1.2 How GPA Works
GPA is an enterprise‑wide, Group Policy administration solution that helps you take advantage of the powerful features Group Policy offers. GPA provides a mechanism for creating, changing, and testing GPOs away from your Active Directory environment, along with a complete change management workflow. To perform these functions, GPA uses several software components:
-
GPA Console
-
GP Repository
-
GPA Server
1.2.1 Understanding GPA Components
GPA consists of software components you can install in a number of ways to integrate with your Active Directory environment and meet your Group Policy management objectives. Deciding which components to install and where to install them depends on the GPA features you want to implement and the requirements of your network environment. For example, if you want to restrict the ability to change GPOs in your Active Directory environment to the Export Only service account, you need to install the GPA Server.
Additionally, the GP Repository uses Microsoft SQL Server. If your organization has specific requirements for Microsoft SQL Server, such as installing it only on designated computers that are managed by a separate group of database administrators, you may need to have this group install the GP Repository on one of these computers.
NOTE:This guide uses the terms production environment and test environment to describe how GPA works. A production environment is a live network environment. A test environment is a separate Active Directory network environment that you use exclusively for testing purposes. A test environment limits access to specific users. The term environment is an Active Directory network consisting of one or more domains or a collection of domains grouped in forests. This book uses environment to refer to multiple domains or forests and the term domain to refer to a single domain.
GPA Console
The GPA Console is an MMC snap‑in that enables you to use and administer GPA. You can perform the following tasks using the GPA Console:
-
Define a GPO workflow and security model
-
Edit GPOs in the GP Repository or Active Directory
-
Create comparison, diagnostic, and RSoP analysis reports
-
Ensure GPO consistency between multiple domains
-
Back up and restore GPOs
-
Import and export GPOs between the GP Repository and Active Directory
-
Search for specific GPO settings
GP Repository
The GP Repository provides a secure location away from your production Active Directory environment where you can create, change, analyze, and approve GPOs before you deploy them. The GP Repository also performs the following functions:
-
Enforces version control
-
Maintains a GPO revision history
-
Enables you to roll back to a previous version of a GPO
-
Stores information about the tasks each GPA user can perform using the GPA Console
-
Maintains information about GPA service accounts and the Repository Authorization Code
Event logging records detailed information about the changes made to GPOs in the GP Repository using GPA. The event log includes what changes have been made, who made them, and when they were made. For more information, see Section 3.2.5, Configuring GPA Event Logging or Section 3.2.6, Viewing GPA Event Logs.
GPA Server
The GPA Server performs the following functions:
-
Enables the export of GPOs from the GP Repository to untrusted domains in your Active Directory environment using the Export Only account
-
Allows you to restrict the rights to export GPOs to the Export Only service account
-
Provides centralized event logging for GPO changes made with the GPA Console
-
Sends email notifications of GPO changes made with the GPA Console
-
Indexes GPOs in Active Directory and the GP Repository to provide accurate data for GPA Search reports
The event log includes what changes have been made, who made them, and when they were made. For more information, see Section 3.2.5, Configuring GPA Event Logging or Section 3.2.6, Viewing GPA Event Logs.
1.2.2 Understanding Test and Production Environments
The GP Repository enables you to create, change, and evaluate GPOs without having to deploy them to your production Active Directory environment. This capability allows you to thoroughly test and evaluate GPOs before you implement them, which minimizes the risk of introducing harmful Group Policy errors into your production Active Directory environment.
However, you cannot be fully certain what a GPO will do until you actually deploy it to Active Directory. To insulate your production Active Directory environment as much as possible from any unintended consequences caused by an error or oversight in a GPO, you can first deploy a GPO into a test Active Directory environment.
A typical test Active Directory environment consists of a separate domain or forest with its own set of users and computers. To further separate the test Active Directory environment from production, the test Active Directory environment is typically untrusted by the production Active Directory environment.
Setting up a separate test Active Directory environment enables you to take full advantage of the managed GPA workflow while ensuring the GPOs you deploy to your production Active Directory environment work as intended. How you choose to implement GPA depends on your particular environment and GPO management requirements. For more information about test Active Directory environments, see Section 2.3.2, Understanding Test Environment Configurations.
1.2.3 Understanding the GPA Workflow
GPA provides a managed change control workflow to help you administer Group Policy in your Active Directory environment. The following figure shows a basic GPA workflow using separate production and test Active Directory environments. Having a separate test Active Directory environment is the most effective way to ensure the security and reliability of your production Active Directory environment. For more information about test Active Directory environments, see Section 2.3.2, Understanding Test Environment Configurations.
The GPA Server is used in environments with untrusted domains or if you want to use features like centralized logging or GPO change notification. To emphasize the basic GPA workflow, which remains the same whether or not you install the GPA Server, the GPA Server is not included in this figure. For more information about the GPA Server, see Section 1.2.1, Understanding GPA Components.
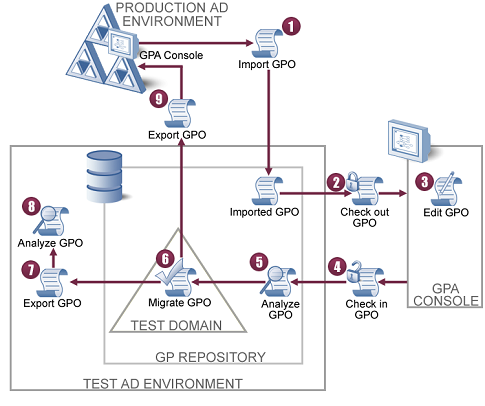
A high‑level GPO change management workflow using GPA includes the following steps, which correspond to the numbers in the preceding illustration:
-
Import GPOs from your production Active Directory environment into the GP Repository.
-
Check out a GPO, locking it from changes by other users.
-
Edit the GPO as needed.
-
Check in the updated GPO, unlocking the GPO and updating the version number of the GPO.
-
Analyze the GPO to verify your changes (for example, RSoP analysis), and then approve the GPO.
-
Migrate the approved GPO to a test domain in the GP Repository.
-
Export the approved GPO into the Active Directory test domain.
-
Analyze the GPO to verify your changes (for example, RSoP analysis or diagnostic reports).
-
Export the GPO to Active Directory in the production environment.
1.2.4 Supported GPOs
GPA supports managing GPOs for all editions, service packs, and releases of the following Microsoft Windows operating systems, unless otherwise noted:
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2022
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2019
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2016
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2012
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2008
-
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
-
Microsoft Windows 11
-
Microsoft Windows 10
-
Microsoft Windows 8.1
-
Microsoft Windows 8
-
Microsoft Windows 7
-
Microsoft Windows Vista
-
Microsoft Windows XP
NOTE:If you know that the GPMC supports managing the GPO, you can trust that GPA supports it as well.