2.10 Localizing Provisioning Objects
Designer allows you to translate the names and descriptions of provisioning objects into multiple languages. Table 2-8 describes the types of provisioning objects that you can translate.
Table 2-8 Localizable Objects
To localize the provisioning objects listed in Table 2-8:
-
Verify that the locale (or language) is supported by the User Application driver. See Section 2.10.2, Supported Languages for the list of languages supported by default.
-
If necessary, add the new locale (or language) to the User Application driver and to the resource groups. For more information, see Section 2.9.2, Defining the User Application’s Supported Locales.
-
Translate the names and descriptions in one of the following ways:
-
Directly within Designer.
NOTE:You cannot edit the provisioning request definitions in the Attestation category. For this reason, you cannot use this method for localizing them. You must use the method described in Step 3.b.
For more information, see Section 2.10.1, Using Designer to Localize.
-
By exporting the set of localizable objects into an external properties or XML file, translating the contents of the file, then importing the data back into the project.
For more information, see Section 2.10.3, Exporting and Importing Data to Localize).
-
2.10.1 Using Designer to Localize
-
Click the localize button.

When you click this button, Designer displays a dialog box that lets you add the localized text. This is an example of the Localization dialog box.
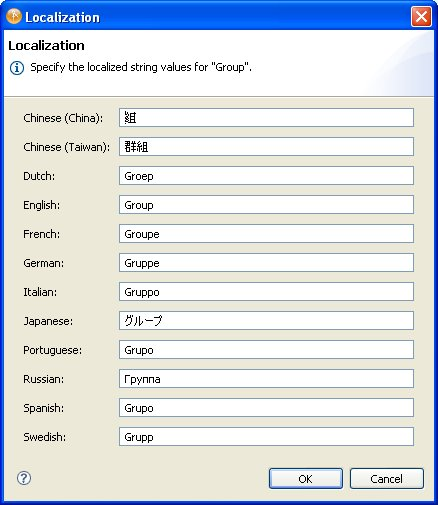
The languages displayed in this dialog box are the languages currently supported by the User Application driver. If your language is not shown in this dialog, you must add it. For more information, see Section 2.9.2, Defining the User Application’s Supported Locales.
The directory abstraction layer editor provides multiple ways to localize data. You can access the localization dialog boxes in these ways:
Table 2-9 Accessing the Localization Dialog Boxes
2.10.2 Supported Languages
You can localize the display labels, display names, and descriptions into the languages listed in the localization dialog box. This list represents the languages (locales) supported by the User Application driver. For information about adding new languages to this list, see Section 2.9, Specifying Locales and Localization Resource Groups.
The locale configuration is stored in the driver’s <default-locale> element in the AppConfig.AppDefs.locale-configuration XMLData attribute.
You must provide a display label for the User Application driver’s default language, or the User Application generates the following runtime error: The resource resolver com.novell.soa.common.i18n.LocalizedMapResolver did not return a resource for the default locale of <locale>. It is required that a resource exist for the default local.
2.10.3 Exporting and Importing Data to Localize
You can export the localizable data (such as display names and descriptions) in your project to an XML or properties file. After the data in that file is translated, you can import it back to the Designer project. You can export an entire driver, one object, or a subset of objects.
Exporting Data to Localize
-
Right-click a container node or an object in the Provisioning view.
-
Select .
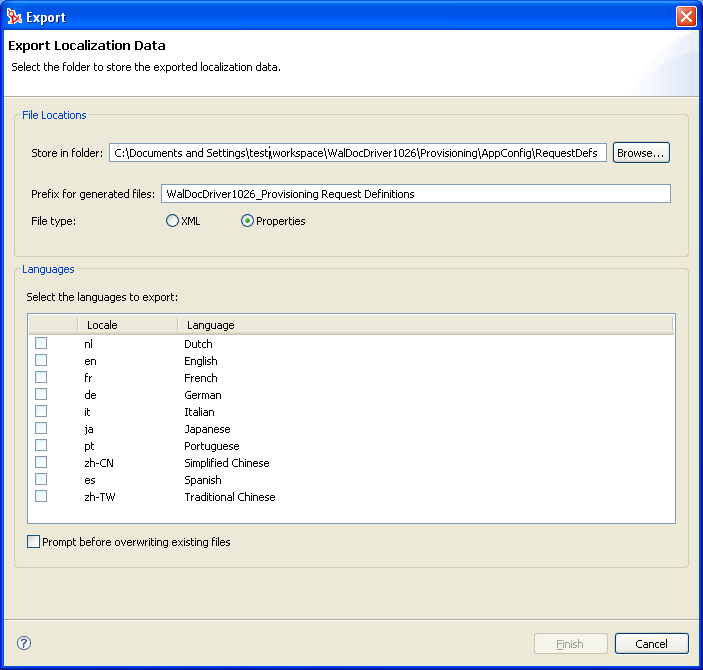
-
Fill in the fields as follows:
-
Click . Designer displays a message describing the result of the export operation and the location of the exported data.
Importing Localized Files
-
Right-click a container node or an object in the Provisioning view, then select .
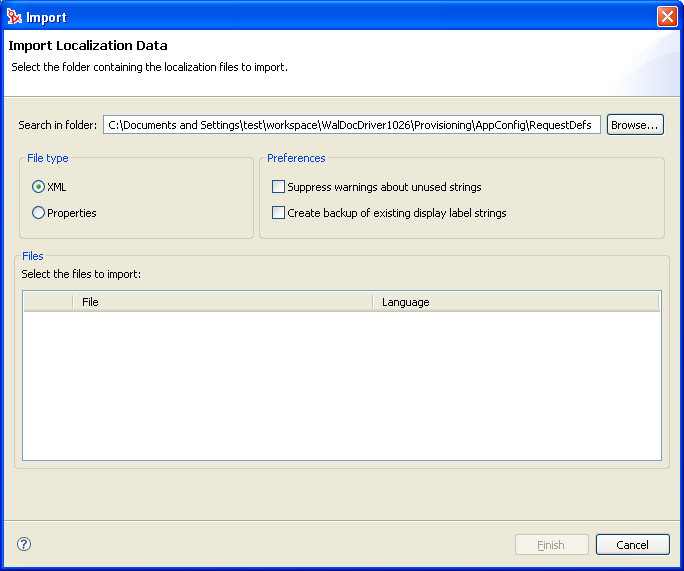
-
Fill in the fields as follows:
-
Click to complete the import. Designer displays a status dialog box that describes the results including any errors reading the files and any warnings about display label keys that are unused.