5.8 Configuring Policies
Policies contain configuration settings for the Advanced Authentication methods, events, and so on. For example, to use the Email OTP method, you must configure the server and port settings in the Mail sender policy and to use the Multitenancy mode, you must enable the Multitenancy options policy.
Advanced Authentication provides the following policies:
To configure a policy, perform the following steps:
-
Click Policies in the Administration portal.
-
Click the Edit icon
 against the policy you want to configure.
against the policy you want to configure.
You can also double-click on the policy to edit the configuration.
-
Make the required changes for a specific policy.
A top administrator can enforce the configurations of a policy on secondary tenants. After configuring a policy, you can lock the settings for that specific tenant. The tenant cannot edit the locked settings in the tenant administrator console.
To enforce the configurations for a specific tenant, perform the following steps:
-
In Tenancy settings, click +.
-
Move the tenant to whom you want to enforce the configurations from the Available to the Used list in the Force the configuration for the tenants section.
-
After you add a tenant, the Hide forced settings option is displayed. You can turn this option to ON if you want to hide the configurations that you have enforced on the tenant.
NOTE: The Tenancy settings are not supported for the following policies: CEF log forwarding, Event categories, HTTPS Options, Logo, and Multitenancy options.
A tenant administrator cannot access the CEF log forwarding and Multitenancy options policies.
-
-
Click Save.
IMPORTANT:The configured policies are applied for all the Advanced Authentication servers.
5.8.1 Authentication Agent
In this policy, you can configure the Daemon host. The Daemon host is address of the server that contains a background service to manage connections and incoming requests from the Authentication Agents. The Daemon host is secured by default.
NOTE:To initiate an authentication process using the Authentication Agent installed on a Windows machine, you must configure the Authentication Agent chain in the configuration file of the respective Clients. For more information about how to configure the Authentication Agent in different Clients, see Linux Client, Mac Client and Windows Client.
To configure the Authentication Agent policy, perform the following steps:
-
Specify the IP address of the Advanced Authentication server that manages requests from Authentication Agents in Daemon host. The loop-back address (127.0.0.1) is set by default. The Loop-back address is self-address of a particular computer. With the loop-back address, a computer can transmit signals to itself to communicate and check network connectivity.
For more information about how to configure DNS in the Authentication Agent to discover the daemon host, see Setting DNS for Server Discovery.
NOTE:In a cluster, if there are multiple Advanced Authentication servers, you must specify the address of one server in Daemon host that can accept connections and manage requests from the Authentication Agents. The server stores these connection details in the memory and are not replicated. Therefore, in a cluster do not retain the default address (127.0.0.1) in Daemon host.
-
By default, Verify SSL is set to ON to secure the daemon host. Ensure that a valid SSL certificate is uploaded in Server Options tab of the Advanced Authentication server which is configured as daemon host.
-
Click Save.
5.8.2 Authenticator Management Options Policy
This policy allows you to configure the following two settings:
-
Enable sharing of authenticators: This setting allows a user to authenticate with his or her authenticator to another user’s account. The helpdesk administrator can share an authenticator of one user with another user.
To enable sharing authenticators, set Enable sharing of authenticators to ON.
NOTE:Shared authenticators work only in the online mode. Cached login does not work for the shared authenticators.
The supported methods for sharing authenticators are TOTP, HOTP, Password, Fingerprint, Card, and FIDO U2F.
For more information, see
Sharing Authenticators
in the Advanced Authentication- Helpdesk Administrator guide. -
Disable re-enrollment: This setting allows you to restrict users from re-enrolling, editing, and deleting the enrolled authenticators in the Self-Service portal.
To disable re-enrollment or removal of authenticators, set Disable re-enrollment to ON.
WARNING:If you access the Administration portal with local user credentials such as local\admin, you might get into a lockout situation. This can happen when the administrator's password expires and it is not possible to change the password through the Self-Service portal. Therefore, to use the Disable re-enrollment option, you must configure the access of a repository account to the Administration portal. To do this:
-
Add authorized users or a group of users from a repository to the FULL ADMINS role.
-
Assign chains, which contain methods that are enrolled for users, to the AdminUI event (at a minimum with an LDAP Password method).
NOTE:This setting disables re-enrollment and removal of the authenticators only in the Self-Service portal. The setting has no effect on the Helpdesk portal.
-
5.8.3 Cache Options Policy
In this policy, you can disable the local caching of authenticators. The policy is supported for Windows Client, Mac OS X Client, and Linux PAM Client for chains that use the methods: LDAP Password, Password, HOTP, TOTP, Smartphone (offline mode), Card, FIDO U2F, Fingerprint, and PKI.
This policy allows you to configure the following settings:
-
By default, the Enable local caching option is enabled. To disable the caching, set the option to OFF and click Save.
The caching functionality enables the storing of credentials on the Client for offline authentication when the Advanced Authentication server is not available. Therefore a user who has successfully logged in once to the server with the authentication, can now login with the offline authentication.
-
By default, the Cache expire time is set to 0 to indicate that the cache never expires. You can set the duration (in hours) for storing the user’s authenticators in the Client cache using the Cache expire time option. The maximum expiry time that you can set is 24 * 366 (8784 hours). This setting is applicable for all Advanced Authentication Clients.
When a user logs in with the cached authenticators, Advanced Authentication compares the last online login time with the current offline authentication time. If the time duration is less than or equal to the specified duration in the Cache expire time, the user is authenticated to Clients.
For example, consider the Cache expire time is set to 2 hours, the last online log in time of the user to Client is 1:00 PM. When the user tries to log in to Windows Client using cached authenticator credentials at 2:30 PM, the authentication is successful and the user is logged in to Windows Client. But, if the user tries to log in with cached authenticator credentials at 4:00 PM, the offline authentication fails and a message: Authenticators of <user name> were not cached. Press OK and try again to log in as local user or cached user. is displayed because the cache has expired.
NOTE:If the authenticator data (HOTP, TOTP, or U2F counters) is changed on Client, the server performs the following tasks:
-
Updates the corresponding authenticator in the database.
-
Updates the authenticator in Client.
Client compares the updated authenticator with existing authenticator, if there is any mismatch in authenticators then such authenticators are removed from cache. Therefore, users cannot use the removed authenticators for the next offline login.
NOTE:You can use the enforced cached logon in place of the default online logon to improve the logon and unlock speed on Clients. Refer the following topics for more information. Refer the following topics for more information:
-
For Linux, see “Configuring the Enforced Cached Login” in the “Advanced Authentication- Linux PAM Client” guide.
-
For mac OS, see “Configuring the Enforced Cached Logon” in the “Advanced Authentication - Mac OS X Client” guide.
-
For Windows, see “Configuring the Enforced Cached Login” in the “Advanced Authentication - Windows Client” guide.
5.8.4 CEF Log Forward Policy
In this policy, you can configure settings to forward the logs to an external Syslog server. The central logging server can be used for log forwarding. To configure the policy, perform the following steps:
-
Set Enable to ON.
-
Specify the IP address of the remote logging server in Syslog server.
-
Specify the port of the remote logging server in Port.
-
Select an applicable transfer protocol from Transport.
-
Click Save.
NOTE:The same Syslog configuration is used for each server type. Each server type in the appliance records its own log file.
Only logs from the Syslog section are forwarded to the external Syslog server. For more information about Syslog, see Section 12.0, Logging.
For more information about how to integrate Advanced Authentication with external log management server, see an example Configuring Integration with Sentinel.
5.8.5 Custom Messages
In this policy, you can customize the error messages, method message and prompt message of a specific language.
For example, you can customize the default logon error message in English to Your login failed. In the Self-Service portal, when the user specifies wrong user name, the customized error message is displayed.
To customize the messages, perform the following tasks:
NOTE:The customized messages are cached in the Advanced Authentication server. The refresh interval for custom messages is one hour. Therefore, when you customize a message or upload a custom localization file, the respective message is displayed on the corresponding Advanced Authentication portals after an hour.
To customize the authentication request message, see Customizing Authentication Request Message For Smartphone Method.
Customizing Messages in the Custom Localization File
To customize preferred messages using the Custom localization file, perform the following steps:
-
Click Custom Messages.
-
Perform one of the following action to download the custom localization file on your local drive:
-
Click Download original to save the custom_messages.tar.gz file that contains the default messages.
-
If you have customized the messages, click Download current messages to save the current_custom_messages.tar.gz file that contains the latest messages.
-
-
Extract the files from the custom_messages.tar.gz file.
-
Navigate to the preferred language folder.
To customize English messages, use the custom_messages.pot file and for other languages use the custom_messages.po file.
-
Open the custom_messages.pot file in the text format.
-
Specify the message in the msgstr "".
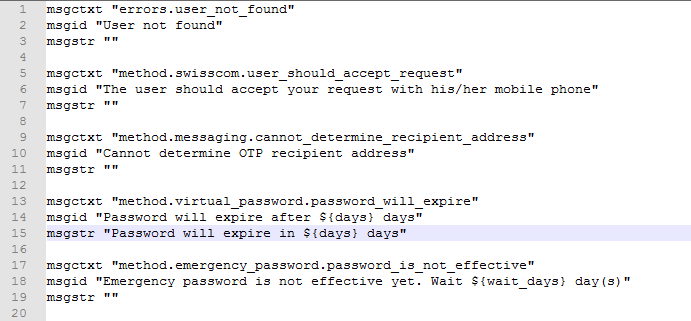
-
Save the changes.
-
Compress the custom_messages folder to .tar.gz or .zip format.
-
Click Browse and select the compressed custom_messages file from the local drive.
-
Click Upload.
Customizing a Specific Message on the Portal
To customize a specific message on the portal, perform the following steps:
-
Click Custom Messages.
-
Use the Message filter to search for a specific message or you can find the preferred message manually.
-
Use the Message Group to search a specific message by group. Options available are All, Method messages, Error messages, and Other messages.
-
Click the Edit
 icon next to the preferred message. You can also double-click on the message to edit the content.
icon next to the preferred message. You can also double-click on the message to edit the content.
-
Specify the message in the preferred language.
-
Click Save.
Customizing Authentication Request Message For Smartphone Method
You can customize the authentication request message that is displayed on the NetIQ Auth app when user initiates Smartphone authentication. The authentication can be either to the endpoint or to the Advanced Authentication portals.
To customize the message for smartphone method, perform the following steps:
-
Click Custom Messages.
-
Search for one of the following keys:
-
method.smartphone.authentication_hint to edit the request message specific to endpoint authentication.
-
method.smartphone.authentication_hint_no_endpoint to edit the request message for any authentication that does not use endpoint such as Advanced Authentication portals login.
-
-
Click
 for the preferred key.
for the preferred key.
-
Specify any of the following parameters in the preferred language message as per your requirement:
-
{user} to fetch the user name.
-
{client_ip} to fetch the client IP address.
-
{event} to fetch the event name.
-
{tenant} to fetch the tenant name.
-
{endpoint} to fetch the endpoint name.
-
-
Click Save.
NOTE:The customized authentication request message will reflect on the NetIQ smartphone app after an approximate delay of one hour.
For example, to customize the endpoint specific authentication message for the smartphone method you must search the key method.smartphone.authentication_hint and specify the message {user} requested for authentication request from the client {client_ip} for the {event} to access the {endpoint} in the field corresponding to English language. When the user tries to authenticate to Windows Client using the smartphone method then the customized message is displayed on the NetIQ smartphone app as:
Bob requested for authentication request from the client 10.3.10.5 for the Windows logon to access the Windows-machine-589.
5.8.6 Custom CSS
This policy allows you to use a customized css for all the Advanced Authentication portals.
To use a customized css, perform the following steps:
-
Place the css file in Content.
For example, you can place the following sample css file.
body { color: #000000; background-image: url("http://cgcreative.com/videos/poster/MicroFocus_2017_Brand_Cutdown_AMC_01.jpg") !important; } .skin-ias .main-header { background: linear-gradient(90deg,#0ecce4,#5c1bd7); color: #ffffff; } table.table-hover tr:hover td { background-color: #808080; } .skin-ias .sidebar-menu li a:hover { background-color: #808080; } .skin-ias .sidebar-menu li.active.open { background-color: #D3D3D3; } .content-wrapper { color: #000000; background: transparent !important; } .well { background: transparent !important; border: 0px; border-radius: 0px; box-shadow: none; } .box { color: #000000; background: transparent !important; } .main-footer { color: #000000; background: transparent !important; } .auth .content .login { background: transparent !important; } .auth .content .login .header-row { background: #ffffff; } -
Click Save.
To revert the changes, remove the custom code from Content and click Save.
5.8.7 Delete Me Options
In this policy, you can configure settings that enable deleting all the user data from the server, including the enrolled methods.
When you set Enable the Delete me policy to ON, the users can view the Delete me option in a drop-down by clicking on the user name on the top-right corner of the Self-Service portal.
NOTE:To comply with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), you must set the Enable the Delete me policy option to ON.
5.8.8 Endpoint Management Options
In this policy, you can configure settings for endpoint management.
Set Require admin password to register endpoint/workstation to ON for endpoints to provide the local administrator's credentials during the registration of endpoint.
You must disable the option when installing any components from the Advanced Authentication distributives package that uses endpoints (Advanced Authentication Windows Client, Mac OS X Client, Linux PAM Client, Logon Filter, and RDG plug-in). Otherwise, the endpoints are not created. You must use the option for third-party integrations only.
5.8.9 Event Categories
In this policy you can add categories, which can be used in an event to support multiple enrollments for a method. For each event, you can specify one category.
To add a category, perform the following steps:
-
Click Event categories.
-
Click Add.
-
Specify a name and description for the category.
-
Click Save.
-
Click Events and edit the required event to specify the category.
Ensure that users or helpdesk administrators enroll authenticators for the new category.
NOTE:
-
You can enroll only one authenticator of one type for each category.
-
The Authenticator category option in Events is not displayed when no category is created.
-
The LDAP Password method is an exception. There is one LDAP password authenticator always, it can be used with any category.
5.8.10 Geo Fencing Options
In this policy, you can create authentication zones by drawing boundaries for a geographical location. When you enable the geo-fencing policy, users can authenticate with their Smartphones only from the allowed geographical locations.
To enable geo-fencing, set Enable Geo-fencing to ON. For more information about how to configure the geo-zones, see the Smartphone
method.
NOTE:When you enable the Geo-fencing options policy, the functioning of the TOTP mode of the Smartphone method, which is used in the offline mode, is affected. An error message TOTP login is disabled is displayed to the users when they try to authenticate with this method.
5.8.11 Google reCAPTCHA Options
The Google reCAPTCHA Options policy helps to prevent the Advanced Authentication web portals login page from bots and to confirm that the user is a human and not a robot. This policy adds an additional layer of security before users go through multi-factor authentication. A series of images are displayed and the users must select the images for the specified condition to login.
To configure the Google reCAPTCHA for Advanced Authentication, you must perform the following configuration tasks:
Registering the Google reCAPTCHA Account
Before you configure Google reCAPTCHA in Advanced Authentication, you must have a Google reCAPTCHA account.
To register for the Google reCAPTCHA account, perform the following steps:
-
Log in to the Google reCAPTCHA website with your Google account.
-
Click Get reCAPTCHA.
-
Specify a Label, select reCAPTCHA V2 from Choose the type of reCAPTCHA.
-
Specify the IP address or the domain name of the Advanced Authentication server in Domain.
-
Accept the terms of Google reCAPTCHA.
-
Click Register.
-
Copy the Site key and Secret key to configure reCAPTCHA in Advanced Authentication. For more information, see Configuring Google reCAPTCHA for Advanced Authentication.
NOTE:If you forget the generated secret key, you can retrieve it from your Google account.
WARNING:If you have enabled the Google reCAPTCHA policy for the Admin UI event, you must consider the following guidelines. Otherwise, a deadlock scenario can happen and you will not be able to access the Administration portal without the cluster re-installation:
-
If the site key or secret key gets deleted at the Google server, you will not be able to get the same site key or secret key. The site key and secret key used on the Administration portal are no more valid and there is no way to bypass the reCaptcha on the Administration portal.
-
If you have registered the reCAPTCHA for one domain name and you change the domain name or migrate the Advanced Authentication server to another domain name, the site key or secret key used on the Administration portal are no more valid.
-
Configuring Google reCAPTCHA for Advanced Authentication
To configure Google reCAPTCHA for Advanced Authentication, perform the following steps:
-
Log in to the Administration portal.
-
Click Policies > Google reCAPTCHA Options.
-
Specify the Site Key and Secret Key that you received when you registered for a Google reCAPTCHA account.
For more information about how to register the Google reCAPTCHA account, see
Registering the Google reCAPTCHA Account
. -
Click Test to test the policy after the configuration.
-
Click Save.
Enabling the Google reCAPTCHA Options Policy for Events
After you configure the Google reCAPTCHA policy, you must enable the policy for the respective events.
To enable the policy for events, perform the following steps:
-
Click Events.
NOTE:You can enable the Google reCAPTCHA policy only for the Admin UI event, Authenticators Management event, Helpdesk event, Helpdesk User event, Report logon event, Search Card event, Tokens Management event, and Web authentication events such as OAuth and SAML 2.0 events.
-
Set Enable Google reCAPTCHA to ON.
-
Click Save.
5.8.12 Helpdesk Options
In this policy, you can configure the following settings for the Helpdesk portal:
-
Ask for the credentials of the managed user: Set this to ON to prompt the helpdesk administrator to provide the credentials of the managed user in the Helpdesk portal. This enhances security, however reduces convenience of the operations.
When this setting is enabled, the helpdesk administrator must know the users’ credentials to manage their authenticators. Ensure that you have specified a chain (with all the methods of the chain enrolled for the users) for the Helpdesk User event. When you set the option to OFF, the user management becomes faster, but less secure.
-
Allow to unlock user accounts: Set to ON to allow a helpdesk administrator to unlock users who are locked in the Advanced Authentication server local repository. Users are locked when the Lockout options policy is enabled. The helpdesk administrator can view and unlock the users in the Helpdesk portal under the Locked Users tab.
-
Allow to manage endpoints: Set Allow to manage endpoints to ON to allow a helpdesk administrator to manage the endpoints of the Advanced Authentication server. When the helpdesk administrator logs in to the Helpdesk portal, an Endpoints tab is displayed where all the endpoints are listed. The helpdesk administrator can remove the endpoints. This option is disabled by default. For more information, see Managing Endpoints.
5.8.13 HTTPS Options
In this policy, you can configure settings to ensure that the appliance is safe from security vulnerabilities.
This policy allows you to configure the following settings:
-
Enable TLS 1.0: This option is disabled by default to ensure security vulnerabilities are prevented because TLS 1.0 is considered as an unsafe protocol. In some scenarios, you can enable the option to support the older versions of browsers. For more information on browser support for TLS, see TLS support for web browsers.
-
Enable TLS 1.1: This option is disabled by default to prevent security vulnerabilities and have secure connection between the server and web portals such as Helpdesk, Self-Service and so on. It is recommended to keep default setting because TLS 1.1 is considered as an unsafe protocol. In some scenarios, you can enable the option to support the older versions of browsers.
-
Enable HTTP compression: This setting allows you to enable the HTTP compression to accelerate performance in the scenarios of low bandwidth or when the network connectivity is slow.
-
Frame Ancestor URLs One URL per line: This setting allows some of the domains to load the Advanced Authentication pages in an iFrame. Previously, none of the domains were allowed to load the pages in iFrame. You can specify any number of domain names.
-
Enable Client SSL for Webauth Service: This option allows you to enable the Client SSL to authenticate to any web environment using the details available in the client SSL certificate. This option is used for virtual smartcard support of the PKI method. The Client SSL also ensures privacy of transmitted data to the server.
When this option is set to ON, the Client SSL CA Certificate Store is displayed where you can upload the CA certificate that is essential to validate the Client SSL certificate for OAuth 2.0 and SAML 2.0 events authentication.
When this option is set to OFF, user must use the PKI device to authenticate to any device or web service.
-
Enable Auto Enrollment base on certificate: This option allows you to enable the auto enrollment of PKI method using the client SSL certificate on the user’s browser.
When this option is set to ON, the PKI method gets auto-enrolled if following conditions are true:
-
The PKI method and another authentication method are added to the chain that is associated to either OAuth 2.0 or SAML 2.0 event and user has enrolled other method that is available in the chain.
-
A valid client SSL certificate is available in the user’s browser.
When this option is set to OFF, the PKI method does not auto-enroll even though the browser has valid client SSL certificate.
-
5.8.14 Kerberos SSO Options
In this policy, you can select an Active Directory repository that points to a domain for which you want to configure the single sign-on (SSO). Kerberos SSO is supported for the AdminUI, Authenticators Management, Helpdesk, and Report logon events.
The Figure 5-1 displays the architecture of Kerberos SSO.
Figure 5-1 Kerberos SSO Architecture
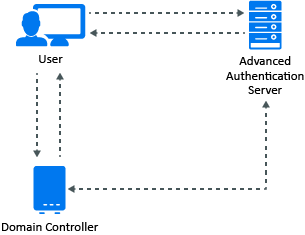
By default, the basic authentication window is displayed in your browser while accessing an Advanced Authentication portal. Advanced Authentication servers’ sites must be added to the local intranet in the browser on the domain-joined workstations to avoid it. Perform the following steps to do it for Internet Explorer:
-
From the Start menu, navigate to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Internet Options.
-
In the Internet Properties window, click the Security tab and select Local intranet.
-
Click Sites.
-
In the Local intranet window, click Advanced.
-
Add the Advanced Authentication Servers’ sites to the zone. For example: https://v5.netiq.loc or v5.netiq.loc.
-
Click Close.
Perform the following steps to configure Advanced Authentication to perform an SSO authentication:
-
Ensure that the Multitenancy options policy is disabled.
-
Go to Policies > Kerberos SSO options.
-
Select Active Directory as repository in Repository.
NOTE:This feature works only for a single Active Directory repository at a time.
-
Click Save.
-
Log in to a Domain Controller.
-
Generate the keytab files for the Kerberos authentication for each Advanced Authentication server.
A Sample command to create the keytab file is:
ktpass /princ HTTP/aas1.netiq.loc@NETIQ.LOC /mapuser aas1srv@authasas.local /crypto ALL /ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL /mapop set /pass Q1w2e3r4 /out C:\Temp\keytab_aas1srv
where
-
aas1 is a server name (according to the record in DNS), the domain name is netiq.loc.
-
aas1srv is a service account created in the Active Directory for the Advanced Authentication server. The password of this account is Q1w2e3r4.The keytab file keytab_aas1srv is created in the C:\Temp folder.
-
-
Go to the Advanced Authentication Administration portal.
-
Click Server Options.
-
Scroll down to the Keytab file section.
-
Click Browse and select a keytab file for the Advanced Authentication server.
-
Click Upload.
-
Repeat Step 8 to Step 11 for the other Advanced Authentication servers.
-
Click Events on the Global Master server.
-
Open the properties of any supported event: AdminUI, Authenticators Management, Helpdesk, or Report logon.
-
Scroll down and set Allow Kerberos SSO to ON.
IMPORTANT:You must add the Advanced Authentication server sites to the local intranet in the browser of the domain-joined workstations. To know how to do this for the Internet Explorer, see the above procedure.
By default, Firefox browser does not support SSO. If you use the Firefox browser, you can enable SSO by performing the steps defined on the Single Sign-On in Firefox page.
NOTE:The basic authentication window is displayed while accessing a configured Advanced Authentication portal, if the Kerberos SSO option is enabled for Authenticators Management event and security is set to High for Local intranet in the Internet Explorer.
5.8.15 Linked Chains
This policy allows you to perform the following settings:
-
Enable linked chains: This policy allows users to use a simple chain within a few hours of authentication done with a high-security chain. You must enable this policy for the Require chain option while creating a chain.
NOTE:This policy has replaced the Last Logon Tracking Options policy.
For example, if a user authenticates with the LDAP Password+Card chain once in a day, the user can further use a linked chain with only the Card method without the LDAP Password method, or if a user authenticates with the Fingerprint+Smartphone chain once in every four hours, the user can authenticate once with this chain and next authentication he can use only the linked Smartphone chain. The duration for which he can use the linked chain depends on the grace period that you specify in the Require chain option.
-
Hide required chain: After using the required chain within the grace period, a user will see both the required and linked chain on Windows Client, Mac Client, and Linux PAM Client. This policy allows to hide the required (high-security) chain after you authenticate once. Therefore, instead of displaying both the chains, after authenticating with the required chain, only the linked chain will be displayed. By default, this policy is disabled. Enable the policy to hide the high security chain.
5.8.16 Lockout Options
In this policy, you can configure settings to lock a user’s account when the user reaches the maximum failure attempts of login. This enhances security by preventing the guessing of passwords and one-time passwords (OTPs).
You can configure the following options in this policy:
-
Enable: An option to enable the lockout settings.
-
Attempts failed: The limit of failure attempts of authentication, after which the user’s account is locked. The default value is 3.
-
Lockout period: The period within which the user’s account is locked and the user cannot authenticate. The default value is 300 seconds.
-
Lock in repository: The option to lock the user account in repository. You cannot use Lockout period if you enable this option. Only the system administrator must unlock the user in the repository.
IMPORTANT:You must configure the appropriate settings in your repository for the options to function appropriately. For Active Directory Domain Services, you must enable the Account lockout threshold policy on Domain Controllers.For NetIQ eDirectory, you must configure the Intruder Detection properly.
After a user’s account is locked (not in the repository), you can unlock the user account. To do this, click Repositories > Edit > Locked Users and click Remove against the user’s account name.
The Helpdesk administrator can also unlock the locked users, if the Allow to unlock user accounts is enabled in the Helpdesk Options policy.
5.8.17 Login Options
In this policy, you can configure the settings to add default repository and ensure not to disclose valid username for malicious attack.
This policy allows you to configure the following settings:
-
Default repository: You can add repositories that are used as default repositories. Therefore while logging in, you need not prefix the repository name before the username for authentication.
For example, if pjones is a member of the company repository, then while logging in, instead of specifying company\pjones, you can specify only pjones.
To add a repository as default, move the repository from Available to Default and click Save.
-
Username disclosure: This option is set to OFF by default. It is recommended to keep default setting to prevent security vulnerabilities and to make it difficult for hackers to predicting the valid username.
If you set Username disclosure to ON and a user specifies an invalid username on the Advanced Authentication login page, an error message User not found is displayed. When the user specifies valid username, the associated chain details are prompted to confirm the specified username and disclosing valid username. This can cause security vulnerability making it easy for attackers to guess the valid username.
When this option is set to OFF, chain details are displayed instead of error message even though a user specifies an invalid username on the login page. A user can select a preferred authentication method. If the input data specific to the selected method is incorrect, a generic message Invalid credentials is displayed. This does not disclose whether username or first-factor authentication is incorrect.
For example, a user specifies an invalid username, selects the SMS OTP method from the authentication chain. In this case, the SMS with OTP is not sent to the user. If the user specifies some random 6 digit as OTP, the server prompts an error message Incorrect OTP password. This helps the user to determine that specified username is valid though it is invalid.
5.8.18 Logo
This policy allows you to set and customize an image as a logo for the Administration and Self-Service portal. You can also set an alternate text instead of an image as logo.
To set a logo for the Administration and Self-Service portal, perform the following steps:
-
In the Logo page, set Use image to ON.
-
Specify an alternate text for the image in Text as an alternate for image.
-
Specify the URL that is redirected when you click on the logo.
-
Select an image for the logo. The image resolution must be 230x50 pixels. The supported formats are .jpg and .png.
-
You can also set a mini logo with an image. This mini logo is displayed when the navigation pane on the left is collapsed. The image resolution for the mini logo must be 50x50 pixels.
-
Click Save.
NOTE:The logo is applied for all the tenants. A tenant administrator cannot customize the logo.
5.8.19 Logon Filter for Active Directory
In this policy you can configure settings to enable the use of Logon Filter that you must install on all the Domain Controllers in the domain and configure it. Logon Filter allows you to automatically update group membership if you login with the Advanced Authentication Windows Client.
To enable the policy, set Enable filter to ON and click Save.
NOTE: Before enabling the policy, you must ensure the Advanced Authentication Logon Filter is installed on all the Domain Controllers in the domain. Else, you might face problems with password validation during password synchronization on workstations that have the Windows Client installed.
For information about how to configure Logon Filter, see Configuring Logon Filter.
5.8.20 Mail Sender
In the Mail sender policy, you can configure settings for the Email OTP method to facilitate sending email messages with one-time passwords to users.
To configure the Mail sender settings, perform the following steps:
-
Specify the following details:
-
Host: The outgoing mail server name. For example, smtp.company.com.
-
Port: The port number. For example, 465.
-
Username: The username of an account that is used to send the authentication email messages. For example, noreply or noreply@company.com.
-
Password: The password for the specified account.
-
Sender email: The email address of the sender.
-
TLS and SSL: The cryptographic protocol used by the mail server.
-
-
You can test the configurations for the Mail sender policy in the Test section.
-
Specify the email address in E-mail to which you want to send the Email OTP.
-
Specify a message to be sent to the phone in Message.
-
Click Send test message!.
-
-
Click Save.
Real messaging uses async sender. Ensure that you have configured a chain with the Email OTP method and assigned it to an event. Login to the Self-Service portal and test the Email authenticator. If it does not work, click async log.
Authentication Flow
The authentication flow for the Mail sender is described in the following image.
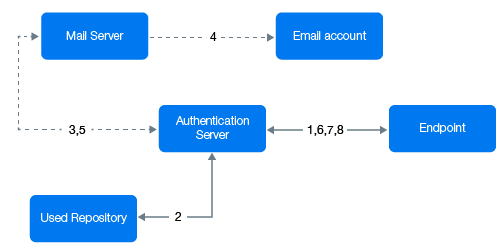
A user wants to authenticate on an endpoint such as a laptop or a website with the Email OTP method. The following steps describe the authentication flow:
-
When the authentication request is initiated, the endpoint contacts the Advanced Authentication server.
-
The Advanced Authentication server validates the user’s credentials and gets an email address of the user from a repository.
-
Advanced Authentication server sends the request to a configured mail server to send an email message with the content that includes a one-time password (OTP) for authentication.
-
Mail server sends the message to the user's email address.
-
Mail server sends the sent signal to the Advanced Authentication server.
-
Advanced Authentication server sends a request to the user to specify an OTP on the endpoint.
-
The user specifies the OTP from the email message. The Advanced Authentication server gets the OTP.
-
Advanced Authentication server validates the authentication. The authentication is done or denied.
HTTPS protocol is used for the internal communication.
Access configuration
Advanced Authentication server - Mail Server (SMTP, outbound).
5.8.21 Multitenancy Options
In this policy, you can enable the Multitenancy mode.
A tenant is a company with a group of users sharing common access with specific privileges. The Multitenancy options policy helps you to create a single instance of Advanced Authentication solution that supports multiple tenants.
Enable Multitenancy mode to support more than one tenant on a single appliance.
For workstations with Windows Client, Mac OS X Client, or Linux PAM Client installed, you must perform the following steps before you enable Multitenancy options:
-
Ensure that you have installed Advanced Authentication 5.4 or later Client components.
-
Configure the Clients to point to a tenant.
-
For information about how to configure Multitenancy in Windows Client, see Configuration Settings for Multitenancy.
-
For information about how to configure Multitenancy in Mac OS X Client, see Configuration Settings for Multitenancy.
-
For information about how to configure Multitenancy in Linux PAM Client, see Configuration Settings for Multitenancy.
-
These steps are critical and if not performed, the users on the workstations cannot login.
IMPORTANT:The Multitenancy options policy is hidden when your license does not have the Multitenancy feature. To have the policy, you must apply for a license that contains the Multitenancy feature.
5.8.22 Password Filter for Active Directory
In this policy, you can configure settings to synchronize the password update between the appliance and Active Directory through the Password Filter. The Password Filter automatically updates the LDAP Password stored in Advanced Authentication, whenever the password is changed or reset in the Active Directory. This helps you to authenticate without getting any prompt to synchronize the password after it is changed or reset.
You can perform the following settings in this policy:
-
Set Update password on change to ON to update the LDAP password automatically in Advanced Authentication when it is changed in the Active Directory. This helps you to authenticate without getting a prompt to synchronize the password after it is changed.
Set Update password on change to OFF to prompt the user to synchronize the LDAP password while logging in to Windows when the password is changed in the Active Directory.
-
Set Update password on reset to ON to update the LDAP password automatically in Advanced Authentication when it is it is reset in the Active Directory.This helps users to authenticate without getting a prompt to synchronize the password if it is reset.
Set Update password on reset to OFF to prompt the user to synchronize the LDAP password while logging in to Windows when the user's password has been reset in the Active Directory.
NOTE:If Enable local caching is set to ON in the Cache Options policy and when the password is changed or reset in the Active Directory. Then, a user is prompted to synchronize the password while logging in to Windows irrespective of the status of the following Password Filter for AD settings:
-
Update password on change
-
Update password on reset
If Enable local caching is set to OFF, the Password Filter works according to the settings configured in this policy.
-
NOTE:Endpoint for the Password Filter must be trusted. To do this, perform the following steps:
-
Click Endpoints in the Advanced Authentication Administration portal.
-
Edit an endpoint of the Password Filter.
-
Set Is trusted to ON and add a description.
-
Save the changes.
5.8.23 Public External URLs (Load Balancers)
In this policy, you can set the external URLs used for the OOB authentication and methods such as Smartphone, and Voice. You can specify multiple server URLs for the different sites, which are callback URLs, for the authentication to happen between the sites.
NOTE:You must specify different public external URLs for the different Advanced Authentication sites. It is not possible to specify a public external URL of a common load balancer for all the sites.
The following work flow describes the working of this policy in a multi-site environment for the Smartphone authentication.
-
Smartphone app receives and updates the list of callback URLs during enrollment and in the background when the Smartphone app starts.
-
When a user opens the Smartphone app, the app sends the request get salt to all callback URLs.
-
Only one callback URL returns the salt to the Smartphone and this is an Advanced Authentication server, which initiated the authentication.
-
The Smartphone app sends the user's answer (Accept/Reject) only to this Advanced Authentication server.
NOTE: A tenant administrator cannot access the Public external URLs policy.
5.8.24 Replica options
In this policy, you can configure the setting for monitoring the replication process of all the servers in a cluster. Advanced Authentication performs the following actions in the replication process:
-
Generates and sends the replication report on daily basis to the configured email address.
-
Sends notification email to the configured email address when a conflict is detected.
-
Tracks and provides the specific time from when the replication has not happened between the conflicting servers.
NOTE:You can configure the Replica Monitor policy only in the DB Master server.
To configure the replication monitor settings, perform the following steps:
-
Specify the Email address of the recipient who wants to receive the replication report and conflict notification.
-
Set Everyday report to ON to send the data replication status report daily to the configured email address.
-
Set Notify if Problem to ON to send an email notification to the configured email address whenever a replication conflict is detected.
-
Set Delete old endpoint device and update endpoint last session to OFF to allow the Advanced Authentication server to perform the following thus prevents any new conflicts related to the endpoints:
-
Do not delete the existing endpoint device specific record though there are two devices with the same Endpoint ID and Endpoint Secret.
-
Do not update the last login session time of each device.
When Delete old endpoint device and update endpoint last session option is set to ON (default behavior), the server performs the following:
-
Deletes the old device specific record if there are two devices that contain the same Endpoint ID and Endpoint Secret.
-
Updates the last login session time of each device that logs in.
-
-
Click Save.
NOTE:Ensure that you configure the Mail Sender policy with sender details to send the replication status report and notification on a replication conflict to the configured email address.
5.8.25 Reporting Options
In this policy, you can configure settings to delete the history about the login information of users that is recorded in the reports.
Specify a value in History max age(days). The default value is 30 (days). This indicates that the history about the login information of users will be recorded from the current date to the previous 30 days. Any data before that will be deleted.
5.8.26 SMS Sender
In this policy, you can configure the settings for the SMS OTP method. The SMS OTP method sends SMS messages with one-time passwords to the users. Advanced Authentication contains predefined settings for Twilio and MessageBird services.
The Sender Service consists of the following three options:
To configure SMS sender manually perform the following steps:
-
Select Generic in Sender service.
-
Specify a Service URL value. For example, Clickatell http://api.clickatell.com/http/sendmsg?.
-
Leave HTTP Basic Authentication Username and HTTP Basic Authentication Password blank.
-
Select POST from HTTP request method.
-
Click Add and create the following parameters in HTTP request body.
-
name: user
value: name of your account
-
name: to
value: {phone}
-
name: text
value: {message}
-
name: api_id, this is a parameter that is issued after addition of an HTTP sub-product to your Clickatell account. A single account may have multiple API IDs associated with it.
-
name: from
value: sender’s phone number
-
-
Click Add secure and create the following parameter in HTTP request body.
-
Name: password
Value: current password that is set on the account
For more information about the additional parameters for Clickatell, see the Clickatell documentation.
NOTE:The parameters may differ for different SMS service providers. But the {phone} and {message} variables are mandatory.
-
To configure SMS sender settings for Twilio service, perform the following steps:
-
Select Twilio in Sender service.
-
Specify the following details:
-
Account sid and Authentication token: In Twilio, the Account SID acts as a username and the Authentication Token acts as a password.
-
Use Copilot: The copilot option is used to send SMS from a Twilio’s phone number of your location. This is helpful when SMS messages have to be sent across the geographical locations. For example, with copilot, SMS will be sent from Indian phone number to the Indian users. Without copilot, SMS will be sent from US phone number to the Indian users.
For more information on Copilot option and its features, see https://www.twilio.com/copilot#phone-number-intelligence and https://www.twilio.com/docs/api/rest/sending-messages-copilot#features.
-
Messaging Service SID: Service SID.
-
-
Sender phone: Sender’s phone number.
-
For more information, see the Twilio website.
To configure SMS sender settings for MessageBird service, perform the following steps:
-
Select MessageBird in Sender service.
-
Specify the Username, Password, and Sender name.
For more information, see the MessageBird website.
IMPORTANT:MessageBird API v2 is not supported. To activate MessageBird API v1, perform the following steps:
-
Go to the MessageBird account.
-
Click Developers in the left navigation bar and open the API access tab.
-
Click Do you want to use one of our old API's (MessageBird V1, Mollie or Lumata)? Click here.
You can test the configurations for the SMS sender policy in the Test section.
-
Specify the phone number in Phone to which you want to send the SMS OTP.
-
Specify a message to be sent to the phone in Message.
-
Click Send test message!.
-
Click Save.
Real messaging uses async sender. Ensure that you have configured a chain with the SMS method and assigned it to an event. Then sign-in to the Self-Service portal and test the SMS authenticator. If it does not work, see the async logs.
Authentication Flow
The authentication flow for the SMS sender in Advanced Authentication is described in the following image.
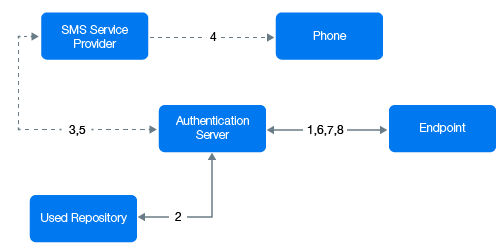
A user wants to authenticate on an endpoint such as a laptop or a website with the SMS method. The following steps describe the authentication flow:
-
When the authentication request is initiated, the endpoint contacts the Advanced Authentication server.
-
The Advanced Authentication server validates the user’s credentials and gets a phone number of the user from a Repository.
-
Advanced Authentication server sends the request to a configured SMS Service Provider to send an SMS message with the content that includes a one-time password (OTP) for authentication.
-
SMS Service Provider sends the SMS message to the user's phone.
-
SMS Service Provider sends the 'sent' signal to the Advanced Authentication server.
-
Advanced Authentication server sends a request to the user to specify an OTP on the endpoint.
-
The user specifies the OTP from the SMS message. The Advanced Authentication server gets the OTP.
-
Advanced Authentication server then validates the authentication. The authentication is done or denied.
HTTP/HTTPS protocol is used for the communication.
Access configuration
Advanced Authentication server - SMS Service Provider (HTTP/HTTPS, outbound).
5.8.27 Services Director Options
In this policy, you can configure settings required to integrate with the Services Director.
Perform the following steps to configure this policy:
-
Set Enable integration to ON to enable the integration of Advanced Authentication with Services Director.
-
Specify the Public DNS name of Advanced Authentication, Services Director DNS Name, Tenant administrator name, and Tenant administrator password of Services Director to integrate it with Advanced Authentication.
NOTE:You cannot integrate Services Director with Advanced Authentication when the Multitenancy Options policy is enabled.
5.8.28 Voice Sender
In this policy, you can configure the settings for the Voice and Voice OTP methods. Advanced Authentication supports the Twilio service for the Voice methods.
To configure Voice Sender settings for Twilio service, perform the following steps.
-
Specify the following details in the Voice sender policy:
-
Account sid and Authentication token: In Twilio, the Account SID acts as a username, and the Authentication Token acts as a password.
-
Sender phone: The phone number of the sender.
-
Server url: The public URL to which the Twilio service connects for authentication. This URL points to the Public External URLs (Load Balancers) policy. You can use http protocol for testing purpose, but for production environment you must use https protocol. You must have a valid certificate when you use https.
-
-
You can test the configurations for the Voice sender policy in the Test section.
-
Specify the phone number in Phone to which you want to send the Voice OTP.
-
Specify a message to be sent to the phone in Message.
-
Click Send test message!.
-
-
Click Save.
Real messaging uses async sender. Ensure that you have configured a chain with the Voice OTP method and assigned it to an event. Then sign-in to the Self-Service portal and test the Voice authenticator. If it does not work, see the async logs.
IMPORTANT:The users may receive calls with the voice Application error. This happens because of incorrect settings or invalid certificates. Ensure that the certificate is valid and is not expired. Invalid certificates cannot be applied by Twilio.
Authentication Flow
The authentication flow for the Voice sender in Advanced Authentication is described in the following image.
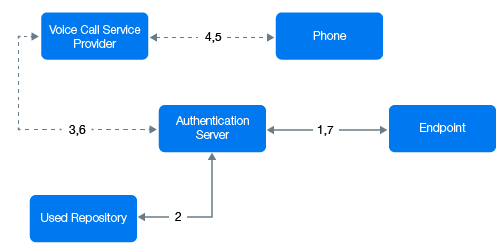
A user wants to authenticate on an endpoint such as a laptop or a website with the Voice Call method. The following steps describe the authentication flow:
-
When the authentication request is initiated, the endpoint contacts the Advanced Authentication server.
-
The Advanced Authentication server validates the user’s credentials and gets a phone number of the user from a repository.
-
Advanced Authentication server sends the request to a configured voice call service provider (Twilio) to call the user.
-
The voice call service provider calls the user.
-
The user picks up the phone, listens to the call, and specifies the PIN followed by the hash (#) sign.
-
Voice call provider sends the specified PIN to the Advanced Authentication server.
-
Advanced Authentication server then validates the authentication. The authentication is done or denied.
HTTP/HTTPS protocol is used for the communication.
Access configuration
Advanced Authentication server - Voice Call Service Provider (HTTP/HTTPS, inbound/ outbound).
5.8.29 Web Authentication
This policy replaces the SAML 2.0 options policy. The Web Authentication policy allows you to perform the following settings:
Configuring Settings for the SAML 2.0 Events
You can configure the settings to specify the Identity Provider’s URL to download the SAML 2.0 metadata file. The downloaded SAML 2.0 metadata file is used to configure the service provider.
For more information about configuring this policy, see SAML 2.0
.
NOTE:From Advanced Authentication 6.1 onwards, the web authentication services such as SAML 2.0, OAuth 2.0 are available only on the 8443 port. Any OAuth 2.0 or SAML 2.0 requests to the 443 port (default SSL) are redirected with a 308 status to the 8443 port. The third-party solutions that integrates with Advanced Authentication using the OAuth 2.0 or SAML 2.0 services must manage the URL redirection or append the port number 8443 with the IP address or domain name in the following format:
https://<ip address>:8443/osp… or https://<dns name>:8443/osp…
Customizing the Login Page of Web Authentication Events
You can customize the login page of the OAuth 2.0, SAML 2.0, or Open ID Connect events. To do this, perform the following steps:
-
Set Custom Branding to ON.
-
Click Download Template.
-
Save the osp-custom-resources.jar file.
-
Unzip the osp-custom-resources.jar file and in the resources folder open the file that you want to customize.
-
To customize logo
You can edit the logo displayed on the login page of web authentication event using the parameter OIDPENDUSER.LoginProductImage available in the Login page properties.
For example, if you want to edit the logo of the login page of an OAuth 2.0 event in the English language, open the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file and edit the following attribute:
OIDPENDUSER.LoginProductImage=company_img.png.
Ensure that you add the image that you want as a logo to the images folder with the name that matches with the attribute value in OIDPENDUSER.LoginProductImage. By default the images folder contains the company_img.
-
To edit copyright text
You can edit the copyright text displayed on the login page of web authentication event using the parameter OIDPENDUSER.50004 available under the JSP Strings.
For example, if you want to remove the copyright note that is displayed in the login page of an OAuth 2.0 event in the English language, open the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file and search the following parameter:
#OIDPENDUSER.50004=Copyright [copy] [year] NetIQ[nbsp]Corporation, a Micro[nbsp]Focus company. All rights reserved
Uncomment the parameter by removing the suffixed hash sign(#) and set the parameter with blank value as follows:
OIDPENDUSER.50004=
This removes the copyright note from the web authentication event - login page.
-
To edit branding text
You can edit the branding text displayed on the login page of web authentication event using the parameter OIDPENDUSER.LoginProductName available in the Login page properties section.
For example, if you want to remove the branding text NetIQ Access that is displayed on the login page of an OAuth 2.0 event in the English language, open the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file and search the following parameter:
#OIDPENDUSER.LoginProductName=Company[nbsp]Name[reg]
Uncomment the parameter by removing the suffixed hash sign(#) and set the parameter with blank value as follows:
OIDPENDUSER.LoginProductName=
This removes the branding text NetIQ Access from the web authentication event - login page.
Similarly, you can edit the other attributes in the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file.
NOTE:Ensure that you edit the attributes in the Login page properties section of the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file for the custom branding of the login pages.
-
-
After you edit the file, zip the file osp-custom-resources.jar and click Browse to upload.
-
Click Save.
NOTE: When you upload the custom branding changes for the first time, you must restart the Advanced Authentication server to reflect the changes on the login pages of the web authentication events. This is applicable per tenant.
You can also upload a customized css file to reflect changes for the login pages:
-
Open the osp-custom-resources.jar file.
-
Upload your css file to the css folder.
-
Open the resources folder.
-
Open the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file.
-
UnComment the line OIDPENDUSER.LoginCss=reset.css,uistyles.css,uistyles_loginselect.css by removing the # sign.
-
Save the oidp_enduser_custom_resources_en_US.properties file.
-
After you edit the file, zip the file osp-custom-resources.jar and click Browse to upload.
-
Click Save.
Customizing Messages and Authentication Method Names for the Web Authentication Events
You can customize the messages and authentication methods name for the Web Authentication events in the Custom Messages policy. Set Use Custom Messages to ON to enable using the custom messages for the OAuth, SAML 2.0, or Open ID Connect events. You must customize the messages in the Custom Messages
policy.