6.2 Creating Projects
A project can consist of any combination of consolidation candidates, protection candidates, workloads, and scenarios. Consolidation candidates are workloads on the network that you might want to move to virtual machines. Protection candidates are workloads you might want to create standby VM duplicates of for disaster recovery.
You create and compare scenarios in a project. The Project Report consists of scenario comparison results, which help in determining the best consolidation scenario for the environment.
Before you create a project, identify and group consolidation candidates. The identified candidates allow you to create and compare consolidation scenarios in a project.
NOTE:Collecting at least 24 hours of data for each workload before starting the project is recommended.
To create a new project:
-
Do any of the following:
-
Click
 , then click .
, then click .
-
In the Project Explorer, click
 .
.
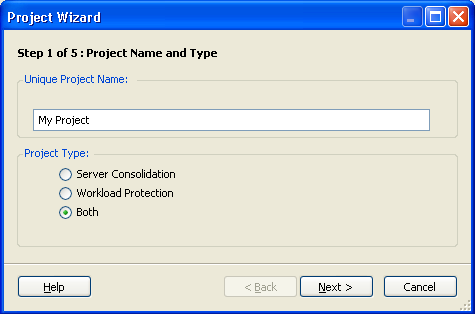
The Project Wizard (Step 1 of 5: Project Name and Type) is displayed.
-
-
Type a unique project name for the project.
-
Select one of the following project types:
-
Server Consolidation: The project produces a recommendation for the best placement of workloads with respect to concurrent execution and CPU and memory headspace requirements.
-
Workload Protection: The project produces a recommendation for deployment of workloads for disaster recovery. Specify existing virtual servers or use server templates to build a scenario.
-
Both: The project produces a recommendation for both consolidation and protection. For example, optimally consolidate servers, and provision the remaining headroom for data protection.
A workload cannot be provisioned for both consolidation and protection in the same project.
-
-
Click .
The Step 2 of 5: Workload Selection dialog box is displayed.
-
Identify the workloads you want to include in the project.
-
Identify the workloads you want to include in the project, and include them in the Workloads to Consolidate panel or the Workloads to Protect panel in any of the following ways:
-
Drag workloads from the tree on the left and drop them into the Workloads to Consolidate panel or the Workloads to Protect panel on the right.
-
Select servers in the right pane, then click the arrow pointing to the panel to which you want to add them.
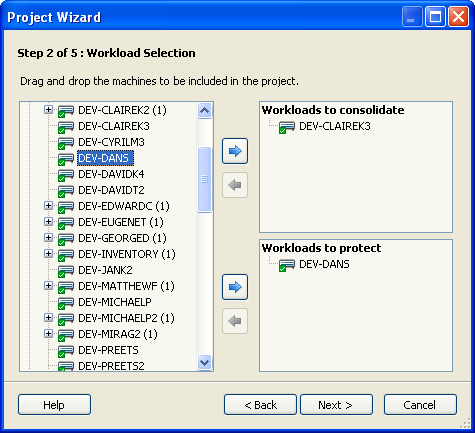
If the existing virtual hosts have been inventoried by PlateSpin Recon, they can be added to the project as potential target servers. The existing servers take precedence over the server template that you provide when generating scenarios. Select any virtual hosts that exist in your environment to be used for consolidation or protection. Drop the target servers into either the Protection or Consolidation panel.
NOTE:PlateSpin Recon always considers a Solaris 10 machine as a target server for consolidation because the machine has the global zone enabled by default. Therefore, you cannot consider a Solaris 10 machine as a consolidation source.
To remove a server from the Workloads to Consolidate panel or the Workloads to Protect panel, select the server in the panel, then click the arrow pointing towards the server list.
Servers cannot be targeted for consolidation and protection within the same project.
-
-
Click .
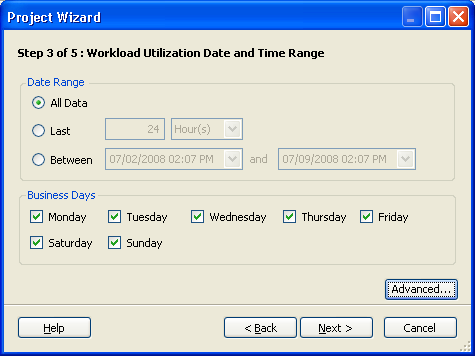
The Step 3 of 5: Workload Utilization Date and Time Range dialog box is displayed.
-
Set the date and time range to summarize the workload data.
and are required for calculating the 24H profile of workloads.
-
(Optional) To manually set workload scaling factors, click .
The Workload Scaling dialog box is displayed.
-
Use the slide controls to adjust values or type the desired number.
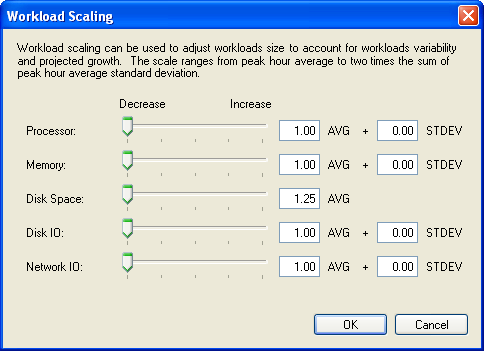
Workloads can be scaled across five dimensions to account for workload variability and projected growth. Server resources allocated to workloads on target servers are based on scaled workloads. By scaling workloads upward, more server resources might be required, potentially resulting in lower consolidation ratios. When scaling pointers are moved, workload scaling factors change.
Workloads cannot be scaled below their peak hourly averages.
-
Click .
-
Click .
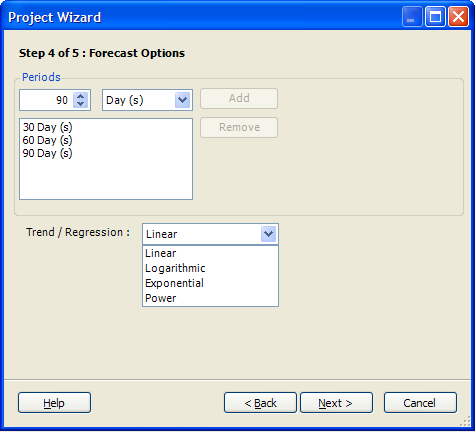
The Step 4 of 5: Forecast Options dialog box is displayed.
-
Select forecast options and a trend type.
Workloads can be forecasted to account for future growth.
-
Click .
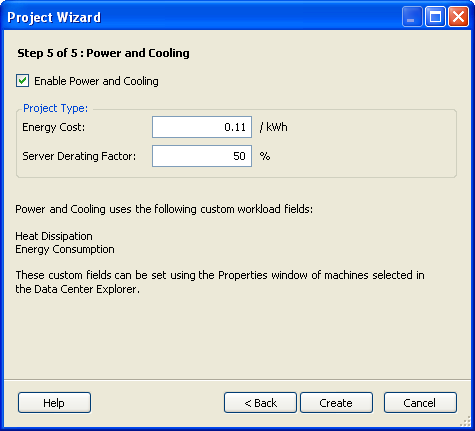
The Step 5 of 5: Power and Cooling dialog box is displayed.
-
Specify the values for the , or deselect the check box if these values are not to be included.
Energy Cost: Cost of energy per kilowatt hour.
Server Derating Factor: Percentage of total energy consumption by the average server. For example, a server rated at 800 watts uses 400 watts with a server derating factor of 50%.
-
Click .
The new project is displayed in the Project Explorer.
When creating a project, a 24H Profile of workloads is computed. This includes calculating Processor Speed (MHz), Memory (MB), Disk Space Used (GB), Disk IO (MB/s), and Network IO (MB/s) over a 24-hour period for each workload. The 24H Profile comprises 24 values of workloads that correspond to each hour of the day (0 to 23). Each value in the 24H Profile is calculated by taking the peak value from all values observed for that hour.