3.1 Configuring mosdaemon
A daemon is a program that runs continuously and exists for the purpose of handling periodic service requests that a computer system expects to receive. The daemon program forwards the requests to other programs or processes as appropriate.
The Operations Center daemon service, known as mosdaemon, controls the following two features:
-
Licensing service with which all components must register
-
Launching and contacting service programs
The Operations Center server is an example of a service program launched by the daemon.
To configure mosdaemon:
3.1.1 Starting mosdaemon
To start mosdaemon:
Starting mosdaemon on Windows
On Windows-based servers, mosdaemon starts automatically as a service program. Running mosdaemon as a Windows service is preferable because the mosdaemon process and all programs it launches terminate when the user logs off.
To manually start mosdaemon, do one of the following:
-
Click Start > Programs > NetIQ Operations Center > Start NetIQ Operations Center on the desktop.
Starting Operations Center via the Windows Start menu, starts the Operations Center server locally, but not as a service. Therefore, when you log out, the Operations Center server stops.
-
From the /OperationsCenter_install_path/bin directory, type mosdaemon at the command prompt.
Starting mosdaemon on UNIX
On UNIX-based servers, mosdaemon needs to be integrated into the operating system’s startup scripts, if required.
Running mosdaemon on UNIX servers is platform specific. Refer to the operating system documentation for information about creating an initiation script.
Automating the mosdaemon Startup
The daemon can be configured to restart automatically in the event of a catastrophic failure.
To automate the mosdaemon setup:
-
In a text editor, open the /OperationsCenter_install_path/config/monitor.properties file.
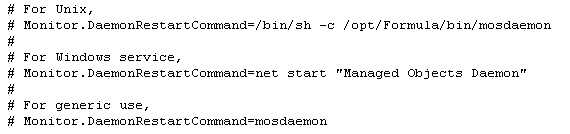
-
Remove the pound sign (#) next to the appropriate UNIX, Windows, or generic Monitor.DaemonRestartCommand.
This enables automatic restart of the Operations Center daemon on your chosen operating system.
3.1.2 Configuring Access to mosdaemon
By default, any host can connect to the Operations Center mosdaemon. It is possible to prevent any host machine from accessing the Operations Center mosdaemon. When the access restriction security option is enabled, access is denied to all hosts except for those hosts whose IP addresses are specified in the mosdaemon.properties file.
To restrict access to mosdaemon:
-
From a text editor, open the /OperationsCenter_install_path/config/mosdaemon.properties file.
-
Enter CORBA.Allow=host_IP_address at the command prompt.
Use the IP address for host machines allowed to access to the Operations Center mosdaemon.
-
Save the file.
-
Stop and restart the Operations Center server.
3.1.3 Checking the mosdaemon Status
Enter mosstatus at a command prompt. The operational status of the following programs started by the mosdaemon program is returned:
-
Operations Center server (uptime, version, license expiry date, and patch level)
-
Operations Center server database
-
Database connections
-
Service Warehouse
-
Adapters
-
Users currently logged in