Authorization Code
In authorization code, an authorization server acts as an intermediary between the client and the resource owner. Instead of requesting authorization directly from the resource owner, the client directs the resource owner to an authorization server, which in turn directs the resource owner back to the client with the authorization code.
The authorization grant type depends on the method used by the application to request authorization, and the grant types supported by the API.
The following diagram describes the workflow of authorization code grant.
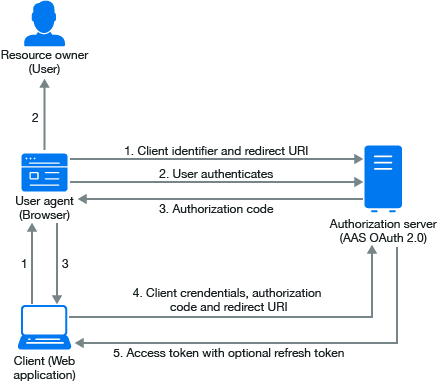
The workflow for authorization code includes the following steps:
-
The OAuth client initiates the flow when it directs the user agent of the resource owner to the authorization endpoint. The OAuth client includes its client identifier, requested scope, local state, and a redirection URI.
-
The authorization server authenticates the resource owner through the user agent and recognizes whether the resource owner grants or denies the access request.
-
If the resource owner grants access, the OAuth client uses the redirection URI provided earlier to redirect the user agent back to the OAuth client. The redirection URI includes an authorization code and any local state previously provided by the OAuth client.
-
The OAuth client requests an access token from the authorization server through the token endpoint. The OAuth client authenticates with its client credentials and includes the authorization code received in the previous step. The OAuth client also includes the redirection URI used to obtain the authorization code for verification.
-
The authorization server validates the client credentials and the authorization code. The server also ensures that the redirection URI received matches the URI used to redirect the client in Step 3. If valid, the authorization server responds back with an access token.