3.5 Working with Relationships
The Relationships node allows you to define relationships between entities defined in the directory abstraction layer. The relationships you define are used in the User Application by the Organization Chart and in iManager for defining the members within a group.
The relationship you define can be between like entities (such as user/user) or unlike entities (such as user/device). You can define conditions for the relationship to further refine it. For example, you might want to create a condition that shows all Manager-Employee relationships and then refine it to show only employees in one particular region, or show all the subordinates of a vice president located in the eastern region.
The following relationships are defined, by default, for the User Application:
-
Group’s membership (Org Chart only)
-
Manager-Employee (Org Chart and Management)
-
User groups (Org Chart only)
A relationship can only be used by Management when the Source and Target entities are both related to the InetOrgPerson object.
To successfully deploy a relationship, all of the components (entities and attributes) of the relationship must already be deployed.
-
Create a new relationship in any of these ways:
From Designer’s menus:
-
Select . Choose , then click .
-
Select .
From the Provisioning view:
-
Right-click , then select .
From the directory abstraction layer editor:
-
Click the button.
-
Right-click , then select .
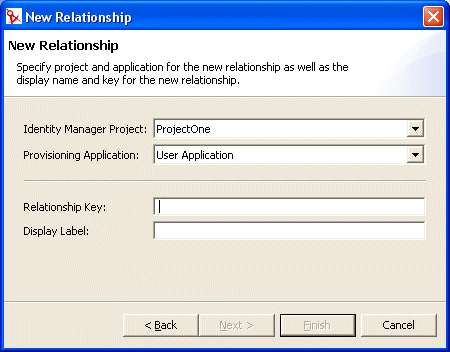
The New Relationship dialog box displays.
NOTE:When launched from the menu, the dialog box contains fields not displayed when launched in other ways.
-
-
Fill in the fields as follows:
-
Click .
The editor creates the relationship and opens the property page for editing.
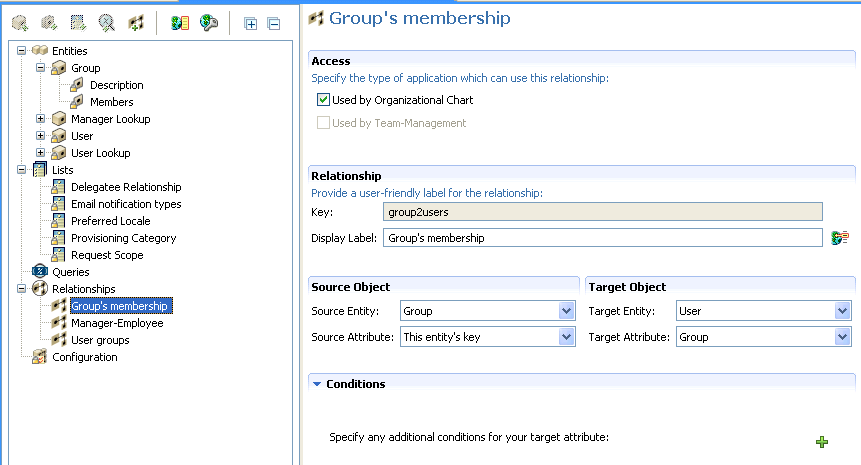
For property definitions, see Section 3.7.4, Relationship Properties.
To delete a relationship:
-
Right-click the relationship you want to delete, then click .
To add a relationship condition:
-
Click .
-
Use the drop-down list box (on the left) to select an attribute. The attributes in this drop-down are attributes on the entity.
-
Select an operator from the middle drop-down list box.
-
Use the text field on the right to specify the comparison value to complete the condition. For example:
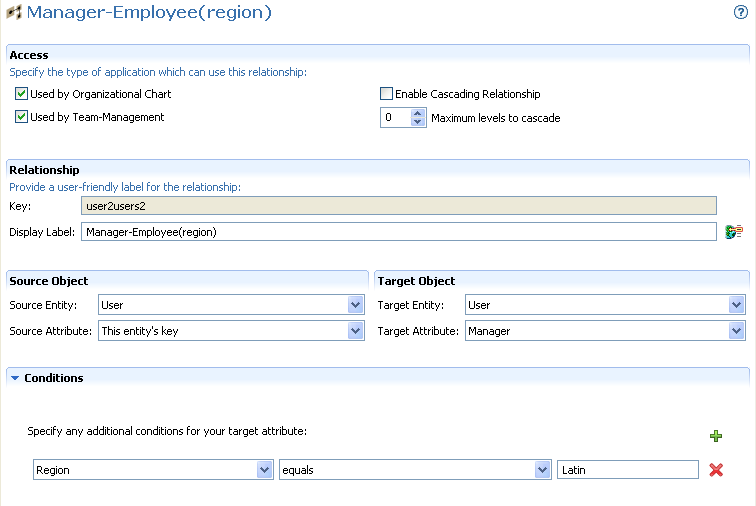
You can create a condition that filters on more than one attribute or condition and connect the attributes by using the logical operations: and, or. The conditions are evaluated in the order in which you define them.