8.8 Understanding the Authentication Process of the Access Gateway Service
When a user requests access to a protected resource, the request can be in one of the following states:
-
No session or cookie is established, because this is the user’s first request.
-
The user’s session is a public session because only public resources have been accessed.
-
A session is established, the user is authenticated, and the requested resource is from the same cookie domain and uses the same contract.
-
A session is established, the user is authenticated, and the requested resource is from the same cookie domain but uses a different contract or the contract has expired.
-
A session is established, the user is authenticated, but the request doesn’t have a session cookie because the resource is on a different cookie domain.
-
A session no longer exists or doesn’t exist on the proxy servicing the request.
The Access Gateway Service must handle these conditions and others as it determines whether it needs to forward a plogin request to the Embedded Service Provider or use the user’s existing authentication credentials. The following flow charts take you through this process.
Figure 8-4 Identifying the Requester
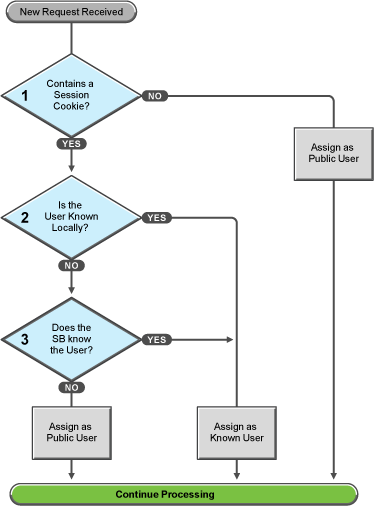
These first steps determine whether the Access Gateway knows the user that has submitted the request. In decision point 1, the Access Gateway checks for a session cookie in the request.
-
If the request contains a session cookie, the session cookie needs to be validated. Processing continues with the task in decision point 2.
-
If the request does not contain a session cookie, the user is unknown and is assigned as a public user. The Access Gateway continues processing with the tasks outlined in Figure 8-5.
When the request contains a session cookie, the Access Gateway checks its local user store for a user that matches the session cookie. Each Access Gateway in the cluster maintains its own list of known users.
-
If the session cookie matches one of the locally known users, the user is assigned that identity. The Access Gateway continues with the tasks outlined in Figure 8-5.
-
If the session cookie doesn’t match one of the locally known users, the Access Gateway needs to know if one of the other Access Gateways in the cluster knows the user. Processing continues with the task in decision point 3.
The Access Gateway queries the session broker to see if one of the other Access Gateways in the cluster knows this user.
-
If a match is found, the user is assigned that identity. The Access Gateway continues with tasks outlined in Figure 8-5.
-
If a match is not found, the user is unknown and is assigned as a public user. The Access Gateway continues with the tasks outlined in Figure 8-5.
Figure 8-5 Determining the Type of Request
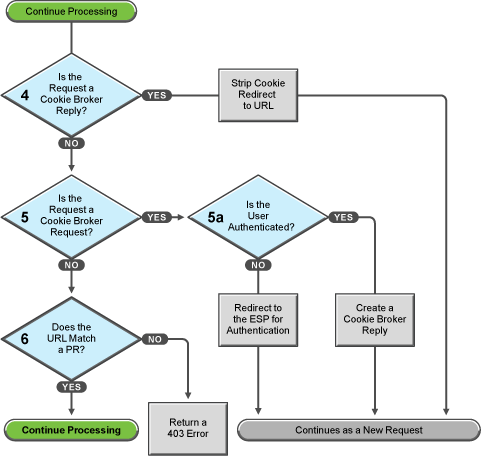
The Access Gateway examines the request to determine what type of request it is.
If the request is a cookie broker reply, the Access Gateway strips the cookie from the URL and redirects the request to the URL. The redirect is handled as a new request, and this new request flows to the task in decision point 6, where the URL is examined.
If the request isn’t a cookie broker reply, the Access Gateway examines the request to see if it is a cookie broker request. If it is a cookie broker request, the Access Gateway determines whether the user is authenticated with the contract required by the protected resource.
-
If the user is authenticated, the Access Gateway creates a cookie broker reply. This reply is handled as a new request, and flows to the task in decision point 4.
-
If the user is not authenticated, the request is redirected to the Embedded Service Provider (ESP). The ESP interacts with the Identity Server to authenticate the user. The Identity Server, the ESP, and the reverse proxy all maintain authentication information. The ESP returns a new request, which flows to the task in decision point 6, where the URL is examined.
If the URL does not match a URL of a protected resource (PR), the Access Gateway returns an HTTP 403 error to the user.
If the URL in the request matches a URL of a protected resource, the Access Gateway needs to examine the protection type assigned to the resource. The Access Gateway continues with the tasks outlined in Figure 8-6.
Figure 8-6 Determining the Protection Type Assigned to the Resource
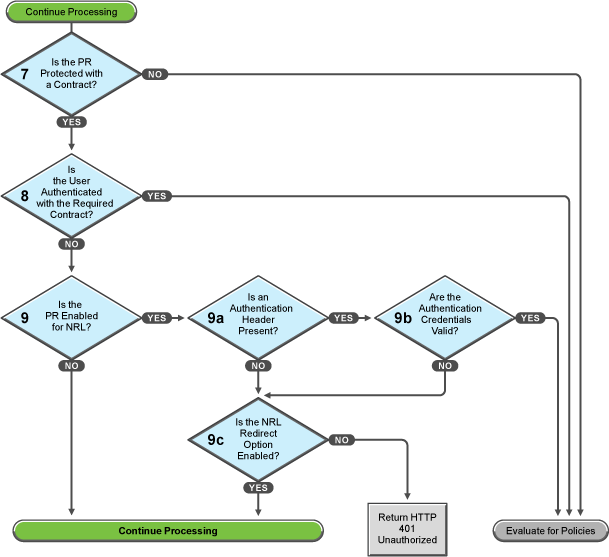
You configure a protected resource as a public resource when an authentication procedure/contract is not assigned to the protected resource. In decision point 7, the Access Gateway checks to see if a contract has been assigned to the protected resource.
-
If the protected resource has not been assigned a contract, the Access Gateway is finished with its authentication checks and continues with policy evaluation.
-
If the protected resource has been assigned a contract, the Access Gateway continues with the task in decision point 8.
For a user to gain access to a resource protected by a contract, the user must have authenticated with that contract, or if the contract is configured for it, the user can authenticate with another contract as long as the contract is of a equal or higher level.
-
If the user is authenticated with the required contract, the Access Gateway is finished with its authentication checks and continues with policy evaluation.
-
If the user is not authenticated with the required contract, the Access Gateway continues with the task in decision point 9.
Before the user is prompted for credentials, the Access Gateway needs to know whether the protected resource has been enabled for non-redirected login (NRL).
-
If the resource has not been configured for non-redirected login, the Access Gateway continues with the tasks outlined in Figure 8-7.
-
If the resource has been configured for non-redirected login, the Access Gateway needs to examine the request for an authentication header and determine whether the header is valid. Processing continues with the tasks outlined in decision points 9a, 9b, and 9c.
If the request does not contain an authentication header, the Access Gateway needs to determine how non-redirected login has been configured. On the Authentication Procedure configuration page, you can select to enable the option.
-
If this option is enabled, the Access Gateway continues with the tasks outlined in Figure 8-7.
-
If this option is disabled, the Access Gateway returns an HTTP 401 unauthorized message.
If the request does contain an authentication header, the Access Gateway must verify that the credentials are valid.
-
If the authentication credentials are valid, the Access Gateway is finished with its authentication checks and continues with evaluating the protected resource for policies.
-
If the authentication credentials are not valid, the process is the same as if the request did not contain an authentication header and continues with the task in decision point 9c.
Figure 8-7 Evaluating the Cookie Domain
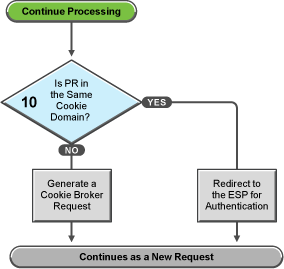
If you have configured your Access Gateway to use multiple domain-based proxy services, you can configure them to share the same cookie domain (domains of development.novell.com and support.novell.com can share the cookie domain of novell.com) or configure them so that they cannot share a cookie domain (domains of a.slc.com and b.provo.com cannot share a cookie domain).
When the Access Gateway reaches the task in decision point 10, it has determined that the protected resource requires a contract and that user is not authenticated with that contract.
-
If the protected resource is in the same cookie domain, the Access Gateway redirects the request to the Embedded Service Provider (ESP). The ESP interacts with the Identity Server to authenticate the user. The ESP returns a new request, which flows to the task in decision point 6, where the URL is examined.
-
If the protected resource is in a different cookie domain, the Access Gateway generates a cookie broker request. This new request flows to the task in decision point 5.