21.2 Understanding the Review Process
Figure 21-1 Review Process
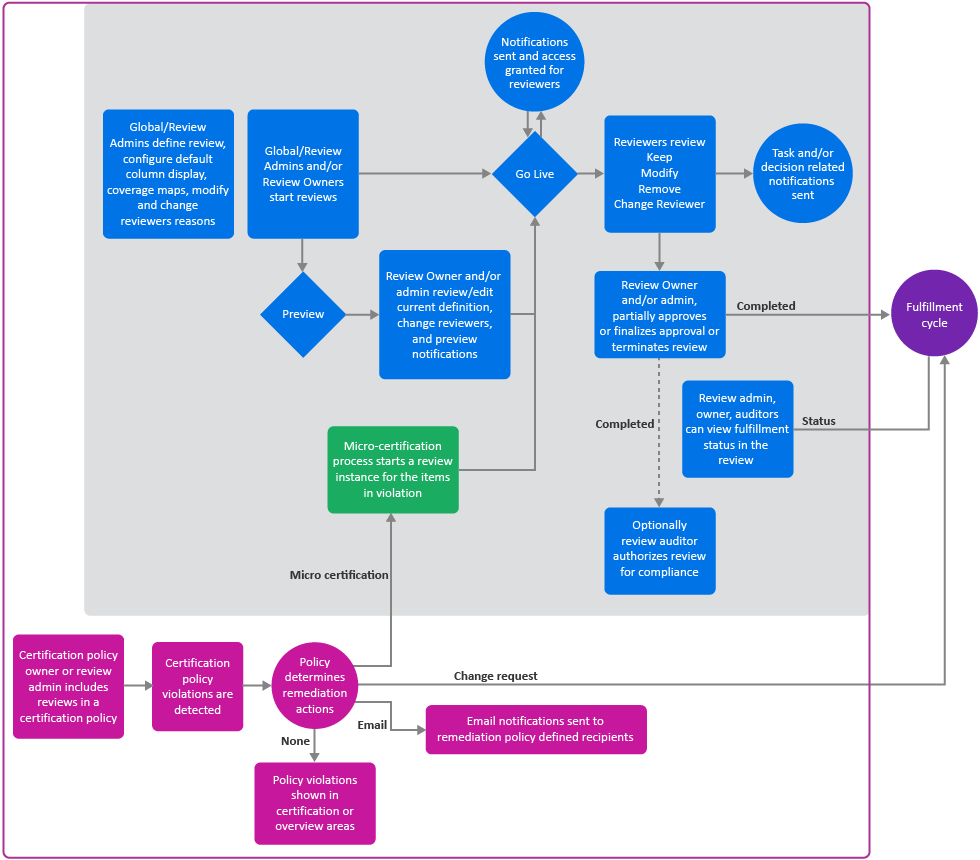
Reviews provide a way to monitor access to your business systems. Many users take part in the overall review process:
-
Review administrators create review definitions, preview review definitions, and manage reviews.
-
(Optional) Review administrators can request Data administrators to configure additional selection criteria such as custom identity, permissions, permission assignment, or business role attributes for selecting review items and refine review definitions.
-
Review owners start, preview, monitor, complete, and terminate reviews.
-
Reviewers, such as supervisors and application owners, act on review items.
-
Escalation reviewers review items in the exception queue
-
Fulfillers manage change requests.
-
Auditors accept or reject completed reviews.
-
Review or data administrator create certification policies to check for violations and set remediation action which triggers remediations including micro certifications (focused reviews)
NOTE:The Identity Governance server needs a 30-minute gap between runs of the same review. For example, you terminate a scheduled review that is in progress. To schedule that review to run again, allow at least 30 minutes to lapse after terminating the previous run. Otherwise, the second run fails to start and Identity Governance does not notify you of the failure.
21.2.1 Understanding Review Definitions
You can run a review once or multiple times either by starting the review manually or by scheduling it to start at the specified time or interval. Each review is based on a review definition that is based on a specific type of review object and defines all parameters for that particular review. Review Administrators or Global Administrators create review definitions using the provided default review definitions with preselected criteria. These definitions enable you to select what you want to review. For example, you can select review objects such as User profiles, Technical role assigned to users, Accounts and their permissions, or Business roles assigned to users. These review objects are specific to a review type (review template). Each review type provides selection criteria that help review administrators to focus their reviews based on varying combinations of identity, application, account, permission, permission assignment, or business role attributes. For example, you can focus the User profiles review by specifying that reviewers should review users with risk greater than 80. Identity Governance provides a default list of attributes for selection when creating review definitions. Review administrators can request Global or Data administrators to add other attributes as selection criteria. Items that do not meet the specified criteria in a review definition are filtered out of the review.
Review definitions also assign reviewers based on their relationship to the review items. Often, administrators use review definitions to split up responsibility for reviewing items to prevent bottlenecks and overloading reviewers. Review definitions can also be referenced in certification policies to enable a comprehensive view of your organization's compliance with specific certification controls such as Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
HINT:For information about certification policies, see Section 23.0, Creating and Managing Certification Policies. Once a review definition is referenced in an active certification policy, it cannot be deleted. For detailed procedures about creating review definitions, see Section 21.4, Creating a Review Definition.
21.2.2 Adding Selection Criteria for Review Items
In addition to the default selection criteria, Identity Governance provides the ability to enable other attributes including custom attributes as selection criteria. In the attribute definition editor of the catalog, an administrator with Data or Global Administrator authorization can specify whether an attribute can be used as a review criteria by selecting an attribute in the Data Administration > Attributes pages and specifying Display in review item selection criteria. For example, in the Identity Attributes page, a Data Administrator can enable Job Code as selection criteria and then a Review administrator can create a review of users based on Job Code value. In the Permission Assignments page, a Data Administrator can enable Assignment Type and then a Review administrator can create a review of permissions based on assignment type.
HINT:When you specify a boolean attribute in your review criteria and there are null attribute/column values in the database these records will be ignored. Global or Data administrators will need to ensure that there are no null values if you intend to use the attribute as review criteria or add transformation code to convert a null to be true or false or use bulk data update settings to change the null values to true or false. For more information see, Editing Attribute Values in Bulk.
21.2.3 Setting Review Notifications
Email notifications let reviewers, escalation reviewers, owners, and others know when a review is at various stages of a review run. The Notifications area of a review definition allows you to set up several standard notifications to go to whomever you specify during the various phases of a review. Standard notifications include Reviewer start, Review end, Reviewer task past due and so forth. Review the details of the email notification and update it as needed.
You can click an email name to view who will receive the email, why they will receive it, when they will receive it, and how often they will receive it. You can either accept the default settings or change the settings and add other recipients based on relationships. You can view the name of the email source, preview the email, and email the notification to a specified email address. If you change the default settings, we recommend that you also change the description of the notification. For example, if you change who receives the notification, change the recipient name in the description.
Regarding notifications received by escalation reviewers, when a review item is escalated, Identity Governance sends the reminder notification to the escalation reviewer as it would to any other next reviewer. By default, the escalation reviewer will not receive the Reviewer task past due notifications as these are typically emailed to the reviewer and reviewer’s supervisor when overdue tasks remain in the reviewer queue. However, you can add an escalation reviewer as a recipient in the CC field if needed.
In addition to changing the settings when defining a review, you can also remove a default notification, customize the template of a default notification, and add new notifications by selecting an email template provided by Identity Governance. For information about customizing the templates, see Section 3.1, Customizing the Email Notification Templates. For information about disabling email notifications such as notification when a running review is terminated or notification when permissions are revoked, see Disabling Review Email Notifications.
21.2.4 Setting Review Expiration Policy
Review definitions contain an expiration policy. Review administrators and owners specify the actions that Identity Governance takes when a review expires without being completed:
-
Complete the review with any final decisions that have been made and send these to fulfillment and the auditor, if these are defined, and leave all other items with no decision
-
Complete the review with any final decisions that have been made and send these to fulfillment and the auditor, if these are defined, and keep all other items with no user profile changes or with assigned accounts, permissions, roles, or direct report relationship
-
Complete the review with any final decisions that have been made, assign remove or remove assignment decision to all other items, and send all to fulfillment and the auditor, if these are defined
NOTE:This option is not available for User Profile Review nor Business Role Definition Review.
-
Extend the review for a grace period that will continue to renew each time the review expires without being completed or terminated
-
Terminate the review and discard all decisions
For Identity Governance 2.0 and later, review definitions have the default expiration policy set to complete the review. For review definitions migrated from earlier versions of Identity Governance, review definitions have the default expiration policy set to terminate the review and discard any decisions.
21.2.5 Previewing a Review
Administrators can start a review run, or review instance, in preview mode or live mode. In preview mode, administrators can:
-
Preview review definition version, assigned reviewers, review items, and notification emails
-
Change review properties such as review owner, auditor, review options, or duration properties
-
If needed, change reviewers per review item or in bulk
-
Preview recipients of notifications
-
Export review items to CSV
-
Track details of review assignment changes
-
Go live
NOTE:Review description and reviewer changes made in preview mode will apply only to the current review instance. Changes made to the Reviews > Definitions, will apply to future review run instances.
21.2.6 Reviewing Items
When a review run or review instance is live, the server generates review items based on the criteria. Assigned reviewers decide what action to take on each review item and submit their decisions. If allowed, by the review definition, reviewers might reassign items to a different reviewer instead of making a decision.
In a review with multiple reviewers for each review item, Identity Governance shows decisions made when the first reviewer submits actions for any of the review items. When any reviewer has submitted a decision for a review item, the other reviewers cannot take any action on that item unless the reviewer has authorization as an administrator. Review items with no actions remain in each reviewer’s list until someone submits actions for them.
In a review with multiple stages, reviewers must act on review items in the order that the stages are defined in the review definition. For more information about multistage reviews, see Section 21.8.1, Understanding Multistage Reviews.
NOTE:When Identity Governance cannot determine an identity associated with an account or functional assignment, such as supervisor, to assign a review item to a specific person, the review owner becomes the assignee for the review item. All review items assigned in this way show in an exceptions section in the list of reviewers on the review owner view.
21.2.7 Downloading Reviewers and Review Item Lists
Identity Governance enables you to download all or a filtered list of review items assigned to you as reviewers. In addition, review administrators and owners can download list of all reviewers, a list of review items in a specific reviewer’s queue, and a list of all review items. You can download these lists as a CSV file for manual review and comparison.
The list of reviewers includes rows for each reviewer by queue type. For example, if a reviewer is a supervisor and also an exception reviewer, you will see two rows for the user in the downloaded file. When review items are assigned to multiple reviewers, for example when a reviewer is a group, you will see a row for each reviewer with the same number of review items. In all the scenarios, each row will include columns of all the user attributes that were enabled to display in the quick info view in the Data Administration > User menu including custom attributes.
The list of review items you download from the Review Items tab will always include all review items. Except for User Profile Review, all other review item lists will include final decisions made on the review items. User Profile Review will include only the original values of the selected attributes.
The list of review items you download from the Your Review Items tab includes rows for review items assigned to the reviewer with columns that you, as an administrator, included in the Configuration > Review Display Customization menu. You can filter the review items and download only the items you want to review manually.
NOTE:The download list items count will not match the actual number of review items in an Account Review that includes permissions. The count only reflects the number of accounts that match the search criteria. However, all the permissions under each account will also be included in the download resulting in more review items than the number displayed on the review page.
All downloaded files will be saved to a download folder. You can then click the Download icon on the application title bar to access the saved file and download the file to your local machine.
21.2.8 Escalating Review Items
Identity Governance provides escalation options to help Review Owners and Administrators ensure that the review process proceeds in a timely manner. You can set one or more escalation reviewers, and a timeout value to instruct Identity Governance to escalate the process and move pending review items to escalation reviewer queues. If a review definition does not set escalation reviewers, the review owner is the default escalation reviewer and in a multistage review, review items will be escalated to the next reviewer in the queue.
NOTE:If a review definition specifies a group as the reviewers and a member of the group is the person being reviewed, Identity Governance uses the self-review policy to determine which group members can review the item. The self-review policy can either allow users to review their own items (self review), send self-review items to the exception queue, or prevent self review but allow other reviewers to complete the item if it is assigned to multiple reviewers in the same stage. For more information about the self-review policy see Section 21.4.2, Specifying Self-Review Policy.
21.2.9 Completing or Terminating a Review
Aside from letting the expiration policy complete the review run, a review run concludes in one of several ways:
-
All specified reviewers submit actions for their review items, and the Review Owner approves or terminates the review run.
-
Reviewers do not submit actions for all their review items, and the Review Owner completes the review run.
-
Reviewers do not submit actions for all their review items, and the Review Owner terminates the review run.
After reviewers have made decisions and submitted all review items, the Review Owner approves or terminates the review run and Identity Governance moves the review run details to a list of completed reviews.
A Review Owner has the option to complete an in-progress review even if reviewers have not submitted decisions for all review items. When a Review Owner completes a review, Identity Governance takes the following actions:
-
Forwards any final decisions that reviewers have made to fulfillment. In multistage reviews, a decision is considered final only when all multi-stage reviewers of a review item have submitted their decisions.
-
Marks the remaining review items Keep, Remove, Keep Assignment, Remove Assignment, No profile changes or as no decision made based on the review definition expiration policy
-
Shows the review status as a percentage of completion in review history
A Review Owner also has the option to terminate an in-progress review. When a Review Owner terminates a review, Identity Governance takes the following actions:
-
Does not forward anything to fulfillment
-
Marks the review run as terminated
21.2.10 Fulfilling Changes and Audit Acceptance
The fulfillment process begins when a review run completes or when a review owner approves review items individually. For more information about fulfillment, see Section 14.6, Fulfilling the Changeset for a Review Instance.
The Review Auditor, if specified, accepts or rejects the review run after the review owner approves it. Although a review audit is a legal stamp, accepting a review has no impact on the fulfillment of the requested changes.
21.2.11 Creating Certification Policies and Remediating Violations
A global, review, or data administrator creates certification policies and sets remediation action for violations. Identity Governance calculates violations and after initial setup automatically triggers remediation action. Remediation actions include email notifications, change requests, or micro certification.
For more information about micro certification and certification policies, see Section 21.3, Understanding Micro Certification and Section 23.0, Creating and Managing Certification Policies.