1.6 Setting Up Firewalls
Access Manager should be used with firewalls. Figure 1-8 illustrates a simple firewall setup for a basic Access Manager configuration of an Identity Server, an Access Gateway, and an Administration Console.
Figure 1-8 Access Manager Components between Firewalls
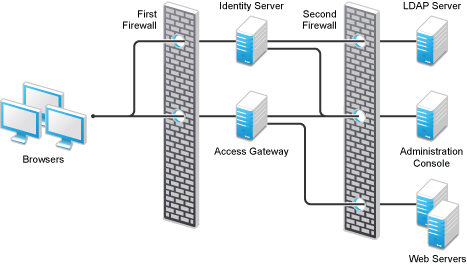
The first firewall separates the Access Manager from the Internet, allowing browsers to access the resources through specific ports. The second firewall separates Access Manager components from Web servers they are protecting and the Administration Console.This is one of many possible configurations. This section describes the following:
1.6.1 Required Ports
The following tables list the ports that need to be opened when a firewall separates one component from another. Some combinations appear in more than one table. This allows you to discover the required ports whether a firewall is separating an Access Gateway from the Administration Console or a firewall is separating an Administration Console from the Access Gateway.
With these tables, you should be able to place Access Manager components of your system anywhere within your existing firewalls and know which ports need to be opened in the firewall.
Table 1-2 When a Firewall Separates an Access Manager Component from a Global Service
|
Component |
Port |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
NTP Server |
UDP 123 |
Access Manager components must have time synchronized else the authentication fails. We recommend that you configure all components to use an network time protocol (NTP) server. Depending upon where your NTP server is located, you might need to open UDP 123, so that Access Manager components can use the NTP server. |
|
DNS Servers |
UDP 53 |
Access Manager components must be able to resolve DNS names. Depending upon where your DNS servers are located, you might need to open UDP 53, so that Access Manager components can resolve DNS names. |
|
Remote Linux Administration Workstation |
TCP 22 |
If you want to use SSH for remote administration of Access Manager components, open TCP 22 to allow communication from your remote administration workstation to your Access Manager components. |
|
Remote Windows Administration Workstation |
Configurable |
If you want to use RDP or VNC for remote administration of Access Manager components, open the ports required by your application from the remote administration workstation to your Access Manager components. You need to open ports for console access and for file sharing. For console access, VNC usually uses TCP 5901 and RDP uses TCP 3389. For file sharing, UDP 135-139 are the default ports. |
Table 1-3 When a Firewall Separates the Administration Console from a Component
|
Component |
Port |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Access Gateway, Identity Server |
TCP 1443 |
For communication from the Administration Console to the devices. |
|
TCP 8444 |
For communication from devices to the Administration Console. |
|
|
TCP 1289 |
For communication from devices to the Audit server on the Administration Console. |
|
|
TCP 524 |
For NCP certificate management with NPKI. The port needs to be opened so that both the device and the Administration Console can use the port. |
|
|
TCP 636 |
For secure LDAP communication from devices to the Administration Console. |
|
|
HTTP 2443 HTTP 8443 |
For the installer to communicate with the Administration Console. You can close these port after installation is complete. |
|
Importing an Access Gateway Appliance |
ICMP |
During an import, the Access Gateway Appliance sends two pings through ICMP to the Administration Console. When the import has finished, you can disable the ICMP echo requests and echo replies. |
|
LDAP User Store |
TCP 524 |
Required only if the user store is eDirectory. When configuring a new eDirectory user store, NCP is used to enable Novell SecretStore by adding a SAML authentication method and storing a public key for the Administration Console. It is not used in day-to-day operations. |
|
Administration Console |
TCP 524 |
Required to synchronize the configuration data store. |
|
TCP 636 |
Required for secure LDAP communication. |
|
TCP 427 |
Used for SLP (Service Location Protocol) communication. |
|
TCP 8080, 8443 |
Used for Tomcat communication. |
|
TCP 705 |
Used by Sub Agent-Master Agent communication inside the Administration Console. |
|
|
UDP 161 |
Used for communication by an external Network Monitoring System with the Administration Console by using SNMP. |
|
|
Browsers |
TCP 8080 |
For HTTP communication from browsers to the Administration Console. |
|
TCP 8443, 2443, 2080. |
For HTTPS communication from browsers to the Administration Console. NOTE:2443 and 2080 are optional ports required when the Administration Console and Identity Server are collocated. |
|
|
TCP 8028, 8030 |
To use iMonitor or DSTrace from a client to view information about the configuration store on the Administration Console. |
Table 1-4 When a Firewall Separates the Identity Server from a Component
|
Component |
Port |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Access Gateway |
TCP 8080 or 8443 |
For authentication communication from the Access Gateway to the Identity Server. The default ports for the Identity Server are TCP 8080 and 8443. They are configurable. You need to open the port that you configured for the base URL of the Identity Server. |
|
TCP 80 or 443 |
For communication from the Identity Server to ESP of the Access Gateway. This is the reverse proxy port that is assigned to be ESP (see the Reverse Proxy /Authentication page). This is usually port 80 or 443. |
|
Administration Console |
TCP 1443 |
For communication from the Administration Console to devices. This is configurable. |
|
TCP 8444 |
For communication from the Identity Server to the Administration Console. |
|
|
TCP 1289 |
For communication from the Identity Server to the Audit server on the Administration Console. |
|
|
TCP 524 |
For NCP certificate management with NPKI from the Identity Server to the Administration Console. |
|
|
TCP 636 |
For secure LDAP communication from the Identity Server to the Administration Console. |
|
|
Identity Server |
TCP 8443 or 443 |
For HTTPS communication. You can use iptables to configure this for TCP 443. See Section 3.5, Translating the Identity Server Configuration Port. |
|
TCP 7801, 7802 |
For back-channel communication with cluster members. You need to open two consecutive ports for the cluster, for example 7801 and 7802. The initial port (7801) is configurable. |
|
LDAP User Stores |
TCP 636 |
For secure LDAP communication from the Identity Server to the LDAP user store. |
|
Service Providers |
TCP 8445 |
If you have enabled identity provider introductions, open a port to allow HTTPS communication from the user’s browser to the service provider. |
|
TCP 8446 |
If you have enabled identity provider introductions, open a port to allow HTTPS communication from the user’s browser to the service consumer. |
|
|
Browsers |
TCP 8080 |
For HTTP communication from a browser to the Identity Server. You can use iptables to configure this for TCP 80. SeeSection 3.5, Translating the Identity Server Configuration Port. |
|
TCP 8443 |
For HTTPS communication from a browser to the Identity Server. You can use iptables to configure this for TCP 443. See Section 3.5, Translating the Identity Server Configuration Port. |
|
|
CRL and OCSP Servers |
Configurable |
If you are using x.509 certificates that include an AIA or CRL Distribution Point attribute, you need to open the port required to talk to that server. Ports 80/443 are the most common ports, but the LDAP ports 389/636 can also be used. |
|
Active Directory Server with Kerberos |
TCP 88, UDP 88 |
For communication with the KDC on the Active Directory Server for Kerberos authentication. |
Table 1-5 When a Firewall Separates the Access Gateway from a Component
|
Component |
Port |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Identity Server |
TCP 8080 or 8443 |
For authentication communication from the Access Gateway to the Identity Server. The default ports are TCP 8080 and 8443, which are configurable. You need to open the port of the base URL of the Identity Server. |
|
TCP 80 or 443 |
For communication from the Identity Server to ESP of the Access Gateway. This is the reverse proxy port that is assigned to be ESP (see the Reverse Proxy /Authentication page). This is usually port 80 or 443. |
|
Administration Console |
TCP 1443 |
For communication from the Administration Console to the Access Gateway. This is configurable. |
|
TCP 8444 |
For communication from the Access Gateway to the Administration Console. |
|
TCP 1289 |
For communication from the Access Gateway to the Audit server on the Administration Console. |
|
TCP 524 |
For NCP certificate management with NPKI from the Access Gateway to the Administration Console. |
|
TCP 636 |
For secure LDAP communication from the Access Gateway to the Administration Console. |
|
Access Gateway |
TCP 7801, 7802 |
For back-channel communication with cluster members. You need the first port plus 1. The initial port (7801) is configurable. It is set by the Identity Server cluster configuration that the Access Gateway trusts. See Configuring a Cluster with Multiple Identity Servers in the NetIQ Access Manager 4.1 Administration Guide . |
|
Browsers/Clients |
TCP 80 |
For HTTP communication from the client to the Access Gateway. This is configurable. |
|
TCP 443 |
For HTTPS communication from the client to the Access Gateway. This is configurable. |
|
|
Web Servers |
TCP 80 |
For HTTP communication from the Access Gateway to the Web servers. This is configurable. |
|
TCP 443 |
For HTTPS communication from the Access Gateway to Web servers. This is configurable. |
NOTE:On SLES 11 SP2 (or a higher version), you can use YaST to configure UDP ports and internal networks.
1.6.2 Sample Configurations
Access Gateway and Identity Server in DMZ
First Firewall
If you place a firewall between browsers and Access Gateway and Identity Server, you need to open ports so that browsers can communicate with the Access Gateway and the Identity Server and the Identity Server can communicate with other identity providers.
See, Figure 1-8
Table 1-6 Ports to Open in the First Firewall
|
Port |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
TCP 80 |
For HTTP communication. |
|
TCP 443 |
For HTTPS communication. |
|
Any TCP port assigned to a reverse proxy or tunnel. |
|
|
TCP 8080 |
For HTTP communication with the Identity Server. For information about redirecting the Identity Server to use port 80, see Section 3.5, Translating the Identity Server Configuration Port. |
|
TCP 8443 |
For HTTPS communication with the Identity Server. For information about redirecting the Identity Server to use port 443, see Section 3.5, Translating the Identity Server Configuration Port. |
|
TCP 8445 |
For HTTP Identity Provider introductions. If you do not enable Identity Provider introductions, you do not need to open this port. |
|
TCP 8446 |
For HTTPS Identity Provider introductions. If you do not enable Identity Provider introductions, you do not need to open this port. |
Second Firewall
The second firewall separates Web servers, LDAP servers, and the Administration Console from the Identity Server and the Access Gateway. You need the following ports opened in the second firewall:
Table 1-7 Ports to Open in the Second Firewall
|
Port |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
TCP 80 |
For HTTP communication with Web servers. |
|
TCP 443 |
For HTTPS communication with Web servers. |
|
Any TCP connect port assigned to a Web server or to a tunnel. |
|
|
TCP 1443 |
For communication from the Administration Console to the devices. |
|
TCP 8444 |
For communication from the devices to the Administration Console. |
|
TCP 1289 |
For communication from the devices to the Audit server installed on the Administration Console. If you do not enable auditing, you do not need to open this port. |
|
TCP 524 |
For NCP certificate management in NPKI. The port needs to be opened so that both the device and the Administration Console can use the port. |
|
TCP 636 |
For secure LDAP communication of configuration information. |
A Firewall Separating Access Manager Components from the LDAP Servers
You can configure your Access Manager components so that your Administration Console is on the same side of the firewall as your Access Manager components and have a firewall between them and the LDAP servers.
Figure 1-9 A Firewall Separating the Administration Console and the LDAP Server
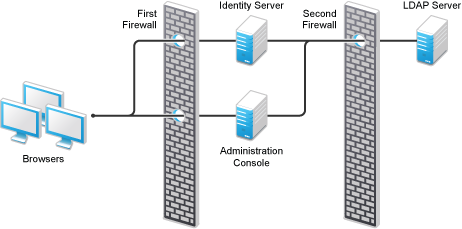
In this configuration, you need to have the following ports opened in the second firewall for the Administration Console and the Identity Server.
Table 1-8 Ports to Open in the Second Firewall
|
Ports |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
TCP 636 |
For secure LDAP communication. This is used by the Identity Server and the Administration Console. |
|
TCP 524 |
For configuring eDirectory as a new User Store. NCP is used to enable SecretStore by adding a SAML authentication method and storing a public key for the Administration Console. During day-to-day operations, this port is not used. If your LDAP server is Active Directory or Sun ONE, this port does not need to be opened. |