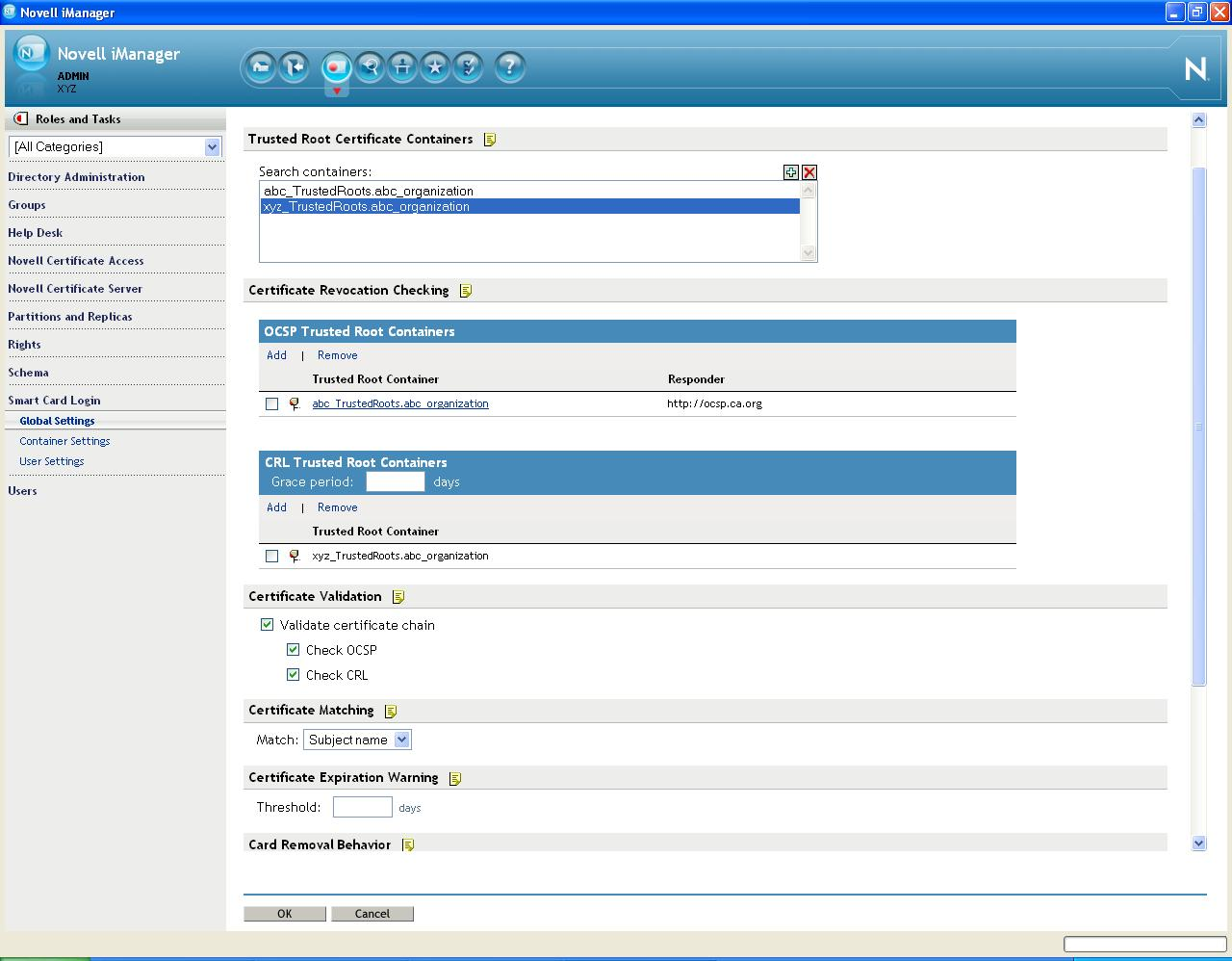
3.2 Configuring Certificate Revocation Checking
Configuration Level: Global
Certificate revocation checking is part of the certificate validation process. In order to be considered valid, a certificate must not be revoked. The method supports On-Line Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) checking. The type of revocation checking performed is configured on a per trusted root container basis.
Trusted root containers are automatically added to the OCSP and CRL certificate revocation checking lists. Modify the lists as necessary and enable the proper revocation checking option.
If a trusted root container is not listed in the OCSP or CRL list, revocation checking is not performed for certificates that chain to the trusted root container. If a trusted root container is listed in both the OCSP and the CRL list, both types of revocation checks are performed.
3.2.1 OCSP Trusted Root Containers
Certificates that chain to trusted root certificates in containers in this list use OCSP checking. An OCSP responder URL can be specified for each container in the list. If specified, the responder URL overrides OCSP information in a user's certificate.
An OCSP response is signed by using the responder's certificate, and the responder's certificate must be trusted in order for the response to be considered valid. Place the OCSP responder's certificate in the trusted root container to ensure that the certificate is trusted.
3.2.2 CRL Trusted Root Containers
Certificates that chain to trusted root certificates in containers in this list use CRL checking. The CRL distribution point information in the user certificate is used to retrieve the CRL. CRLs are cached in memory on the server after retrieval. This improves the performance of future logins.
The setting specifies the number of days after a CRL has expired that it is treated as valid. This allows revocation checking to continue, if a new CRL cannot be retrieved from the CRL Distribution Point. If a grace period is not specified and the CRL expiration date has passed, all certificates are considered invalid until a new CRL can be retrieved from the distribution point.
3.2.3 Example
In Figure 3-1, both OCSP and CRL revocation checking are enabled. OCSP revocation checking is performed for certificates chaining to the abc_TrustedRoots container. CRL checking is performed for certificates chaining to the xyz_TrustedRoots container.
When using OCSP validation, the OCSP response is signed by the responder’s certificate. In order for the response to be considered valid, the responder’s certificate must be trusted. Place the OCSP responder’s trusted root certificate in the trusted root container to identify it as trusted.
Figure 3-1 Certificate Validation and Search Containers