11.6 Identity Vault Guidelines
Identity Vault (eDirectory) stores the objects that are synchronized through the Identity Manager solution. The follow sections contain guidelines that help you plan your deployment of Identity Vault.
11.6.1 Understanding Identity Manager Objects in Identity Vault
The following list indicates the major Identity Manager objects that are stored in Identity Vault and how they relate to each other. No objects are created during the installation of Identity Manager. The Identity Manager objects are created during the configuration of the Identity Manager solution.
-
Driver Set: A driver set is a container that holds Identity Manager drivers and library objects. Only one driver set can be active on a server at a time. However, more than one server might be associated to one driver set. Also, a driver can be associated with more than one server at a time. However, the driver should only be running on one server at a time. The driver should be in a disabled state on the other servers. Any server that is associated with a driver set must have the Identity Manager server installed on it.
-
Library: The Library object is a repository of commonly used policies that can be referenced from multiple locations. The library is stored in the driver set. You can place a policy in the library so that every driver in the driver set can reference it.
-
Driver: A driver provides the connection between an application and the Identity Vault. It also enables data synchronization and sharing between systems. The driver is stored in the driver set.
-
Job: A job is automates a recurring task. For example, a job can configure a system to disable an account on a specific day, or initiate a workflow to request an extension of a person’s access to a corporate resource. The job is stored in the driver set.
11.6.2 Replicating the Objects that Identity Manager Needs on the Server
If your Identity Manager environment calls for multiple servers in order to run multiple Identity Manager drivers, your plan should make sure that certain Identity Vault objects are replicated on servers where you want to run these Identity Manager drivers.
You can use filtered replicas, as long as all of the objects and attributes that the driver needs to read or synchronize are included in the filtered replica.
Keep in mind that you must give the Identity Manager Driver object sufficient Identity Vault rights to any objects it is to synchronize, either by explicitly granting it rights or by making the Driver object security equivalent to an object that has the desired rights.
An Identity Vault server that is running an Identity Manager driver (or that the driver refers to, if you are using the Remote Loader) must hold a master or read/write replica of the following:
-
The Driver Set object for that server.
You should have one Driver Set object for each server that is running Identity Manager. Unless you have specific needs, don’t associate more than one server with the same Driver Set object.
NOTE:When you create a Driver Set object, the default setting is to create a separate partition. Novell recommends creating a separate partition on the Driver Set object. For Identity Manager to function, the server is required to hold a full replica of the Driver Set object. If the server has a full replica of the location where the Driver Set object is installed, the partition is not required.
-
The Server object for that server.
The Server object is necessary because it allows the driver to generate key pairs for objects. It is also important for Remote Loader authentication.
-
The objects that you want this instance of the driver to synchronize.
The driver cannot synchronize objects unless a replica of those objects is on the same server as the driver. In fact, an Identity Manager driver synchronizes the objects in all the containers that are replicated on the server unless you create rules for scope filtering to specify otherwise.
For example, if you want a driver to synchronize all user objects, the simplest way is to use one instance of the driver on a server that holds a master or read/write replica of all your users.
However, many environments don’t have a single server that contains a replica of all the users. Instead, the complete set of users is spread across multiple servers. In this case, you have three choices:
-
Aggregate users onto a single server. You can create a single server that holds all users by adding replicas to an existing server. Filtered replicas can be used to reduce the size of the eDirectory database if desired, as long as the necessary user objects and attributes are part of the filtered replica.
-
Use multiple instances of the driver on multiple servers, with scope filtering. If you don’t want to aggregate users onto a single server, you need to determine which set of servers holds all the users, and set up one instance of the Identity Manager driver on each of those servers.
To prevent separate instances of a driver from trying to synchronize the same users, you need to use scope filtering to define which users each instance of the driver should synchronize. Scope filtering means that you add rules to each driver to limit the scope of the driver’s management to specific containers. See Using Scope Filtering to Manage Users on Different Servers.
-
Use multiple instances of the driver on multiple servers, without scope filtering. If you want to have multiple instances of a driver running on different servers without using filtered replicas, you need to define policies on the different driver instances that enable the driver to process different sets of objects within the same Identity Vault.
-
-
The Template objects you want the driver to use when creating users, if you choose to use templates.
Identity Manager drivers do not require you to specify Identity Vault Template objects for creating users. However, if you specify that a driver should use a template when creating users in Identity Vault, the Template object must be replicated on the server where the driver is running.
-
Any containers you want the Identity Manager driver to use for managing users.
For example, if you have created a container named Inactive Users to hold user accounts that have been disabled, you must have a master or read/write replica (preferably a master replica) of that container on the server where the driver is running.
-
Any other objects that the driver needs to refer to (for example, work order objects for the SAP User Management driver).
If the other objects are only to be read by the driver, not changed, the replica for those objects on the server can be a read-only replica.
11.6.3 Using Scope Filtering to Manage Users on Different Servers
Scope filtering means adding rules to each driver to limit the scope of the driver’s actions to specific containers. The following are two situations in which you would need to use scope filtering:
-
You want the driver to synchronize only users that are in a particular container.
By default, an Identity Manager driver synchronizes objects in all the containers that are replicated on the server where it is running. To narrow that scope, you must create scope filtering rules.
-
You want an Identity Manager driver to synchronize all users, but you do not want all users to be replicated on the same server.
To synchronize all users without having them replicated on one single server, you need to determine which set of servers holds all the users, and then create an instance of the Identity Manager driver on each of those servers. To prevent two instances of the driver from trying to synchronize the same users, you need to use scope filtering to define which users each instance of the driver should synchronize.
NOTE:You should use scope filtering even if your server’s replicas don’t currently overlap. In the future, replicas could be added to your servers and an overlap could be created unintentionally. If you have scope filtering in place, your Identity Manager drivers do not try to synchronize the same users, even if replicas are added to your servers in the future.
Figure 11-4 shows an example of an Identity Vault with three containers that hold users: Marketing, Finance, and Development. It also shows an Identity Management container that holds the driver sets. Each of these containers is a separate partition. In this example, the Identity Manager administrator has two Identity Vault servers, Server A and Server B. Neither server contains a copy of all the users. Each server contains two of the three partitions, so the scope of what the servers hold is overlapping.
Figure 11-4 Scope Filtering Defines Which Drivers Synchronize Each Container
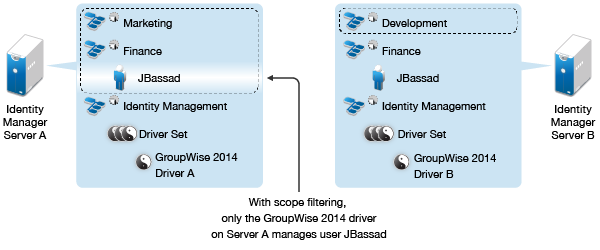
The administrator wants all the users in the tree to be synchronized by the GroupWise 2014 driver, but does not want to aggregate replicas of the users onto a single server. He chooses instead to use two instances of the GroupWise 2014 driver, one on each server. He installs Identity Manager and sets up the GroupWise 2014 driver on each Identity Manager server.
Server A holds replicas of the Marketing and Finance containers. Also on the server is a replica of the Identity Management container, which holds the driver set for Server A and the GroupWise 2014 Driver object for Server A.
Server B holds replicas of the Development and Finance containers, and the Identity Management container holding the driver set for Server B and the GroupWise Driver object for Server B.
Because Server A and Server B both hold a replica of the Finance container, both servers hold the user JBassad, who is in the Finance container. Without scope filtering, both GroupWise Driver A and GroupWise Driver B would synchronize JBassad. Scope filtering prevents both instances of the driver from managing the same user, because it defines which drivers synchronize each container.
Identity Manager comes with predefined rules. There are two rules that help with scope filtering. Event Transformation - Scope Filtering - Include Subtrees
and Event Transformation - Scope Filtering - Exclude Subtrees
are documented in NetIQ Identity Manager Understanding Policies Guide.
For this example, you would use the Include Subtrees predefined rule for Server A and Server B. You would define the scope for each driver differently so that they would only synchronize the users in the specified containers. Server A would synchronize Marketing and Finance. Server B would synchronize Development.
11.6.4 Improving Identity Vault Performance
eDirectory, the underlying infrastructure for the Identity Vault, is I/O intensive application rather than being processor-intensive. Two factors increase performance of Identity Vault: more cache memory and faster processors. For best results, cache as much of the Directory Information Base (DIB) Set as the hardware allows.
While eDirectory scales well on a single processor, you might consider using multiple processors. Adding processors improves performance in areas such as user logins. Also, having multiple threads active on multiple processors improves performance.
The following table provides a general guideline for server settings, based on the expected number of objects in your Identity Vault.
|
Objects |
Memory |
Hard Disk |
|---|---|---|
|
100.000 |
384 MB |
144 MB |
|
1 million |
4 GB |
1.5 GB |
|
10 million |
2+ GB |
15 GB |
For example, a base installation of Identity Vault with the standard schema requires about 74 MB of disk space for every 50,000 users. However, if you add a new set of attributes or completely fill in every existing attribute, the object size grows. These additions affect the disk space, processor, and memory needed. Also, requirements for processors depend on additional services available on the computer as well as the number of authentications, reads, and writes that the computer is handling. Processes such as encryption and indexing can be processor intensive.