3.0 Configuring Local Authentication
To guard against unauthorized access, Access Manager supports a number of ways for users to authenticate. These include name/password, RADIUS token-based authentication, and X.509 digital certificates. You configure authentication at the Identity Server by creating authentication contracts that the components of Access Manager (such as an Access Gateway) can use to protect a resource.
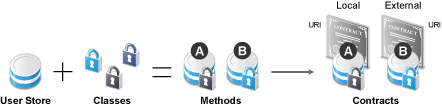
Figure 3-1 illustrates the components of a contract:
Figure 3-1 Local Authentication
-
User stores: The user directories to which users authenticate on the back end. You set up your user store when you create an Identity Server cluster configuration. See Section 3.1, Configuring Identity User Stores.
-
Classes: The code (a Java class) that implements a particular authentication type (name/password, RADIUS, and X.509) or means of obtaining credentials. Classes specify how the Identity Server requests authentication information, and what it should do to validate those credentials. See Section 3.2, Creating Authentication Classes.
-
Methods: The pairing of an authentication class with one or more user stores, and whether the method identifies a user. See Section 3.3, Configuring Authentication Methods.
-
Contracts: The basic unit of authentication. Contracts can be local (executed at the server) or external (satisfied by another Identity Server). Contracts are identified by a unique URI that can be used by Access Gateways and agents to protect resources. Contracts are comprised of one or more authentication methods used to uniquely identify a user. You can associate multiple methods with one contract. See Section 3.4, Configuring Authentication Contracts.
This section also explains the following: