7.2 Approval Activity
The Approval activity is a user-facing activity that displays an approval form to the user. On the approval form, the user can approve, deny, or refuse a provisioning request. The Approval activity can have multiple outgoing flow paths, but only one of the paths is executed at runtime.
You can customize the approval form to suit your application requirements. For details on customizing forms, see Section 5.0, Creating Forms for a Provisioning Request Definition.
Before displaying the form to the user, the Approval activity performs any pre-activity data mappings specified for the activity.
After the user submits the form, the Approval activity performs any post-activity mappings specified for the activity. These mappings typically include copying data from form fields into the flowdata object.
7.2.1 Properties
The Approval activity has the following properties:
Table 7-3 Approval Activity Properties
|
Property Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Provides a name for the activity. |
|
|
Specifies a dynamic expression that identifies the addressee for the activity. The addressee is the approver of the workflow. The addressee is determined at runtime, based on evaluation of the expression. Designer validates that the expression is a valid ECMA expression. It cannot validate whether the expression resolves to a valid object (such as a role) or whether that object will exist at runtime. For information on specifying addressees (such as specifying a role as the approver), see Specifying the Addressee Property. For more information about developing valid Addressee expressions, and about how Addressee interacts with the Approver Type property, see Section 7.2.4, Addressing an Approval Activity. HINT:To simplify the process of testing a new workflow, you can set the addressee to be the recipient. This removes the need to log out of the User Application and log in again as a manager each time you want to test your forms. This technique is particularly useful when the workflow involves multiple levels of approval. After the testing phase is complete, you can change the addressee to the correct value. For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions. For descriptions of the system variables available in a workflow, see Section 6.5.3, Understanding Workflow Data. |
|
|
Specifies a dynamic expression that defines, in milliseconds, the time at which the first reminder e-mail should be sent. The start value is an offset from the time of the first assignment associated with the activity. You can pick predefined expressions that represent common intervals (for example, hour, day, week) in the pane of the ECMA expression builder. This is part of the reminder e-mail function. If this activity is considered important and needs to be acted on quickly, you can configure the activity to send a reminder e-mail to the activity addressee. For example, you can set the reminder settings to send a reminder e-mail 5 days before the activity times out, and on a daily basis until the activity times out. To do this, specify a time, a , and the e-mail to be sent (see Section 7.2.3, E-Mail Notification). For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions. For descriptions of the system variables available in a workflow, see Section 6.5.3, Understanding Workflow Data. |
|
|
Specifies a dynamic expression that defines the interval between which reminder e-mails are sent. You can pick predefined expressions that represent common intervals (for example, hour, day, week) in the pane of the ECMA expression builder. |
|
|
Not available when the approver type is or Specifies a dynamic expression that identifies the user who should get this task if the timeout limit has been reached. The escalation addressee is determined at runtime, based on how the expression is evaluated. For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions. For descriptions of the system variables available in a workflow, see Section 6.5.3, Understanding Workflow Data. |
|
|
Not available when the approver type is or . Specifies the number of times to retry the activity in the event of a timeout. When an activity times out, the workflow process can try to complete the activity again, depending on the escalation count specified for the activity. With each retry, the workflow process can escalate the activity to another user. In this case, the activity is reassigned to another user (the user’s manager, for example) to give this user an opportunity to finish the work of the activity. If the last retry times out, the activity can be marked as approved, denied, refused, timedout, or in error, depending on the final timeout action specified for the activity. The interval (see in this table) takes precedence over the For example, if you set the timeout to 10 minutes, and specify an Escalation Count of 3 and Escalation Interval of 5 minutes, the activity finishes after 10 minutes without attempting all of the retries. In this example, the second retry would be canceled, and the workflow would finish processing for the activity. At the conclusion of the activity, the workflow engine would follow the link defined by the final timeout action. |
|
|
Not available when the approver type is or . Specifies a dynamic expression that defines the period of time allotted for the addressee to complete the task. The escalation interval applies each time the activity is executed by the addressee. The interval (see in this table) takes precedence over the For example, if you set the timeout to 10 minutes, and specify an of 3 and of 5 minutes, the activity will finish after 10 minutes without attempting all of the retries. In this example, the second retry would be canceled, and the workflow would finish processing for the activity. At the conclusion of the activity, the workflow engine would follow the link defined by the final timeout action. For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions. For descriptions of the system variables available in a workflow, see Section 6.5.3, Understanding Workflow Data. |
|
|
Not available when the approver type is or . Specifies a dynamic expression that defines the time at which the first reminder e-mail (see in this table) should be sent to the . The start value is an offset from the time of the escalation assignment. You can pick predefined expressions that represent common intervals (for example, hour, day, week) in the pane of the ECMA expression builder. |
|
|
Not available when the approver type is or . Specifies a dynamic expression that defines how often messages are sent to the after the first escalation reminder is sent. You can pick predefined expressions that represent common intervals (for example, hour, day, week) in the pane of the ECMA expression builder. |
|
|
Determines the final state of the request in the event that the workflow times out. The choices are
|
|
|
Specifies a dynamic expression that defines the period of time allotted for the addressee to complete the task. The timeout interval applies each time the activity is executed by the addressee. The Timeout setting takes precedence over the and values. If the setting for the activity is reached before one or more of the escalation attempts have been tried, the activity finishes processing without executing these escalation attempts. For example, if you set the timeout to 10 minutes, and specify an of 3 and of 5 minutes, the activity finishes after 10 minutes without attempting all of the escalation attempts. In this example, the second escalation attempt would be canceled, and the workflow would finish processing for the activity. At the conclusion of the activity, the workflow engine would follow the link defined by the final timeout action. For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions. For descriptions of the system variables available in a workflow, see Section 6.5.3, Understanding Workflow Data. |
|
|
Determines the unit of measure used for the timeout interval. The choices are
|
|
|
Specifies the name of the approval form to display at runtime, or lets you define a new form. Select the name of the form you want to use or . When you choose to create a new form, the Create New Form Wizard launches and looks similar to this. 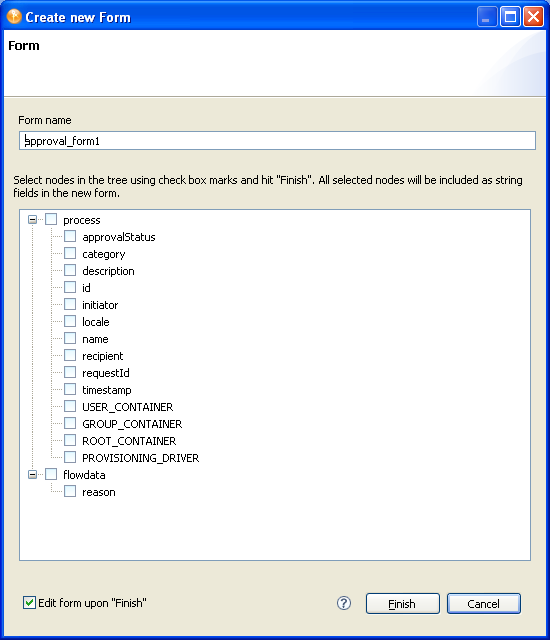
Select the data items to include in the form from the data items listed, then click Finish. The Approval Form Wizard generates each of the selected data items as a String type field in the new form. An Approval activity must have a form associated with it. If no form is specified, an error message is displayed at runtime. |
|
|
Specifies whether requestors can approve their own provisioning requests.
|
|
|
Specifies the number of addresses that are allowed and the approval pattern that is enforced for this activity. The choices are
For information about how the property interacts with the property, see Section 7.2.4, Addressing an Approval Activity. |
|
|
Specifies whether this activity should send e-mail notifications. Set to True to notify by e-mail; otherwise, set to False. You specify the e-mail to send using the E-Mail Notification tab (see Section 7.2.3, E-Mail Notification). To use this feature, the parameter for the provisioning request definition must be set to True (see Table 4-3, Overview Properties). |
|
|
Not available when the approver type is Normal, Group, or Multiple. Allows you to specify a constant value or to create an ECMA expression that specifies a percentage (for example, ’75%’) of approvals that is required before a quorum is achieved, or an absolute number (for example, ’3’) of approvals that are required before a quorum is achieved. |
|
|
See Digital Signature Type in Table 6-17. |
|
|
Specifies a dynamic expression that defines the priority of the approval activity. Valid priority values are 1, 2, or 3. You can also define an expression to determine the priority from workflow data. For example, flowdata.get("Priority"). In the User Application, users can sort the list of tasks by the priority values of the tasks. |
NOTE:To enable delegation to a group DN, you can have an approver type of Group or Normal, but the Addressee value must be an expression that returns the user DNs for each member of that group For example, IDVault.get(groupdn, ‘sales’, ‘members’)
7.2.2 Data Item Mapping
To bind the data items associated with the Approval activity, you define pre-activity and post-activity mappings. The pre-activity mappings initialize data in the approval form with constants, values retrieved from the flowdata object, system process variables, system activity variables, and data retrieved via expression calls to the directory abstraction layer. The post-activity mappings move form data back into the flowdata object.
Table 7-4 Approval Activity Data Item Mappings
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Allows you to specify one or more pre-activity mappings. When this option is selected, you can double-click a cell in the column to specify where the approval form gets data for a particular target form field. The Pre-activity Mapping expression is evaluated twice before the form is presented, once during the initial presentation to the form and then again prior to the post to ensure that all the values on the form have a valid type, even those that were not initialized. Because of this behavior, any calls made to external systems are made twice. For example, a call that retrieves a unique counter for a value makes two calls that allocates two counters with the last one requested being used. NOTE:When the choice is selected, the cells in the column are not editable. |
|
|
Allows you to specify one or more mappings. When this option is selected, you can double-click a cell in the column to specify where data from a form field should be copied after the form has been processed. You cannot use mapping with the and approver types (see Section 7.2.1, Properties). The DNDisplay control is not available for post activity mappings. The form for an Approval activity includes a special internal control called apwaComment. This control causes user comments to be written to the workflow database. It should not have a post-activity mapping. For more information on this control, see Section 5.5.11, DNMaker. NOTE:When the option is selected, the cells in the column are not editable. |
|
|
Specifies a source expression for a pre-activity mapping. When you click a cell in the column, the ECMA expression builder displays to help you define your expression. |
|
|
Specifies a target expression for a post-activity mapping. When you click a cell in the column, the ECMA expression builder displays to help you define your expression. |
For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions.
7.2.3 E-Mail Notification
To enable e-mail notification for the Approval activity, you need to specify the e-mail template to use, as well as source expressions for target tokens in the e-mail body.
Table 7-5 E-mail Notification Settings for the Approval Activity
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies that this e-mail notification is a notification e-mail. |
|
|
Specifies that this e-mail notification is a reminder e-mail. |
|
|
Specifies that this e-mail notification is a retry reminder e-mail. |
|
|
Displays system tokens (for example, TO, CC, BCC, REPLYTO) in the column. |
|
|
Specifies the name of the e-mail template to use. By default, the Approval activity uses the Provisioning Notification template. You can edit an e-mail template in Designer. For more information, see Editing an e-mail template:. |
|
|
Specifies the source expressions for target tokens in the e-mail body. The list of target tokens is determined by the selected e-mail template. You cannot add new tokens, but you can assign values to the tokens by building your own source expressions. At runtime, source expressions are evaluated to determine the value of each token. The available target tokens are listed below:
If you use a provisioning request definition template to create your workflow, each token has a default source expression. The default expressions retrieve values from the workflow process (the process object) or from the data abstraction layer (IDVault object). You can modify these expressions to suit your application requirements. NOTE:When you create a workflow for use with the Resource Request portlet, and you use the “ _default_” as the expression for the TO token, the addressee expression must be an IDVault expression. For details on building ECMA expressions, see Section 9.0, Working with ECMA Expressions. |
NOTE:E-mail notification is supported only when the check box is selected on the tab, and the property for the Approval activity is set to True.
7.2.4 Addressing an Approval Activity
To address an Approval activity, you must enter a valid expression for the property. The Addressee is the approver for the activity. The number of approvals that are required to approve the activity is determined by the relationship between the property and the property as described in Relationship Between Addressee and Approver Type. This section includes the following topics:
Specifying the Addressee Property
To build the addressee expression:
-
Click the
 button in the Addressee property Value column.
button in the Addressee property Value column.

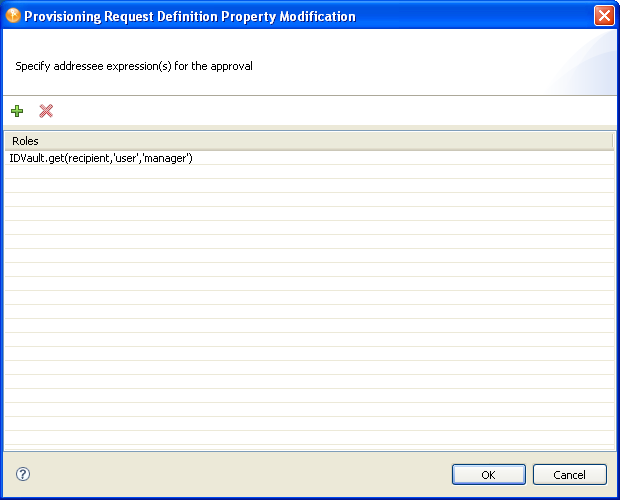
Designer launches the dialog box where you can add or remove an expression. The following dialog only displays when the Approver Type is Group, Multiple, or Quorum.
-
Click + to add a new addressee expression by using the Expression Builder.
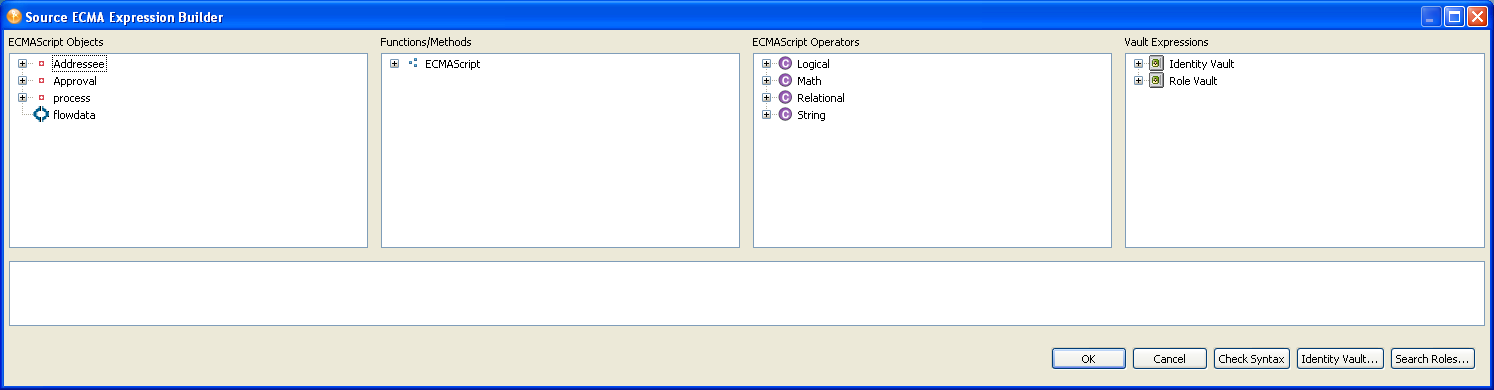
You can choose one of the ECMAScript Objects to build the addressee expression, or use the or buttons to select a specific object. The button is not available when Approver Type is Normal.
-
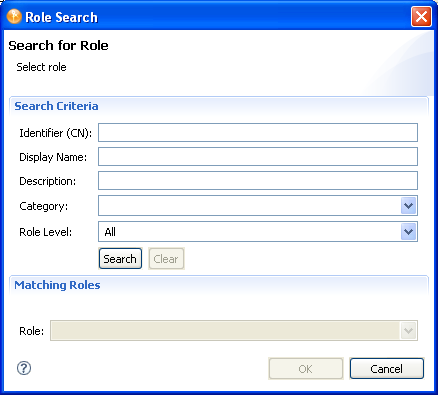
To specify a Role as the Addressee, click .
-
In the dialog box, specify the , , , , and on which you want to search.
For , , and , you can enter a wildcard (such as S*, *S) or regular expressions (such as [A-Zoo-z]*).
You can enter a value for all of the fields or none of the fields. If you do not supply a value in a particular field, the search returns all of the possible values for that field. If you enter values in one or more of the fields, the values are ANDed together to create the search filter. The search occurs on the roles defined locally. Roles matching the search criteria are displayed in the selection list.
-
Select a role from the selection list, then click . The role is added to the expression area.
-
-
Click after you are satisfied with expression.
Valid Addressee Expressions
An Addressee expression must resolve to one of the following at runtime:
-
A valid individual addressee that can be a user DN, a group DN, or a role DN.
-
A valid list of addressees (for example, created using a Java vector object) that can contain multiple User DNs, multiple group DNs, or multiple role DNs, or a mixture of both.
Because the addressee is the approver, the maximum number of approvals possible equals the number of Addressees (the number of User DNs plus the number of Group DNs or Role DNs) and does not include or count the individual members of a Group or Roles.
NOTE:A Group DN or a Role DN is always processed to contribute a single vote (that is, when one member of a group or role claims an activity, the rest of the members of the group or role can no longer see or claim the activity), regardless of the .
The following table provides examples of valid addressee expressions that you can create using the ECMA expression builder.
Table 7-6 Examples of Addressee Expressions
Relationship Between Addressee and Approver Type
Because the addressee is the approver, the behavior of the workflow and the total number of affirmative approvals needed varies depending on the type of Addressee that is specified by the Addressee expression, and the Approver Type that is selected.
Normal Approver Type
The following table describes the workflow behavior when different types of addressee are used with the Normal .
Table 7-7 Workflow Behavior with the Normal Approver Type
Group DNs and Proxy Processing
If a workflow is assigned to a Group and e-mail notification is used for the approvals, all members of the group are sent an e-mail. If a proxy user is assigned to any members of the group, the processing works as follows:
-
If the approver is a single user then the e-mail notification is sent to both users (the original and proxy users).
-
If the approver is a group DN and one of the users in the group is assigned a proxy user, the user who is the proxy is not notified by e-mail when a new request is placed in the task list.
If you want the proxy user to be notified by e-mail, assign the approval task to the members of the group and set the approver type to . For example, if you assign the approval activity to:
IDVault.get('cn=Marketing,ou=groups,ou=idmsample,o=novell' , 'group', 'Member')When you set the approval type to Group, a notification is sent to each member's proxy, if the member has a proxy. One member of the group can claim and act on the approval task which is the same behavior as if you assigned it directly to the group DN.
Group Approver Type
The following table describes the workflow behavior when different types of addressee are used with the Group .
Table 7-8 Workflow Behavior with the Group Approver Type
Multiple Approver Type
The following table describes the workflow behavior when different types of addressee are used with the Multiple .
Table 7-9 Workflow Behavior with the Multiple Approver Type
Quorum Approver Type
The following table describes the workflow behavior when different types of addressee are used with the Quorum .
Table 7-10 Workflow Behavior with the Quorum Approver Type
Troubleshooting Invalid Addressees
If the expression specified in the property of an Approval activity evaluates to a non-existent DN (for example, if the expression was hard-coded incorrectly, calculated incorrectly, or submitted incorrectly by a user selection), no indication is given that the workflow is not processing normally, when it is in fact orphaned. The application server console displays a normal forward message, and the Comment and Flow history shows a normal “assigned” message. To avoid this problem, we recommend that you follow these best practices:
-
Use a Condition activity before the Approval activity and validate the addressee in the Condition activity.
-
Since the addressee could still be deleted after the addressee is validated in the Condition activity, you should specify, for the Approval activity, a timeout interval and a link that performs the desired action in case the workflow times out.