1.2 Auditing and Evaluation Process Workflow
Secure Configuration Manager simplifies and automates the process for demonstrating compliance and managing information security risk. Policy compliance is the assessment, operation, and control of systems and resources according to security standards, best practices, and regulatory requirements. Complex environments, industry standards, and government regulations can make compliance with so many policies a challenge, even for highly-experienced security teams. In most organizations, a variety of individuals perform the complex tasks required to maintain asset compliance.
The following workflow shows how you can streamline the asset auditing and evaluation processes by workflow tasks.
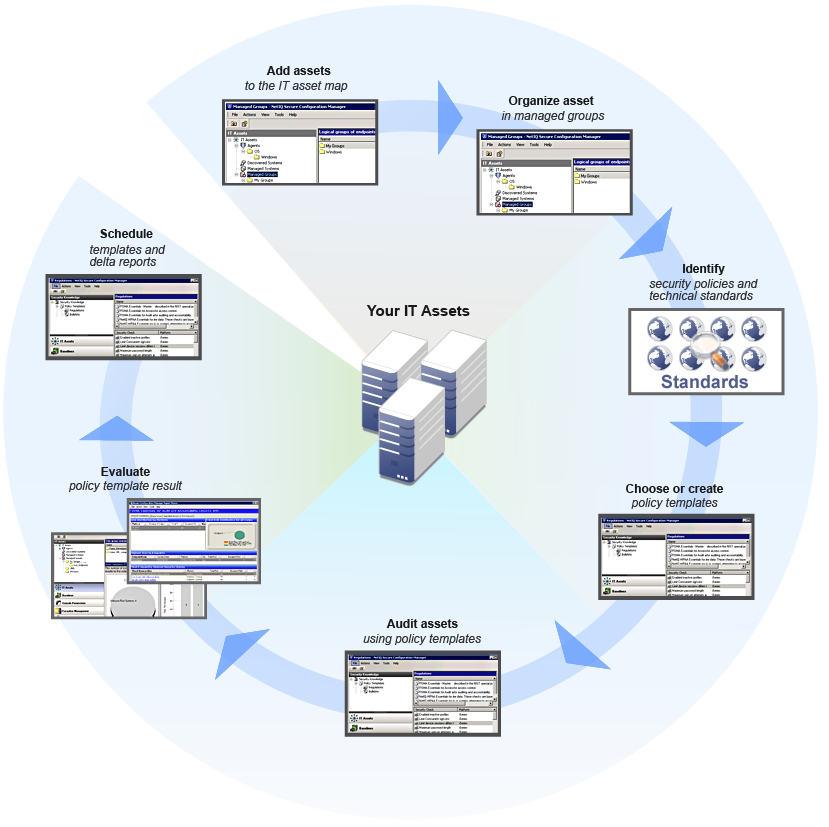
Use the following checklist to guide you through the auditing and evaluation process.
|
Checklist Items |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
