of these versions before you can upgrade to PlateSpin Forge 11.2. For more information about how to upgrade your PlateSpin Server, see the PlateSpin Forge Upgrade Guide.
5.0 Known Issues
NetIQ Corporation strives to ensure our products provide quality solutions for your enterprise software needs. The following issues are currently being researched. If you need further assistance with any issue, please contact Technical Support.
-
983567 Full Replication Breaks Differential Backup for SQL Server. After a full replication for a Microsoft Windows Server 2012 workload running Microsoft SQL Server 2012, the SQL Server’s differential backup fails until a full backup with Microsoft tools runs again.
This issue occurs if Microsoft VSS Writer for SQL Server (the SqlServerWriter option for the Volume Shadow Copy Service) is enabled on the SQL Server during replication. During the VSS shadow copy for replication, SqlServerWriter modifies the database backup configuration in a way that prevents you from using an existing backup file for differential backups. (Bug 983567)
Workaround: We recommend that you follow vendor-specific backup and recovery best practices for SQL Server, which might include stopping some services during replication to ensure application data consistency. When you configure a workload for PlateSpin Failover or Failback, back up and restore the SQL database using backups generated from Microsoft tools.
To prevent the differential backup failures caused by SqlServerWriter, do one of the following:
-
Manage the SQL Server data backups and recovery based on Microsoft recommendations. Disable the Microsoft VSS Writer for SQL Server service on the source workload so that SqlServerWriter does not run during replications or other VSS shadow copies on the server.
-
If Microsoft VSS Writer for SQL Server is running during a replication, the database backups will fail after each replication until a full backup with Microsoft tools runs again. If you use a separate schedule for database backups, after a replication, you must reconfigure the backup destination and run a full backup of the database using Microsoft tools before you run any differential backups.
-
-
No software RAID support for Linux workloads. PlateSpin Forge does not support Linux workloads with volumes on software RAID.
-
949765 Prepare for Sync incorrectly modifies sockets and cores settings on the target VM. In some conditions, Prepare for Sync honors the total number of CPUs set for the target VM, but it can incorrectly modify the settings for cores and sockets. It sets the cores per socket to 1, and the number of sockets to the total number of CPUs.
This issue is observed during two tasks: creating a server-sync contract and preparing the target at reprotect. It affects target VMs only on ESXi 5 and later VM containers, where VMware provides settings for the number of sockets and cores per socket. In addition, the server-sync contract does not display the cores and sockets settings.
For example, on an ESXi 5.5 VM container, if the CPU settings for a target VM are set to 6 sockets and 3 cores per socket, Prepare for Sync incorrectly re-configures the CPU settings to 18 sockets and 1 core per socket.
Workaround: There is no workaround at this time.
-
949579 Failback to Physical fails when the boot mode for source and target are not the same (UEFI <-> BIOS). When you initiate the Save and Failback option for a source workload that uses UEFI boot mode, the failback fails if the physical target workload uses the BIOS boot mode. This occurs because of the mismatch in boot modes for the source and target.
Workaround: Change the boot mode on the target workload to match the boot mode of the source workload.
-
948855 Full replication fails with error "Array index is out of range." For file-based replications, after you upgrade to version 11.2, subsequent full replications can fail if the workload has extended partitions with logical drives. The first full replication after the upgrade and incremental replications are not affected.
Workaround: You can use block-based replication on workloads with extended partitions and logical drives.
-
947597 After you upgrade to 11.2, the settings for SMTP, email notification, and replication reports are not retained. The email notifications and reports are not available after you upgrade to 11.2. Your settings for these features were reset during the upgrade.
Workaround: Reconfigure the SMTP, Email Notification, and Reports settings. See
Configuring Automatic Email Notifications of Events and Reports
in the User Guide. -
947072 After you upgrade to version 11.2, Windows cluster workload replication fails if the DNS resolution fails for the cluster and its nodes. Because of changes in the Windows cluster support in version 11.2, PlateSpin Forge requires full DNS resolution for forward lookup and reverse lookup of the IP addresses for the cluster and its nodes. The incremental replication of an existing cluster workload fails with the following errors:
GatherMachineData service failed. The RPC server is unavailable (Exception from HRESULT: value)Failures can also occur whenever the PlateSpin Forge Server refreshes (re-discovers) the workload, such as for actions where it copies data, but not elsewhere.
Workaround: Ensure that the PlateSpin Forge Server can resolve DNS forward lookup and reverse lookup for the IP addresses of the cluster and its cluster nodes. You can update the DNS server or update the local hosts file (%systemroot%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts) on the Forge VM.
-
946124 Default Cluster IP Address name for Chinese is incorrect. In the MicrosoftClusterIPAddressNames list, the default search entries for the Cluster IP Address resource name in the Chinese Simplified and Chinese Traditional languages are missing a space character before and after the IP characters. When you try to add a workload for a Windows cluster node configured for the Chinese language, the search for the Cluster IP Address resource name fails to match an entry in the MicrosoftClusterIPAddressNames list. The PlateSpin Server cannot discover the cluster workload, and the add workload action fails.
Workaround: In the MicrosoftClusterIPAddressNames list on the PlateSpin Configuration page, add a space before and after IP in the search entries for Cluster IP Address resource name in the Chinese Simplified and Chinese Traditional languages.
For example, change
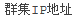 to
to 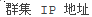 .
.
-
945571 Windows 2012 workload, file-based transfer: Incremental replication causes chkdsk errors on target. In Windows Server 2012 R2, Microsoft introduced an automatic disk cleanup process that runs regularly and attempts to reduce the amount of data that Windows stores in the %systemroot%\WinSxS (Windows side by side) folder. The process can replace files that are no longer in use by smaller compressed versions with the same name. It is highly likely that some of the replaced files were actually hard links. This process can also occur on previous Windows versions if you install and use this Windows Disk Cleanup tool on them.
When PlateSpin performs an incremental replication after the Windows process has run, the replication does not accurately handle the situation of the files that have changed from a hard link to a compressed file. PlateSpin does not properly remove the hard link on the target VM, and the files remain hard linked on the target. After the incremental replication, the failover VM might display chkdsk errors for those files, such as:
Minor file name errors were detected in file 25467. Index entry wucltux.dll.mui in index $I30 of file 56447 is incorrect. Index entry WUCLTU~1.MUI in index $I30 of file 56447 is incorrect.
Workaround: If you encounter this issue, you must run a full replication of the workload to resolve the errors, which will make a complete copy of the source workload to the protection target VM.
-
945090 DNS settings are not sticky at X2P failback on target with multiple NICs. For workloads with multiple NICs, the DNS settings are not automatically configured during the failback.
Workaround: After the failback is complete, you must manually configure the DNS settings on the NICs.
-
944932 Windows Server 2003 R2 cluster: 'Prepare for Failover' is stuck trying to configure the failover VM’s NICs. The Prepare for Failover option can take over 6 hours to complete on a Windows Server 2003 R2 cluster while it tries to configure the failover VM’s NICs. This option is typically used in a production environment to prepare the environment prior to performing a cluster node failover during a scheduled maintenance window. On the same cluster, the Test Failover option or Failover option occurs without issues in an acceptable time.
This issue is not observed on Windows Server 2008 R2 clusters and Windows Server 2012 R2 clusters.
Workaround: On a Windows Server 2003 R2 cluster, perform the failover directly; do not use the Prepare for Failover option.
-
944559 Incremental File-Based Replication does not complete with Encryption enabled. After you enable Encryption for a Windows workload that is configured for file-based data transfer, the Windows receiver might hang at the end of the transfer for incremental replications. The hang occurs if the last byte read of the transfer is incorrectly set by the encryption process to a non-zero value, indicating that more files are being transferred and to continue reading from the stream.
Workaround: You can use block-based data transfer for Windows workloads if you want to enable Encryption for replication data transfers.
-
943932 We should not add non-active node as standalone workload, when 'DiscoverActiveNodeAsWindowsCluster = True'. In PlateSpin Forge 11.2, you can enable or disable the discovery of Windows clusters based on the active node by using the DiscoverActiveNodeAsWindowsCluster = True parameter in the PlateSpin Configuration. During discovery, you might see the non-active node as a standalone workload. You will not receive a warning that the node is part of a protected cluster.
Workaround: Ensure that you use the active node to protect the cluster. Alternatively, you can manage all Windows cluster nodes as standalone workloads by disabling the DiscoverActiveNodeAsWindowsCluster parameter in the PlateSpin Configuration.
-
937476 In a Windows Server 2008 R2 cluster in a PlateSpin failback configuration, the wrong NICs are mapped. After a PlateSpin failover and failback occurs for the Windows Server 2008 R2 cluster, the Microsoft Cluster Management software maps the NICs based on defaults instead of the source assignments for the NICs. The failback does not complete because the mappings do not match the expected configuration.
Workaround: The user must switch the IP configuration to the expected mappings so that the target is successfully configured, which allows the failback to complete successfully.
-
897843 Volumes do not map correctly when doing incremental add of workload at Reprotect for MS Cluster workloads. During reprotect, the workload volumes might not map correctly between the source and the target after an incremental add of a Microsoft Cluster workload where the shared storage volumes on the Failback machine are not the same shared storage volumes that existed on the original source. The Windows System volumes map correctly from the source to the target, but the Quorum and Cluster Resource volume mappings show as not mapped on the Workload Configuration page in the Protect Web UI.
Workaround: When you configure the workload for first replication at reprotect, manually select the correct volume mapping for the shared storage volumes in the Replication Settings > Volume Mapping section for the workload.
-
863173 The X2P failback of Linux workloads causes failure of the X Server graphical interface. A protected Linux workload replicated to a target, failed over, and then failed back to a physical target loses functionality of its X Server interface.
Workaround: The issue is caused by a reconfiguration of the failed-over VM when VMware tools are installed. To correct this, use the following command to find the files with the string BeforeVMwareToolsInstall in the filename:
find / -iname '*BeforeVMwareToolsInstall'
After you identify all such files, move them back to their original locations, then reboot the workload to fix the workload's X Server interface.
-
860917 Cannot prepare OES workload for incremental replication. If you create a VM or modify an existing VM in the VMware Virtual Infrastructure Client (VIC) and select Novell Enterprise Server as the Guest Operating System, the VM appears in the PlateSpin Browser (as an unknown OS type), but it is not listed at all in the Virtual Machine drop down list in the Prepare for Incremental Replication page of the Protect Web UI.
Workaround: To make this VM available as a target for X2V replication, in the VIC, change the operating system type to SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 (64-bit) and refresh the container. The VM is then listed in the Protect Web UI.
-
698611 Full cluster replication failure under certain circumstances. After the node of a Windows Server 2008 R2 cluster flips, the subsequent full replication or initial full sync replication fails with:
Object reference not set to an instance of an object.
This issue occurs only on contracts set up through the Sync to an existing VM method.
Workaround: See Knowledgebase Article 7008771.
-
Replication fails if the Windows Cluster Service fails over to the other node before a workload’s initial replication: If a Windows cluster's active node is added as a workload and the node flips before PlateSpin performs the initial replication, the replication fails.
Workaround: Flip the cluster back to the node that was active when the contract was set up, then perform the initial replication. Alternatively, you can remove the workload, then add the current active node.
-
611105 Missing protection contracts after upgrade. After upgrading your Forge appliance to version 3, protection contracts with workloads in a Ready for Failback or a Ready for Reprotect state might be missing from the user interface. This issue is under consideration for an upcoming fix.
This issue affects only contracts that have been prepared for failback and that have not yet gone past reprotect. The issue should not occur for a contract that completes the full cycle (failover > failback > reprotect > idle).
6.0 Previous Releases
For Release Notes documents that accompanied previous PlateSpin Forge releases, visit the PlateSpin Forge 11.2 Documentation website, and go to Previous Releases at the bottom of the Table of Contents.
7.0 Contacting Micro Focus
Our goal is to provide documentation that meets your needs. If you have suggestions for documentation improvements, click comment on this topic at the bottom of any page in the HTML version of the documentation. You can also email Documentation-Feedback@microfocus.com.
For specific product issues, contact Micro Focus Support at https://www.microfocus.com/support-and-services/.
Additional technical information or advice is available from several sources:
-
Product documentation, Knowledge Base articles, and videos: https://www.microfocus.com/support-and-services/
-
The Micro Focus Community pages: https://www.microfocus.com/communities/
8.0 Legal Notice
For information about legal notices, trademarks, disclaimers, warranties, export and other use restrictions, U.S. Government restricted rights, patent policy, and FIPS compliance, see https:/www.microfocus.com/about/legal/.
© 2015–2017 NetIQ Corporation. All rights reserved.
License Grant
Licenses purchased for PlateSpin Forge 11 or later versions cannot be used for PlateSpin Forge 3.3 or prior versions.
Third-Party Software
Please refer to the PlateSpin Third-Party License Usage and Copyright Information page for information about third party software used in PlateSpin Forge.