4.2 Web Server Accelerator Setup
Figure 4-2 provides a visual map for the information in this section.
NOTE:The letters in Figure 4-2 are referenced in the table that follows. The addresses shown are for illustration purposes only. You need to substitute actual addresses for your network.
Figure 4-2 Web Server Accelerator Setup
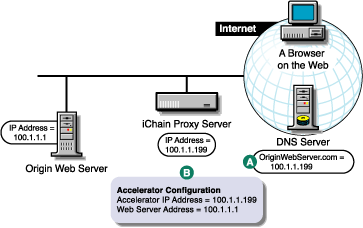
As you set up your Web server, use the information in the following table to determine what tasks you need to complete and how.
|
To |
Do This |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Ensure that your basic network configuration is complete for each proxy server |
||
|
Ensure that DNS resolves browser requests to the proxy server IP addresses configured for the Web server accelerator services |
|
See A in Figure 4-2. |
|
Set up one or more Web server accelerator services |
|
See B in Figure 4-2. If server persistence is enabled in the Web Server Accelerator tab, the proxy server uses the same Web server to fill browser requests during a session. This setting affects all accelerators on the proxy server and saves e-business users from logging in multiple times. If logging is enabled, accelerator log files for the Web server accelerator has the same name as the Web server accelerator. The DNS name is required when:
If you enter DNS names in the Web Server Addresses list, make sure they are not the names that now resolve to proxy server numeric IP addresses. That would create an endless loop. |
IMPORTANT:Do not create more than 250 accelerators. If you create more than 250 accelarators, the proxy.nlm can cause a CPU Hog Abend.
4.2.1 Working with DNS
The steps you take to have DNS resolve requests to the proxy server rather than to the origin server depend on whether the proxy server and the origin Web server are on the same subnet. The following sections explain each alternative.
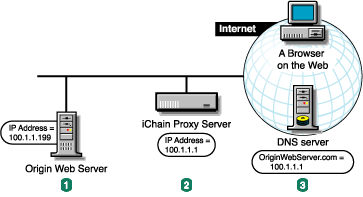
If the proxy server and the origin Web server are on the same subnet, you can swap IP addresses as shown below.
Figure 4-3 Working with DNS
-
The origin Web server's IP address was 100.1.1.1. You change it to 100.1.1.199.
-
You assign the proxy server the IP address 100.1.1.1.
-
DNS is unchanged, but now sends browsers to the appliance instead of the origin Web server.
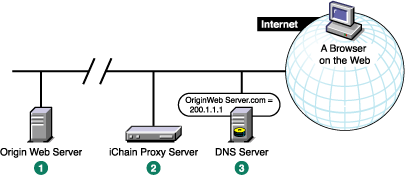
If the origin Web server is on a remote network, you need to alter DNS as shown below.
Figure 4-4 Altering DNS
-
The origin Web server's IP address is 200.1.1.1.
-
You assign the proxy server the IP address 100.1.1.1.
-
DNS had 200.1.1.1 as the IP address for OriginWebServer.com. You change the DNS so that OriginWebServer.com now resolves to 100.1.1.1.